Abstract
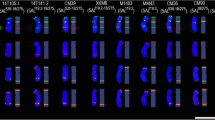
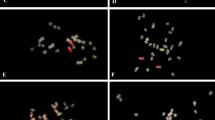
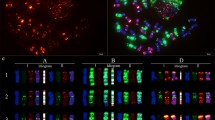
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a powerful tool for the detection of DNA sequences in a specific region of a chromosome as well as for integrated physical mapping. The detailed karyotypes of two onion cultivars (‘Eumjinara’ and ‘Sinseonhwang’), which are resources for the onion genome sequencing project were constructed based on dual color FISH using 5S and 45S rDNAs, telomeric tandem repeats, and Cot-1 DNA. All materials showed 2n = 2x = 16. Four loci of 5S rDNAs were located on the interstitial regions of the short arms of one pair of chromosomes in both onion cultivars. One loci of 45S rDNA signal was distally detected on each short arm of the two pairs of chromosomes in ‘Eumjinara’ and ‘Sinseonhwang’, but the latter possessed another locus of 45S rDNA on the distal part of the long arm in one homolog of a chromosome pair. Co-localization of telomeric tandem repeats and 45S rDNA signals was observed in ‘Eumjinara’ and ‘Sinseonhwang’. A difference in the distribution of 45S rDNA sites and the co-localization of signals observed between the two cultivars are indicators of recent activities in the nuclear genome that may involve homologous recombination or transposition of certain repeats. Cot-1 DNA signals are distributed throughout the chromosomes and show stronger signals in the terminal regions. The elucidation of Cot-1 DNA through in-situ hybridization would only show a large amount of tandemly repeating, non-coding and dispersedly repetitive DNAs in onion genome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Allen, G.C., M.A. Flores-Vergara, S. Krasnyanski, S. Kumar, and W.F. Thompson. 2006. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nature Protocols 1:2320–2325.
Barnes, S.R., A.M. James, and G, Jamieson. 1985. The organization, nucleotide sequence, and chromosomal distribution of a satellite DNA from Allium cepa. Chromosoma 92:185–192.
Bark, O.H. and M. Havey. 1994. Similarities and relationship among populations of the bulb onion as estimated by nuclear RFLPS. Theor. Appl. Genet. 90:407–414.
Castilho, A. and J.S. Heslop-Harrison. 1995. Physical mapping of 5S and 18S-26S rDNA and repetitive DNA sequences in Aegilops umbelluta. Genome 38:91–96.
Do, G.S., B.B. Seo, M. Yamamoto, and G. Suzuki. 2001. Identification and chromosomal location of tandemly repeated DNA sequences in Allium cepa. Genes Genet. Syst. 76:53–60.
Do, G.S. and B.B. Seo. 2000. Phylogenetic relationships among Allium subg. Rhizirideum species based on the molecular variation of 5S rRNA genes. Korean J. Biol. Sci. 4:77–85.
Falquet, J., R. Creusot, and M. Dron. 1997. Molecular analysis of Phaseolus vulgaris rDNA units and characterization of a satellite DNA homologous to IGS subrepeats. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 35:1011–1022.
Flavell, R.B., M.D. Bennett, and J.B. Smith. 1974. Genome size and the proportion of repeated nucleotide sequence DNA in plants. Biochem. Genet. 12:257–269.
Gerlach, W.L. and J.R. Bedrook. 1979. Cloning and characterization of ribosomal rDNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acids Res. 7:1869–1885.
Gernand, D., H. Golczyk, T. Rutten, T. Iinicki, A. Houben, and A. Joachimiak. 2007. Tissue culture triggers chromosomes alterations, amplification, and transposition of repeat sequences in Allium fistulosum. Genome 50:435–442.
Gurushidze, M., S. Mashayekhi, F.R. Blattner, N. Friesen, and R.M. Fritsch. 2007. Phylogenetic relationship of wild and cultivated species of Allium section Cepa inferred by nuclear rDNA ITS sequence analysis. Plant Syst. Evol. 269:259–269.
Hanelt, P. 1990. Allium taxonomy, evolution and history, p. 1–16. In: H.D. Rabinowitch, and J.L. Brewster (eds.). Botany, Physiology and Genetics. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA.
Irifune, K., K. Hirai, J. Zheng, R. Tanaka, and H. Morikawa. 1995. Nucleotide sequence of a highly repeated DNA sequence and its chromosomal localization in Allium fistulosum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 90:312–316.
Jakse, J., J.D.F. Meyer, G. Suzuki, J. McCallum, and F. Cheung. 2008. Pilot sequencing of onion genomic DNA reveals fragments of transposable elements, low gene densities, and significant gene enrichment after methyl filtration. Mol. Genet. Genomics 280:287–292.
Jorgensen, R. and P. Cluster. 1998. Modes and tempos in the evolution of nuclear ribosomal DNA: new characters for evolutionary studies and new markers for genetic and population studies. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 75:1238–1247.
Kim, S., J.Y. Park, and T.J. Yang. 2014. Characterization of three active transposable elements recently inserted in three independent DFR-A alleles and one high-copy DNA transposon isolated from the pink allele of the ANS gene in onion (Allium cepa L.). Mol. Genet. Genomics 290:1027–1037.
Kubis, S., T. Schmidt, and J.S. Heslop-Harrison. 1998. Repetitive DNA elements as a major component of plant genomes. Ann. Bot. 82:45–55.
Levan, A., K. Fredga, and A.A. Sunderge. 1964. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220.
Li, J., S. He, L. Zhang, Y. Hu, F. Yang, L. Ma, J. Huang, and L. Li. 2012. Telomere and 45S rDNA sequences are structurally linked on the chromosomes in Chrysanthemum segetum L. Protoplasma 1:207–215.
Linne Von Berg, G., A. Samoylov, M. Klaas, and P. Hanelt. 1996. Chloroplast DNA restriction analysis and the infrageneric grouping of Alllium L. Plant Syst. Evol. 200:253–261.
Long, E.O. and I.D. David. 1980. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 49:727–764.
Maggini, F., P. Barsanti, and T. Marazia. 1978. Individual variation of the nucleolus organizer regions in Allium cepa and Allium sativum. Chromosoma 66:173–184.
Martins, C. and A.P. Wasko. 2004. Organization and evolution of 5S ribosomal DNA in the fish genome, p. 335–363. In: C.R. Williams (ed.). Genome Research. Nova Science Publishers Inc., Hauppauge, NY, USA.
Martins, C., A.P. Wasko, C. Oliveira, and J.M. Wright. 2000. Nucleotide sequence of 5S rDNA and localization of the ribosomal RNA genes to metaphase chromosomes of the Tilapiine cichlid fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Hereditas 133:39–46.
Mukherjee, A. and S.C. Roy. 2012. Karyotype analysis of five species of Allium. Indian J. Fund. Appl. Life Sci. 2:374–383.
Paolozzi, L., G. Fabozzi, and P. Ghelardini. 1999. Mu DNA reintegration upon excision: evidence for a possible involvement of nucleoid folding. Microbiology 3:591–598.
Pearce, S.R., U. Pich, G. Harrison, A.J. Flavell, J.S. Heslop-Harrison, I, Schubert, and A. Kumar. 1996. The Ty1-copia group retrotransposons of Allium cepa are distributed throughout the chromosomes but are enriched in the terminal heterochromatin. Chromosome Res. 4:357–364.
Peterson, D.G., S.R. Wessler, and A.H. Peterson. 2002. Efficient capture of unique sequences from eukaryotic genomes. Trends Genet. 18:547–550.
Pitch, U. and I. Schubert. 1998. Terminal heterochromatin and alternative telomeric sequences in Allium cepa. Chromosome Res. 6:315–321.
Pich, U., J. Fuchs, and I. Schubert. 1996. How do Alliaceae stabilize their chromosome ends in the absence of TTTAGGG-sequences? Chromosome Res. 4:207–213.
Ricroch, A., E.B. Peffley, and R.J. Baker. 1992. Chromosomal location of rDNA in Allium: in situ hybridization using biotin-and fluorescein-labelled probe. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83:413–418.
Schubert, I. and U. Wobus. 1985. In situ hybridization confirms jumping nucleolus organizing regions in Allium. Chromosoma 92: 143148.
Scitable by nature education. 2014. DNA is constantly changing through the process of mutation. http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/dna-is-constantly-changing-through-the-process-6524898.
Seo, J.H., S.Y. Lee, and B.B. Seo. 2007. Genome analysis using sequence variation and chromosomal localization of tandem repeats of SS rRNA gene in Allium wakegi. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 39:70–76.
Shibata, F. and M. Hizume. 2002a. The identification and analysis of the sequences that allow the detection of Allium cepa chromosomes by GISH in the allodiploid A. wakegi. Chromosoma 111:184–191.
Shibata, F. and M. Hizume. 2002b. Evolution of 5S rDNA units and their chromosomal localization in Allium cepa and Allium schoenoprasum revealed by microdissection and FISH. Theor. Appl. Genet. 105:167–172.
Shiv, I.S., G. Jia, and S. Jia. 2007. Heterochromatin revisited. Nature Rev. Genetics 8:35–46.
Stupar, R.M., J. Song, A.L. Tek, Z. Cheng, F. Dong, and J. Jiang. 2002. Highly condensed potato pericentromeric heterochromatin contains rDNA-related tandem repeats. Genetics 162:1435–1444.
Suzuki, H., S. Sakurai, and Y. Matsuda. 1996. Rat 5S rDNA spacer sequences and chromosomal assignment of the genes to the extreme terminal region of chromosome 19. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 72:1–4.
Vitte, C. and J.L. Bennetzen. 2006. Analysis of retrotransposon structural diversity uncovers properties and propensities in angiosperm genome evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:17638–17643.
Vitte, C., M.C. Estep, J. Leebens-Mack, and J.L. Bennetzen. 2013. Young, intact and nested retrotransposons are abundant in the onion and asparagus genomes. Ann. Bot. 122:881–889.
Wei, W.H., S.F. Zhang, L.J. Wang, B. Chen, X.M. Wu, and Y. Chun. 2007. Karyotyping of Brassica oleracea L. based on COt-1 and ribosomal DNAs. Bot. Stud. 48:255–261.
Yuan, Y., P. San Miguel, and J.L. Bennetzen. 2003. High-cost analysis of the maize genome. The Plant J. 34:249–255.
Yunis, J.J. and W.G. Yasmineh. 1971. Heterochromatin, satellite DNA, and cell function. Science 174:1200–1209.
Zwick, M.S., R.E. Hanson, M.N. Islam-Faridi, D.M. Stelly, and R.A. Wing. 1997. A rapid procedure for the isolation of COt -1 DNA. Genome 40:138–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mancia, F.H., Sohn, SH., Ahn, Y.K. et al. Distribution of various types of repetitive DNAs in Allium cepa L. based on dual color FISH. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 56, 793–799 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-1100-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-1100-3