Abstract
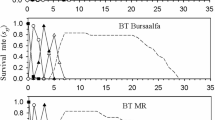
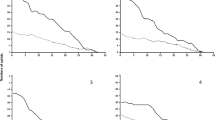
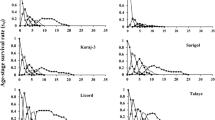
The rose aphid, Macrosiphum rosae (L.), is one of the most important pests on rose plants (Rosa spp.) with a worldwide distribution. As resistance indices, the development, survivorship, and reproduction of this aphid were evaluated on 10 rose cultivars, including Bella Vita, Cool Water, Dolce Vita, Maroussia, Orange Juice, Pinkpromise, Roulette, Tea, Valentine, and Persian Yellow in laboratory at 25 ± 1°C, 65 ± 5% relative humidity, and photoperiod of 16:8 (L/D) h. Rose aphid successfully survived on all 10 rose cultivars, although mortality rate was higher on Tea and Bella Vita. The number of offspring per female differed significantly among the tested rose cultivars, and ranged from 9.2 on Tea to 38.7 nymphs on Orange Juice. Population growth parameters were significantly affected by rose cultivars. The longest mean generation time (T) was observed on Bella Vita (14.8 days) and Tea (14.7 days) and the shortest on Orange Juice (10.0 days). The net reproductive rate (R 0 ) ranged from 6.9 on Tea to 33.2 nymphs on Orange Juice cultivar. Correspondingly, the highest value of intrinsic rate of increase (r m ) was observed on Orange Juice (0.348 day−1) and lower values on Tea (0.131 day−1) followed by Bella Vita (0.154 day−1). Cluster analysis of all the measured parameters of rose aphid on different rose cultivars revealed that Tea and Bella Vita were relatively resistant to M. rosae. These findings could be useful in developing an integrated pest management (IPM) program for this aphid in urbanized areas and commercial rose potting.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford DV (1991) A colour atlas of pests of ornamental trees, shrubs and flower. Wolfe Pub. Ltd, London
Bielza P (2008) Insecticide resistance management strategies against the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis. Pest Manag Sci 64:1131–1138
Birch LC (1948) The intrinsic rate of increase of an insect population. J Anim Ecol 17:15–26
Blackman RL, Eastop VF (2000) Aphids on the world’s crops: an identification and information guide. John Wiley and Sons, London
Carey JR (1993) Applied demography for biologists, with special emphasis on insects. Oxford University Press, New York, p 206
Castle SJ, Berger PH (1993) Rates of growth and increase of Myzus persicae on virus-infected potatoes according to type of virus-vector relationship. Entomol Exp Appl 69:51–60
Castro AM, Martin A, Martin LM (1996) Location of genes controlling resistance to greenbug (Schizaphis graminum Rond.) in Hordeum chilense. Plant Breed 115:335–338
Cisneros JJ, Godfrey LD (2001) Midseason pest status of the cotton aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in California cotton: is nitrogen a key factor? Environ Entomol 30:501–510
Dent D (2000) Host plant resistance. In: Dent D (ed) Insect pest management. CABI Publishing, Oxfordshire, pp 123–179
Dixon AFG (1987) Cereal aphids as an applied problem. Agr Zool Rev 2:1–57
Golizadeh A, Razmjou J (2010) Life table parameters of Phthorimaea operculella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), feeding on tubers of six potato cultivars. J Econ Entomol 103:966–972
Hesler LS, Riedell WE, Kieckhefer RW, Haley SD, Collins RD (1999) Resistance to Rhopalosiphum padi (Homoptera: Aphididae) in wheat germplasm accessions. J Econ Entomol 92:1234–1238
Holtzer T, Anderson RL, Mcmullen MP, Pears FB (1996) Integrated pest management of insects, plant pathogens and weeds in a dry land cropping system. J Prod Agric 9:200–208
Jaskiewicz B (1997) Observation on the occurrence of the rose aphid (Macrosiphum rosae L.) on bushes of Rosa rugosa Thunb. and R. canina L. Folia Hort 9:25–31
Jaskiewicz B (2000) Aphids colonizing the shrubs of Juniperus communis L. and Rosa canina L. in urban conditions. EJPAU 3:1–10
Jaskiewicz B (2006) The effect of the feeding of Macrosiphum rosae (L.) and Chaetosiphon tetrarhodus (Walk.) on the flowering of roses. Acta Agrobot 59:515–520
La Rossa FR, Vasicek A, López MC (2013) Effects of pepper (Capsicum annuum) cultivars on the biology and life table parameters of Myzus persicae (Sulz.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Neotrop Entomol 42:634–641
Legrand A, Barbosa P (2000) Pea aphid (Hom.: Aphididae) fecundity, rate of increase, and within plant distribution unaffected by plant morphology. Environ Entomol 29:987–993
Li Y, Hill CB, Hartman GL (2004) Effect of three resistant soybean genotypes on the fecundity, mortality, and maturation of soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 97:1106–1111
Liu Z, Li D, Gong P, Wu K (2004) Life table studies of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on different host plants. Environ Entomol 33:1570–1576
Maelzer DA (1977) The biology and main causes of changes in numbers of the rose aphid, Macrosiphum rosae (L.), on cultivated roses in South Australia. Aust J Zool 25:269–284
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Campanhola C (2000) Statistical influence on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique, computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Margina A, Lecheva I, Seikova K (1999) Diseases, pests, and weeds on the oil-bearing rose, mint, valleriana, and yellow poppy. Forum 13:27–36
Mehrparvar M, Hatami B (2007) Effect of temperature on some biological parameters of an Iranian population of the Rose Aphid, Macrosiphum rosae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Eur J Entomol 104:631–634
Morgan D, Walters KFA, Aegerter JN (2001) Effect of temperature and cultivar on pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) life history. B Entomol Res 91:47–52
Panda N, Khush GS (1995) Host plant resistance to insects. CAB International, Oxon
Peronti ALBG, Sousa-Silva CR (2002) Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphidoidea) of ornamental plants from São Carlos, São Paulo state, Brazil. Rev Biol Trop 50:137–144
Price PW, Bouton CE, Gross P, Mcpheron BA, Thompson JN, Weis AE (1980) Interactions among three trophic levels: influence of plants on interactions between insect herbivores and natural enemies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:41–65
Razmjou J, Golizadeh A (2010) Performance of corn leaf aphid, Rhopalosiphum maidis (Fitch) (Homoptera: Aphididae) on selected maize hybrids under laboratory conditions. Appl Entomol Zool 45:267–274
Razmjou J, Moharramipour S, Fathipour Y, Mirhoseini SZ (2006) Effect of cotton cultivar on performance of Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Iran. J Econ Entomol 99:1820–1825
Robinson J, Vivar HE, Burnett PA, Calhoun DS (1991) Resistance to Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in barley genotypes. J Econ Entomol 84:674–679
Ruggle P, Gutierrez AP (1995) Use of life tables to assess host plant resistance in alfalfa to Therioaphis trifolii f. maculate (Homoptera: Aphididae): hypothesis for maintenance of resistance. Environ Entomol 24:313–325
Saleem MA, Ahmad M, Aslam M, Sayyed AH (2008) Resistance to selected organochlorin, organophosphate, carbamate and pyrethroid, in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from Pakistan. J Econ Entomol 101:1667–1675
Sarfraz M, Dosdall LM, Keddie BA (2007) Resistance of some cultivated Brassicaceae to infestations by Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 100:215–224
Satar S, Yokomi R (2002) Effect of temperature and host on development of Brachycaudus schwartzi (Homoptera: Aphididae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 95:597–602
Seneta W, Dolatowski J (2003) Dendrologia. PWN, Warszawa
Silva ADA, Varanda EM, Barosela JR (2006) Resistance and susceptibility of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars to the aphid Therioaphis maculata (Homoptera: Aphididae): insect biology and cultivar evaluation. Insect Sci 13:55–60
SPSS Inc (2007) SPSS base 16.0 user’s guide. SPSS Incorporation, Chicago
Tsai JH, Wang JJ (2001) Effects of host plant on biology and life table parameters of Aphis spiracola (Hom.: Aphididae). Environ Entomol 30:44–50
van Emden HF (1991) The role of host plant resistance in insect pest mis-management. B Entomol Res 81:123–126
van Emden HF, Bashford MA (1969) A comparison of the reproduction of Brevicoryne brassicae and Myzus persicae in relation to plant age and leaf amino acids. Entomol Exp Appl 14:349–360
van Lenteren JC, Noldus LPJJ (1990) Whitefly plant relationships, behavioural and ecological aspects. In: Gerling D (ed) White flies: their bionomics, pest status and management intercept, Andover, UK. pp 47–89
Verkerk RHJ, Wright DJ (1996) Multitrophic interactions and management of the diamondback moth: a review. B Entomol Res 86:205–216
Webster JA, Baker CA, Porter DR (1991) Detection and mechanisms of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) resistance in barley. J Econ Entomol 84:669–673
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Department of Plant Protection, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran, which is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Tiago Cardoso da Costa Lima – Embrapa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golizadeh, A., Jafari-Behi, V., Razmjou, J. et al. Population Growth Parameters of Rose Aphid, Macrosiphum rosae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on Different Rose Cultivars. Neotrop Entomol 46, 100–106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-016-0428-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-016-0428-4