Abstract
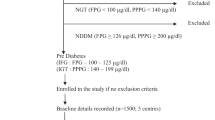
Several studies have documented the beneficial short term effects of yoga in type 2 diabetics. In this prospective two-armed interventional randomized control study, 277 type 2 diabetics of both genders aged above 28 years who satisfied the study criteria were recruited from 5 zones in and around Bengaluru, India. They were allocated to a yoga-based life style modification program or exercise-based life style modification program. Integrated yoga special technique for diabetes included yogasanas, pranayama, meditation and lectures on yogic life style. Control intervention included physical exercises and life style education. Medication score, blood glucose, HbA1c and lipid profile were assessed at baseline and after 9 months. Intention to treat analysis showed better reduction (P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test) in the dose of oral hypoglycemic medication required (Yoga - 12.8 %) (Yoga-12.3 %) and increase in HDL (Yoga-7 %) in Yoga as compared to the control group; FBG reduced (7.2 %, P = 0.016) only in the Yoga group. There was significant reduction within groups (P < 0.01) in PPBG (Yoga-14.6 %, Control-9 %), HbA1c (Yoga-14.1 %, Control-0.5 %), Triglycerides (Yoga-15.4 %, Control-16.3 %), VLDL (Yoga-21.5 %, Control-5.2 %) and total cholesterol (Yoga-11.3 %, Control-8.6 %). Thus, Yoga based life style modification program is similar to exercise-based life style modification in reducing blood glucose, HbA1c, triglycerides, total cholesterol and VLDL. Yoga is better than exercise in decreasing oral hypoglycemic medication requirement and LDL; and increasing HDL in type 2 diabetics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohan V, Jaydip R, Deepa R. Type 2 diabetes in Asian Indian youth. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8 Suppl 9:28–34.
Winer N, Sowers JR. Diabetes and arterial stiffening. Adv Cardiol. 2007;44:245–51.
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Sivasankari S, Hitman GA, Vijay V. Parental influence on the spectrum of type 2 diabetes in the offspring among Indians. J Assoc Physicians India. 2007;55:560–2.
Mohan V, Sandeep S, Deepa R, Shah B, Varghese C. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: Indian scenario. Indian J Med Res. 2007;125:217–30.
Chandola T, Brunner E, Marmot M. Chronic stress at work and the metabolic syndrome: prospective study. BMJ. 2006;332:521–5.
Gross R, Olfson M, Gameroff MJ, Carasquillo O, Shea S, Feder A, et al. Depression and glycemic control in Hispanic primary care patients with diabetes. J Gen Intern Med. 2005;20:460–6.
Williamson DF, Vinicor F, Bowman BA. Primary prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by lifestyle intervention: implications for health policy. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:951–7.
Egede LE. Lifestyle modification to improve blood pressure control in individuals with diabetes: is physician advice effective? Diabetes Care. 2003;26:602–7.
Sigal RJ, Kenny GP, Boule NG, Wells GA. Prud’homme D, Fortier M, et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:357–69.
Surwit RS, van Tilburg MA, Zucker N, McCaskill CC, Parekh P, Feinglos MN, et al. Stress management improves long-term glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:30–4.
Surwit RS, Feinglos MN. The effects of relaxations on glucose tolerance in non-insulindependent diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1983;6:176–9.
Lustman PJ, Griffith LS, Freedland KE, Kissel SS, Clouse RE. Cognitive behavior therapy for depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129:613–21.
Delamater AM, Jacobson AM, Anderson B, Cox D, Fisher L, Lustman P. et al. Psychosocial therapies in diabetes: report of the Psychosocial Therapies Working Group. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1286–92.
Sundar S, Agrawal SK, Singh VP, Bhattacharya SK, Udupa KN, Vaish SK. Role of yoga in management of essential hypertension. Acta Cardiol. 1984;39:203–8.
Nagarathna R, Nagendra HR. Yoga for bronchial asthma: a controlled study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1985;291:1077–9.
Monro R, Powar J, Anil C, Nagarathna R, Dandona P. Yoga therapy for NIDDM- a control trial. J Complemen Med Res. 1992;6:66–8.
Manchanda SC, Narang R. Yoga and coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J. 1998;50:227–8.
Innes KE, Vincent HK. The influence of yoga-based programs on risk profiles in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2007;4:469–86.
Nagarathna R, Nagendra HR, Monro R. Yoga for common ailments. 3rd ed. London: GAIA; 1991.
Damodaran A, Malathi A, Patil N, Shah N, Suryavansihi, Marathe S. Therapeutic potential of yoga practices in modifying cardiovascular risk profile in middle aged men and women. J Assoc Physicians India. 2002;50:633–40.
Singh S, Malhotra V, Singh KP, Madhu SV, Tandon OP. Role of yoga in modifying certain cardiovascular functions in type 2 diabetic patients. J Assoc Physicians India. 2004;52:203–6.
Hegde SV, Adhikari P, Kotian S, Pinto VJ, D’Souza S, D’Souza V. Effect of 3-month yoga on oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes with or without complications: a controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:2208–10.
Madanmohan, Bhavanani AB, Dayanidy G, Sanjay Z, Basavaraddi IV. Effect of yoga therapy on reaction time, biochemical parameters and wellness score of peri and post-menopausal diabetic patients. Int J Yoga. 2012;5:10–5.
Birdee GS, Yeh G. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Therapies for Diabetes: A Clinical Review. Clinical Diabetes. 2010;28:147–55.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39:175–91.
Rai L, Ram K, Kant U, Madan SK, Sharma SK. Energy expenditure and ventilatory responses during Siddhasana–a yogic seated posture. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994;38:29–33.
Schreiber WE, Busser JR, Huebsch S. Which laboratory tests do students in an internal medicine clerkship need to learn about? Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;130:696–701.
Current Index of Medical Specialties (CIMS). India:CMP Medica, 2007 http://www.mims.com/drug/dose. Accessed 17 July 2011.
St John A, Davis TM, Goodall I, Townsend MA, Price CP. Nurse-based evaluation of point-of care assays for glycated haemoglobin. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;365:257–63.
Fossati P, Prencipe L. Serum triglycerides determined colorimetrically with an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Clin Chem. 1982;28:2077–80.
Lindgren FT, Silvers A, Jutaglr R, Layshot L, Bradley DD. A comparison of simplified methods for lipoprotein quantification using the analytic ultracentrifuge as a standard. Lipids. 1977;12:278–82.
Yagi K. Lipid peroxides and human diseases. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987;45:337–51.
Heneghan C, Perera R, Ward AA, Fitzmaurice D, Meats E, Glasziou P. Assessing differential attrition in clinical trials: self-monitoring of oral anticoagulation and type II diabetes. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:18.
Schafer JL, Graham JW. Missing data: our view of the state of the art. Psychol Methods. 2002;7:147–77.
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J Royal Stat Soc, Ser B. 1977;39:1–38.
Gordon LA, Morrison EY, McGrowder DA, Young R, Fraser YT, Zamora EM, et al. Effect of exercise therapy on lipid profile and oxidative stress indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2008;8:21.
Agrawal R, Aradhana R, Hussain S, Sabir M, Kochar D, Kothari R. Influence of yogic treatment on quality of life outcomes, glycaemic control and risk factors in diabetes mellitus. Int J Diabet Dev Ctries. 2003;23:130–4.
Agte VV, Tarwadi K. Sudarshan kriya yoga for treating type 2 diabetes: a preliminary study. Altern Complet Therap. 2004;10:220–2.
Iborra RT, Ribeiro IC, Neves MQ, Charf AM, Lottenberg SA, Negrao CE, et al. Aerobic exercise training improves the role of high-density lipoprotein antioxidant and reduces plasma lipid peroxidation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008;18:742–50.
Fehm HL, Kern W, Peters A. The selfish brain: competition for energy resources. Prog Brain Res. 2006;153:129–40.
Vempati RP, Telles S. Yoga-based guided relaxation reduces sympathetic activity judged from baseline levels. Psychol Rep. 2002;90:487–94.
Chaya MS, Ramakrishnan G, Shastry S, Kishore RP, Nagendra H, Nagarathna R, et al. Insulin sensitivity and cardiac autonomic function in young male practitioners of yoga. Natl Med J India. 2008;21:217–21.
Timmermans RJ, Saris WH, van Loon LJ. Insulin resistance: the role of intramuscular triglyceride and the importance of physical activity. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006;150:122–7.
Singh S, Malhotra V, Singh K, Sharma S. A preliminary report on the role of yoga asanas on oxidative stress in non-insulin dependant diabetes. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2001;16:216–20.
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the Department of Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha and Homoeopathy (AYUSH), Ministry of Health and family welfare, New Delhi, India under the ‘Extra Mural Research’ scheme. The AYUSH technical expert committee had reviewed the study design. We thank Dr Srikanta SS, Dr Vadiraja HS, Dr Shruddha K, Dr Bogavi L, Dr Mallikarjuna, Dr Srividya, Dr Pradhan B, Omkar G, the management, doctors and the paramedical staff of TVS company, and BEML company the management of Satya Sai trust, Diwakar hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarathna, R., Usharani, M.R., Rao, A.R. et al. Efficacy of yoga based life style modification program on medication score and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes—a randomized control study. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 32, 122–130 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-012-0078-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-012-0078-y