Abstract
Objective
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer to metastasize in the brain. Little is known about how receptor subtype, including luminal A, luminal B, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) enriched, and triple negative (TN) affect response to radiation and distant intracranial recurrence (ICR) following radiation therapy.
Methods
We conducted a single-institution retrospective analysis of 38 breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) patients who underwent 93 treatment courses of stereotactic radiosurgery, stereotactic radiotherapy, post-operative radiation, or whole brain radiation therapy. Endpoints included overall survival (OS), treatment response (partial/complete response, PR/CR, or progression), ICR after treatment, and time from breast cancer diagnosis to the first BCBM (time to metastasis, TTM). Subset analyses were performed for triple receptor subtype as well as estrogen receptor (ER) positive versus negative, HER2+ versus HER2-, and age ≤ 50 versus >50 years old.
Results
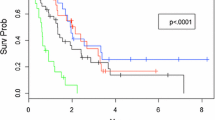
Median OS for the population was 22.5 months, with median follow-up after treatment of 20.5 months. TTM was shortest for HER2 enriched, TN, ER−, and younger patients. TN, HER2-, and younger patients showed the poorest OS. ICR was also greatest in TN and HER2− patients. Radiation failure at the treated BCBM was seen most prominently in HER2+ and ER− patients.
Conclusion
Receptor subtypes that demonstrated poorer OS tended to demonstrate higher intracranial recurrence. A positive response to radiation was not associated with better OS or lower ICR. Identifying patterns based on receptor subtype may guide clinicians in management and surveillance for BCBM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the metropolitan Detroit cancer surveillance system. J Clin Oncol 22:2865–2872
Patchell RA (2003) The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev 29(6):533–540
Lee SS, Ahn JH, Kim MK, et al. (2008) Brain metastases in breast cancer: prognostic factors and management. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111(3):523–530
Steeg PS, Camphausen KA, Smith QR (2011) Brain metastases as preventive and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer 11(5):352–363
Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak AR, Arnaout A, Winer EP (2008) Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer 113(10):2638–2645
Lin NU, Winer EP (2007) Brain metastases: the HER2 paradigm. Clin Cancer Res 13(6):1648–1655
Hu J, Kesari S (2013) Strategies for overcoming the blood-brain barrier for the treatment of brain metastases. CNS Oncol 2(1):87–98
Mehta AI, Brufsky AM, Sampson JH (2013) Therapeutic approaches for HER2-positive brain metastases: circumventing the blood-brain barrier. Cancer Treat Rev 39(3):261–269
Yomo S, Hayashi M, Cho N (2013) Impacts of HER2-overexpression and molecular targeting therapy on the efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from breast cancer. J Neuro-Oncol 112(2):199–207
Arslan UY, Oksuzoglu B, Aksoy S, et al. (2011) Breast cancer subtypes and outcomes of central nervous system metastases. Breast 20(6):562–567
Braccini AL, Azria D, Thezenas S, Romieu G, Ferrero JM, Jacot W (2013) Prognostic factors of brain metastases from breast cancer: impact of targeted therapies. Breast 22(5):993–998
Matsunaga S, Shuto T, Kawahara N, Suenaga J, Inomori S, Fujino H (2010) Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brain tumors from primary breast cancer: treatment indication based on number of tumors and breast cancer phenotype. J Neurosurg 113(Suppl):65–72
Gil-gil MJ, Martinez-garcia M, Sierra A, et al. (2014) Breast cancer brain metastases: a review of the literature and a current multidisciplinary management guideline. Clin Transl Oncol 16(5):436–446
Nam BH, Kim SY, Han HS, et al. (2008) Breast cancer subtypes and survival in patients with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res 10(1):R20
Eichler AF, Kuter I, Ryan P, Schapira L, Younger J, Henson JW (2008) Survival in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer: the importance of HER-2 status. Cancer 112(11):2359–2367
Hung MH, Liu CY, Shiau CY, et al. (2014) Effect of age and biological subtype on the risk and timing of brain metastasis in breast cancer patients. PLoS One 9(2):e89389
Jaboin JJ, Ferraro DJ, Dewees TA, et al. (2013) Survival following gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastasis from breast cancer. Radiat Oncol 8:131
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, et al. (2012) Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(5):2111–2117
Tam M, Narayana A, Raza S, et al. (2014) Role of HER2 status in the treatment for brain metastases arising from breast cancer with stereotactic radiosurgery. Med Oncol 31(2):832
Colzani E, Johansson AL, Liljegren A, et al. (2014) Time-dependent risk of developing distant metastasis in breast cancer patients according to treatment, age and tumour characteristics. Br J Cancer 110(5):1378–1384
Anders CK, Deal AM, Miller CR, et al. (2011) The prognostic contribution of clinical breast cancer subtype, age, and race among patients with breast cancer brain metastases. Cancer 117(8):1602–1611
Weltman E, Salvajoli JV, Brandt RA, et al. (2000) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: a score index for predicting prognosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46(5):1155–1161
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, et al. (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 134(6):907–922
Cho E, Rubinstein L, Stevenson P, et al. (2015) The use of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from breast cancer: who benefits most? Breast Cancer Res Treat 149(3):743–749
Radawski JD, Zhang D, Nelson A, et al. (2012) Her2-enriched breast cancer brain metastases exhibit resistance to gamma knife radiosurgery: findings from a single institutional series review. J Radiat Oncol 1:283
Duru N, Fan M, Candas D, et al. (2012) HER2-associated radioresistance of breast cancer stem cells isolated from HER2-negative breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 18(24):6634–6647
Iyer A, Harrison G, Kano H, et al. (2014) Volumetric response to radiosurgery for brain metastasis varies by cell of origin. J Neurosurg 121(3):564–569
Hoefnagel LD, Van de vijver MJ, Van slooten HJ, et al. (2010) Receptor conversion in distant breast cancer metastases. Breast Cancer Res 12(5):R75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding support is associated with this study.
Conflict of interest
Rebecca Levin-Epstein declares no conflict of interest. Pin-Chieh Wang declares no conflict of interest. Stephen Tenn declares no conflict of interest. Antonio de Salles declares no conflict of interest. Nader Pouratian declares no conflict of interest. Susan McCloskey declares no conflict of interest. Patrick Kupelian declares no conflict of interest. Michael Steinberg declares no conflict of interest. Phillip Beron declares no conflict of interest. Tania Kaprealian declares no conflicts of interest. Michael Selch is a member of the speakers bureau for BrainLab and receives a speaking fee for lectures. Isaac Yang receives consultant fees from BrainLab.
Ethical approval
IRB approval was obtained for this retrospective study. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of retrospective study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levin-Epstein, R., Wang, PC., Tenn, S. et al. Radiation therapy in the management of breast cancer brain metastases: the impact of receptor status on treatment response, intracranial recurrence, and survival. J Radiat Oncol 5, 401–409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-016-0275-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-016-0275-2