Abstract
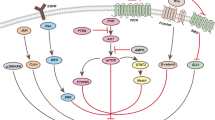
Although melittin, a water-soluble 26-amino acid peptide derived from bee venom of Apis mellifera, is known to exert anti-proliferative effects on various tumor cell lines, very little is known about its potential molecular mechanism(s) of action. In the present study, we investigated the effects of melittin on the AKT/mTOR/S6K1/4E-BP1 activation, associated gene products, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis in several tumor cells. We found that melittin inhibited both constitutive phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR and exerted a significant time-dependent anti-proliferative effect on MM1.S cells as compared to other types of tumor cells. Indeed, melittin clearly suppressed the constitutive activation of AKT/mTOR/S6K1/4E-BP1 signaling cascades, which correlated with the induction of apoptosis. Melittin can cause broad-spectrum inhibition of AKT/mTOR/S6K1/4E-BP1 axes in multiple myeloma cells when compared with various pharmacological AKT/mTOR inhibitors. Aberrant AKT activation by pcDNA3-myr-HA-AKT1 plasmid could not prevent the observed suppressive effect of melittin on constitutive mTOR, S6K1, and 4E-BP1 activation and overexpression of Bcl-2 also attenuated melittin-mediated apoptosis in the cells. Our results clearly indicate that melittin can interfere with multiple signaling cascades involved in carcinogenesis and thereby used as a potential drug candidate for both the prevention and treatment of cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB et al (2006) Targeting signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for prevention and therapy of cancer: modern target but ancient solution. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1091:151–169
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB (2007) Nuclear factor-kappa B: from clone to clinic. Curr Mol Med 7:619–637
Banko JL, Poulin F, Hou L, DeMaria CT, Sonenberg N, Klann E (2005) The translation repressor 4E-BP2 is critical for eIF4F complex formation, synaptic plasticity, and memory in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 25:9581–9590
Barlund M et al (2000) Detecting activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase by complementary DNA and tissue microarray analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1252–1259
Bartlett JM (2010) Biomarkers and patient selection for PI3K/Akt/mTOR targeted therapies: current status and future directions. Clin Breast Cancer 10(Suppl 3):S86–S95
Berset C, Trachsel H, Altmann M (1998) The TOR (target of rapamycin) signal transduction pathway regulates the stability of translation initiation factor eIF4G in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4264–4269
Bortner CD, Oldenburg NB, Cidlowski JA (1995) The role of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 5:21–26
Brunet A et al (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Campone M et al (2009) Safety and pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel and the oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 100:315–321
Chu ST et al (2007) Phospholipase A2-independent Ca2+ entry and subsequent apoptosis induced by melittin in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci 80:364–369
Collado M et al (2000) Inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway induces a senescence-like arrest mediated by p27Kip1. J Biol Chem 275:21960–21968
Dancey JE (2006) Therapeutic targets: MTOR and related pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 5:1065–1073
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB (2008) The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 7:11–20
Ehrenberg B, Montana V, Wei MD, Wuskell JP, Loew LM (1988) Membrane potential can be determined in individual cells from the nernstian distribution of cationic dyes. Biophys J 53:785–794. doi:10.1016/s0006-3495(88)83158-8
Ferre R, Melo MN, Correia AD, Feliu L, Bardaji E, Planas M, Castanho M (2009) Synergistic effects of the membrane actions of cecropin-melittin antimicrobial hybrid peptide BP100. Biophys J 96:1815–1827
Gao N, Zhang Z, Jiang BH, Shi X (2003) Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the cell cycle progression of human prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:1124–1132
Gingras AC et al (1999a) Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: a novel two-step mechanism. Genes Dev 13:1422–1437
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N (1999b) eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 68:913–963
Gold R, Schmied M, Giegerich G, Breitschopf H, Hartung HP, Toyka KV, Lassmann H (1994) Differentiation between cellular apoptosis and necrosis by the combined use of in situ tailing and nick translation techniques. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol 71:219–225
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Hay N (2005) The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell 8:179–183
Hay N, Sonenberg N (2004) Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev 18:1926–1945
Inoki K, Corradetti MN, Guan KL (2005) Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway in human disease. Nat Genet 37:19–24
Jayaraman S (2005) Flow cytometric determination of mitochondrial membrane potential changes during apoptosis of T lymphocytic and pancreatic beta cell lines: comparison of tetramethylrhodamineethylester (TMRE), chloromethyl-X-rosamine (H2-CMX-Ros) and MitoTracker Red 580 (MTR580). J Immunol Methods 306:68–79. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2005.07.024
Jo M et al (2012) Anti-cancer effect of bee venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258:72–81
Kang SS, Pak SC, Choi SH (2002) The effect of whole bee venom on arthritis. Am J Chin Med 30:73–80
Kevil C, Carter P, Hu B, DeBenedetti A (1995) Translational enhancement of FGF-2 by eIF-4 factors, and alternate utilization of CUG and AUG codons for translation initiation. Oncogene 11:2339–2348
Kevil CG, De Benedetti A, Payne DK, Coe LL, Laroux FS, Alexander JS (1996) Translational regulation of vascular permeability factor by eukaryotic initiation factor 4E: implications for tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 65:785–790
Klocek G, Seelig J (2008) Melittin interaction with sulfated cell surface sugars. Biochemistry 47:2841–2849
Kwon YB et al (2002) The water-soluble fraction of bee venom produces antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects on rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Life Sci 71:191–204
Lang CH, Frost RA (2005) Endotoxin disrupts the leucine-signaling pathway involving phosphorylation of mTOR, 4E-BP1, and S6K1 in skeletal muscle. J Cell Physiol 203:144–155
Lazarev VN, Shkarupeta MM, Kostryukova ES, Levitskii SA, Titova GA, Akopian TA, Govorun VM (2007) Recombinant plasmid constructs expressing gene for antimicrobial peptide melittin for the therapy of Mycoplasma and chlamydia infections. Bull Exp Biol Med 144:452–456
Lee JD, Kim SY, Kim TW, Lee SH, Yang HI, Lee DI, Lee YH (2004) Anti-inflammatory effect of bee venom on type II collagen-induced arthritis. Am J Chin Med 32:361–367
Lee JD, Park HJ, Chae Y, Lim S (2005a) An overview of bee venom acupuncture in the treatment of arthritis evid based complement. Altern Med 2:79–84
Lee JY, Kang SS, Kim JH, Bae CS, Choi SH (2005b) Inhibitory effect of whole bee venom in adjuvant-induced arthritis. In Vivo 19:801–805
Lin CJ, Cencic R, Mills JR, Robert F, Pelletier J (2008) c-Myc and eIF4F are components of a feedforward loop that links transcription and translation. Cancer Res 68:5326–5334
Liu S et al (2008a) Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology 47:1964–1973
Liu SI et al (2008b) Melittin-induced [Ca2+]i increases and subsequent death in canine renal tubular cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 27:417–424
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB, Dennis PA (2008) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: effective combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updat 11:32–50
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol Chem 276:18934–18940
McAuliffe PF, Meric-Bernstam F, Mills GB, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2010) Deciphering the role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in breast cancer biology and pathogenesis. Clin Breast Cancer 10(Suppl 3):S59–S65
Moon DO et al (2007) Bee venom and melittin reduce proinflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 7:1092–1101
Moon DO, Park SY, Choi YH, Kim ND, Lee C, Kim GY (2008) Melittin induces Bcl-2 and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis through downregulation of Akt phosphorylation in human leukemic U937 cells. Toxicon 51:112–120
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Nawroth R et al (2011) S6K1 and 4E-BP1 are independent regulated and control cellular growth in bladder cancer. PLoS One 6:e27509
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 139:271–279
Noh WC et al (2004) Determinants of rapamycin sensitivity in breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:1013–1023
Park S et al (2005) Molecular cloning and characterization of the human AKT1 promoter uncovers its up-regulation by the Src/Stat3 pathway. J Biol Chem 280:38932–38941
Park HJ et al (2007) Melittin inhibits inflammatory target gene expression and mediator generation via interaction with IkappaB kinase. Biochem Pharmacol 73:237–247
Park HJ et al (2008) JNK pathway is involved in the inhibition of inflammatory target gene expression and NF-kappaB activation by melittin. J Inflamm (Lond) 5:7
Park JH et al (2010) Melittin suppresses PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by inhibiting NF-kappaB and AP-1-dependent MMP-9 expression. Mol Cells 29:209–215
Park MH et al (2011) Anti-cancer effect of bee venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase pathway via inactivation of NF-kappaB. Prostate 71:801–812
Pullen N, Thomas G (1997) The modular phosphorylation and activation of p70s6k. FEBS Lett 410:78–82
Rosenwald IB, Lazaris-Karatzas A, Sonenberg N, Schmidt EV (1993) Elevated levels of cyclin D1 protein in response to increased expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Mol Cell Biol 13:7358–7363
Sengupta D, Leontiadou H, Mark AE, Marrink SJ (2008) Toroidal pores formed by antimicrobial peptides show significant disorder. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:2308–2317
Shantz LM, Pegg AE (1994) Overproduction of ornithine decarboxylase caused by relief of translational repression is associated with neoplastic transformation. Cancer Res 54:2313–2316
Song CC, Lu X, Cheng BB, Du J, Li B, Ling CQ (2007) Effects of melittin on growth and angiogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402 cell xenografts in nude mice. Ai Zheng 26:1315–1322
Strimpakos AS, Karapanagiotou EM, Saif MW, Syrigos KN (2009) The role of mTOR in the management of solid tumors: an overview. Cancer Treat Rev 35:148–159
Tee AR, Proud CG (2000) DNA-damaging agents cause inactivation of translational regulators linked to mTOR signalling. Oncogene 19:3021–3031
Tee AR, Proud CG (2001) Staurosporine inhibits phosphorylation of translational regulators linked to mTOR. Cell Death Differ 8:841–849
Testa JR, Bellacosa A (2001) AKT plays a central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10983–10985
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:4350–4354
Tu WC, Wu CC, Hsieh HL, Chen CY, Hsu SL (2008) Honeybee venom induces calcium-dependent but caspase-independent apoptotic cell death in human melanoma A2058 cells. Toxicon 52:318–329
van der Hage JA et al (2004) Overexpression of P70 S6 kinase protein is associated with increased risk of locoregional recurrence in node-negative premenopausal early breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 90:1543–1550
van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reutelingsperger CP (1998) Annexin V-affinity assay: a review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine exposure. Cytometry 31:1–9
Wang YQ, Cai JY (2007) High-level expression of acidic partner-mediated antimicrobial peptide from tandem genes in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 141:203–213
Wang NS, Unkila MT, Reineks EZ, Distelhorst CW (2001) Transient expression of wild-type or mitochondrially targeted Bcl-2 induces apoptosis, whereas transient expression of endoplasmic reticulum-targeted Bcl-2 is protective against Bax-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 276:44117–44128. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101958200
Wang C et al (2009) Melittin, a major component of bee venom, sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by activating CaMKII-TAK1-JNK/p38 and inhibiting IkappaBalpha kinase-NFkappaB. J Biol Chem 284:3804–3813
Wendel HG et al (2004) Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature 428:332–337
Yang ZL, Ke YQ, Xu RX, Peng P (2007) Melittin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of malignant human glioma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 27:1775–1777
Yu M, Wang Y, Li X, Fang S, Xue J, Song J (2005) Synthesis of peptide fragment of melittin and the function of rheumatoid arthritis cure. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 22:1031–1035
Zhang C, Li B, Lu SQ, Li Y, Su YH, Ling CQ (2007) Effects of melittin on expressions of mitochondria membrane protein 7A6, cell apoptosis-related gene products Fas and Fas ligand in hepatocarcinoma cells. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 5:559–563
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MoEST) (No. 2011–0006220).
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclosure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chulwon Kim, Dong Sub Kim and Dongwoo Nam contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C., Kim, D.S., Nam, D. et al. Melittin exerts antitumorigenic effects in human MM1.S multiple myeloma cells through the suppression of AKT/mTOR/S6K1/4E-BP1 signaling cascades. Orient Pharm Exp Med 15, 33–44 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0172-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0172-4