Abstract
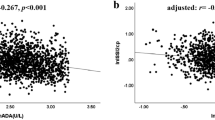
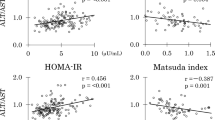
The assessment of insulin resistance is advantageous since it detects those at risk for the development of diabetes mellitus at early stages and minimizes complications. Various methods like euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp technique, fasting serum insulin levels, HOMA and QUICKI have been used to determine insulin sensitivity but they have limitations. Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is an enzyme that has been suggested to be important for modulating the bioactivity of insulin. The aim of this study was to determine the activity of serum adenosine deaminase (ADA) in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus and to evaluate the role of serum adenosine deaminase as a marker for insulin resistance. The study recruited 46 subjects of Type 2 diabetes mellitus and 40 healthy controls matched for age and sex between May 2010 and November 2010. Fasting serum glucose, insulin, adenosine deaminase activity were estimated. QUICKI and HOMA were calculated. Serum ADA was positively correlated with fasting serum glucose, insulin, HOMA and negatively correlated with QUICKI in the diabetic group. At 95 % CI and a cut off of 36.91U/L serum ADA activity in the diabetic group showed a sensitivity and specificity of 98 % and 90 % respectively. Serum ADA activity was increased with an increase in insulin resistance in the diabetic population. ADA may be used as a marker of insulin resistance and can be employed as an effective tool in screening for insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2009;32 Suppl 1:S62–7.
The expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2003;26:S5–20.
Potenza MV, Mechanick JI. The metabolic syndrome: definition, global impact, and pathophysiology. Nutr Clin Pract. 2009;24:560–77.
Kim JA, Montagnani M, Koh KK, Quon MJ. Reciprocal relationships between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: molecular and pathophysiological mechanisms. Circulation. 2006;113:1888–904.
Huang PL. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis Model Mech. 2009;2:231–7.
Muniyappa R, Lee S, Chen H, Quon MJ. Current approaches for assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in vivo: advantages, limitations, and appropriate usage. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;294:15–26.
Borai A, Livingstone C, Ferns GAA. The biochemical assessment of insulin resistance. Ann Clin Biochem. 2007;44:324–42.
Edwards YH, Hopkanson DA, Hams H. Adenosme deaminase lsozymes in human tissues. Ann Hum Genet. 1971;35:207–18.
Van der Weyden MB, Kelly WN. Human adenosine deaminase: distribution and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976;251:5448–56.
Blackburn MR, Kellems RE. Adenosine deaminase deficiency: metabolic basis of immune deficiency and pulmonary inflammation. Adv Immunol. 2005;86:1–41.
Baghanha MF, Pego A, Lima MA, et al. Serum and pleural adenosine deaminase correlation with lymphocyte populations. Chest. 1990;87:605–10.
Ungerer JP, Oosthuizen HM, Bissbort SH, Vermaak WJ. Serum adenosine deaminase: isoenzymes and diagnostic application. Clin Chem. 1992;38:1322–6.
Matteucci E, Giampietro O. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (CD26): knowing the function before inhibiting the enzyme. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16:2943–51.
Kurtul N, Pence S, Akarsu E, et al. Adenosine deaminase activity in the serum of type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Medica(Hradec Kralove). 2004;47:33–5.
Hoshino T, Yamada K, Masuoka K, et al. Elevated adenosine deaminase activity in the serum of patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994;25:97–102.
Warrier A, Rao NY, et al. Evaluation of Adenosine Deaminase activity and lipid peroxidation levels in Diabetes Mellitus. IJCB. 1995;10:9–13.
Rutkiewicz J, Gorski J. On the role of insulin in regulation of adenosine deaminase activity in rat tissues. FEBS Lett. 1990;271:79–80.
McAuley KA, Williams SM, Mann JI, Walker RJ, Lewis-Barned NJ, Temple LA, et al. Diagnosing insulin resistance in the general population. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:460–4.
Gupta A, Gupta V, Agrawal S, Natu SM, Agrawal CG, Negi MPS, Tiwari S. Association between circulating leptin and insulin resistance, the lipid profile, and metabolic risk factors in North Indian adult women. BioScience Trends. 2010;4:325–32.
Giusti G, Galanti B. Colorimetric method. Adenosine deaminase. In: Bergmeyer HU, editor. Methods of enzymatic Analysis. 3rd ed. Weinheim: Verlag chemie; 1984. p. 315–23.
Lee JG, Kang DG, Yu JR, Kim Y, Kim J, Koh G, et al. Changes in adenosine deaminase activity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and effect of DPP-4 inhibitor treatment on ADA activity. Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35:149–58.
Bottini E, Gloria-Bottini F. Adenosine deaminase and body mass index in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1999;48:949–51.
Bopp A, De Bona KS, Bellé LP, Moresco RN, Moretto MB. Syzygium cumini inhibits adenosine deaminase activity and reduces glucose levels in hyperglycemic patients. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2009;23:501–7.
Koopmans SJ, Sips HC, Bosman J, Radder JK, Krans HM. Antilipolytic action of insulin in adipocytes from starved and diabetic rats during adenosine-controlled incubations. Endocrinology. 1989;125:3044–50.
Green A, Newsholme EA. Sensitivity of glucose uptake and lipolysis of white adipocytes of the rat to insulin and effects of some metabolites. Biochem J. 1979;180:365–70.
Musi N, Hirshman MF, Nygren J, Svanfeldt M, Bavenholm P, Rooyackers O, et al. Metformin increases AMP-activated protein kinase activity in skeletal muscle of subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:2074–81.
Pérez-Aguilar MC, Goncalves L, Ibarra A, Bonfante-Cabarcas R. Adenosine deaminase as costimulatory molecule and marker of cellular immunity. Investig Clin. 2010;51:561–71.
Lambeir AM, Durinx C, Scharpé S, De Meester I, Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV from bench to bedside: an update on structural properties, functions, and clinical aspects of the enzyme DPP IV. Sciences. 2003;40:209–94.
Gracia E, Pérez-Capote K, Moreno E, Barkešová J, Mallol J, Lluís C, et al. A2A adenosine receptor ligand binding and signalling is allosterically modulated by adenosine deaminase. Biochem J. 2011;435:701–9.
Samsel M, Dzierzbicka K. Therapeutic potential of adenosine analogues and conjugates. Pharmacol Rep Online. 2011;63:601–17.
Kaya S, Cetin ES, Aridogan BC, Arikan S, Demirci M. Adenosine deaminase activity in serum of patients with hepatitis—a useful tool in monitoring clinical status. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2007;40:288–92.
Kobayashi F, Ikeda T, Marumo F, Sato C. Adenosine deaminase isoenzymes in liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993;88:266–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gowda, M.N.V., Vasudha, K.C., Reshma, S. et al. Serum Adenosine deaminase activity in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 32, 176–181 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-012-0087-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-012-0087-x