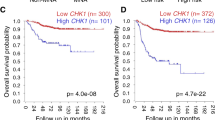
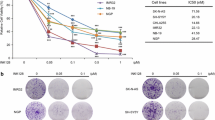
Abstract
Background
In the past, the HDAC inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) has been shown to induce apoptosis in several human tumor types, including neuroblastomas. Amplification and over-expression of the MYCN oncogene is a diagnostic hallmark and a poor prognostic indicator in high-risk neuroblastomas. Here, we studied the relationship between MYCN amplification and over-expression and the anti-tumor effect of SAHA to assess whether this drug may serve as a treatment option for high-risk neuroblastomas.
Methods
Different human neuroblastoma cell lines, over-expressing or not over-expressing MYCN, were used in this study. Targeted knockdown and exogenous over-expression of MYCN were employed to examine correlations between MYCN expression levels and SAHA responses. After various time periods and concentration exposures to the drug, cell viability was measured by MTS assay, and variations in MYCN mRNA and protein levels were assessed by qPCR and Western blotting, respectively.
Results
We found that SAHA decreased cell viability in all cell lines tested through apoptosis induction, and that SAHA had a stronger effect on cell lines carrying an amplified MYCN gene. A decrease in MYCN mRNA and protein levels was observed in the SAHA treated cell lines. Subsequent silencing and exogenous over-expression of MYCN changed the proliferation rate of the cells, but did not have any significant impact on the effect of SAHA on the viability of the cells. We also found that SAHA blocked the expression of MYCN and, by doing so, reduced the effects mediated by this protein.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that SAHA may be used as a single-drug treatment option for neuroblastomas with an amplified MYCN gene, and as an adjuvant treatment option for all neuroblastomas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Maris, Recent advances in neuroblastoma. N. Eng. J. Med. 362, 2202–2211 (2010)
A. Bandino, D. Geerts, J. Koster, A.S. Bachmann, Deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) inhibitor GC7 induces p21/Rb-mediated inhibition of tumor cell growth and DHPS expression correlates with poor prognosis in neuroblastoma patients. Cell. Oncol. 37, 387–398 (2014)
R.A. Ross, J.L. Biedler, B.A. Spengler, A role for distinct cell types in determining malignancy in human neuroblastoma cell lines and tumors. Cancer Lett. 197, 35–39 (2003)
S.L. Cohn, A.D. Pearson, W.B. London, T. Monclair, P.F. Ambros, G.M. Brodeur, A. Faldum, B. Hero, T. Iehara, D. Machin, V. Mosseri, T. Simon, A. Garaventa, V. Castel, K.K. Matthay, The international neuroblastoma risk group (INRG) classification system: an INRG task force report. Int. J. Oncol. 27, 289–297 (2009)
L.J. Valentijn, J. Koster, F. Haneveld, R.A. Aissa, P. van Sluis, M.E. Broekmans, J.J. Molenaar, J. van Nes, R. Versteeg, Functional MYCN signature predicts outcome of neuroblastoma irrespective of MYCN amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 19190–19195 (2012)
T.J. Pugh, O. Morozova, E. Attiyeh, S. Asgharzadeh, J.S. Wei, D. Auclair, S.L. Carter, K. Cibulskis, M. Hanna, A. Kiezun, J. Kim, M.S. Lawrence, L. Lichenstein, A. McKenna, C.S. Pedamallu, A.H. Ramos, E. Shefler, A. Sivachenko, C. Sougnez, C. Stewart, A. Ally, I. Birol, R. Chiu, R.D. Corbett, M. Hirst, S.D. Jackman, B. Kamoh, A.H. Khodabakshi, M. Krzywinski, A. Lo, R.A. Moore, K.L. Mungall, J. Qian, A. Tam, N. Thiessen, Y. Zhao, K.A. Cole, M. Diamond, S.J. Diskin, Y.P. Mosse, A.C. Wood, L. Ji, R. Sposto, T. Badgett, W.B. London, Y. Moyer, J.M. Gastier-Foster, M.A. Smith, J.M. Guidry Auvil, D.S. Gerhard, M.D. Hogarty, S.J. Jones, E.S. Lander, S.B. Gabriel, G. Getz, R.C. Seeger, J. Khan, M.A. Marra, M. Meyerson, J.M. Maris, The genetic landscape of high-risk neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 45, 279–284 (2013)
A. Canette, M. Gerrard, H. Rubie, V. Castel, A. Di Cataldo, C. Munzer, R. Ladenstein, B. Brichard, J.D. Bermúdez, J. Couturier, B. de Bernardi, A.J. Pearson, J. Michon, Poor survival for infants with MYCN amplified metastatic neuroblastoma despite intensified treatment: the international society of paediatric oncology european neuroblastoma experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 1014–1019 (2009)
S. Gherardi, E. Valli, D. Erriquez, G. Perini, MYCN-mediated transcriptional repression in neuroblastoma: the other side of the coin. Front. Oncol. 3, 1–8 (2013)
P.J. Hurlin, N-myc functions in transcription and development. Birth Defects Res. 75, 340–352 (2005)
M. Huang, W.A. Weiss, Neuroblastoma and MYCN. Cold Spring Harbour Perspect. Med. (2013). doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a014415
E. Bell, L. Chen, T. Liu, G.M. Marshall, J. Lunec, D.A. Tweddle, MYCN oncoprotein targets and their therapeutic potential. Cancer Lett. 293, 144–157 (2010)
T.P. Stricker, A. Morales, A. Chlenski, L. Guerrero, H.R. Salwen, Y. Gosiengfiao, E.J. Perlman, W. Furman, A. Bahrami, J.M. Shohet, P.E. Zage, M.J. Hicks, H. Shimada, R. Suganuma, J.R. Park, S. So, W.B. London, P. Pytel, K.H. Maclean, S.L. Cohn, Validation of a prognostic multi-gene signature in high-risk neuroblastoma using the high throughput digital NanoString nCounterTM system. Mol. Oncol. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2014.01.01
S.R. Frank, T. Parisi, S. Taubert, P. Fernandez, M. Fuchs, H.M. Chan, D.M. Livingston, B. Amati, MYC recruits the TIP60 histone acetyltransferase complex to chromatin. EMBO Rep. 4, 575–580 (2003)
R. Francisco, A. Pérez-Perarnau, C. Cortés, J. Gil, A. Tauler, S. Ambrosio, Histone deacetylase inhibition induces apoptosis and autophagy in human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Lett. 318, 42–52 (2012)
F.A. Duijkers, R.X. de Menezes, I.J. Goossens-Beumer, D.J. Stumpel, P. Admiraal, R. Pieters, J.P. Meijerink, M.M. van Noesel, Epigenetic drug combination induces genome-wide demethylation and altered gene expression in neuro-ectodermal tumor-derived cell lines. Cell. Oncol. 36, 351–362 (2013)
O. Witt, H.E. Deubzer, M. Lodrini, T. Milde, I. Oehme, Targeting histone deacetylases in neuroblastoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 15, 436–447 (2009)
D.C. Coffey, M.C. Kutko, R.D. Glick, L.M. Butler, G. Heller, R.A. Rifkind, P.A. Marks, V.M. Richon, M.P. La Quaglia, The histone deacetylase inhibitor, CBHA, inhibits growth of human neuroblastoma xenografts in vivo, alone and synergistically with all-trans retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 61, 3591–3594 (2001)
P.A. Marks, W.S. Xu, Histone deacetylase inhibitors: potential in cancer therapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 107, 600–608 (2009)
M. Fouladi, J.R. Park, C.F. Stewart, R.J. Gilbertson, P. Schaiquevich, J. Sun, J.M. Reid, M.M. Ames, R. Speights, A.M. Ingle, J. Zwiebel, S.M. Blaney, P.C. Adamson, Pediatric phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of vorinostat: a Children’s oncology group phase I consortium report. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, 3623–3629 (2010)
C. Conti, E. Leo, G.S. Elchler, O. Sordet, M.M. Martin, A. Fan, M.I. Aladjem, Y. Pommier, Inhibition of histone acetylase in cancer cells slows down replication forks, activates dormant origins and induces DNA damage. Cancer Res. 70, 4470–4480 (2010)
O. Witt, T. Milde, H.E. Deubzer, I. Oehme, R. Witt, A. Kulozik, A. Eisenmenger, U. Abel, I. Karapanagiotou-Schenkel, Phase I/II intra-patient dose escalation study of vorinostat in children with relapsed solid yumor, lymphoma or leukemia. Klin. Padiatr. 224, 398–403 (2012)
N.K.V. Cheung, M.A. Dyer, Neuroblastoma: developmental biology, cancer genomics and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 397–411 (2013)
S. Breit, M. Schwab, Suppression of MYC by high expression of NMYC in human neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 24, 21–28 (1989)
Y. Nakamura, O. Toshinori, H. Niizuma, M. Ohira, T. Kamijo, A. Nakagawara, Functional characterization of a new p53 mutant generated by homozygous deletion in a neuroblastoma cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 354, 892–898 (2007)
J. Carr, E. Bell, A.D.J. Pearson, U.R. Kees, H. Beris, J. Lunec, D.A. Tweddle, Increased frequency of aberrations in the p53/MDM2/p14/ARF pathway in neuroblastoma cell lines established at relapse. Cancer Res. 66, 2138–2145 (2006)
R. Kleinert, Immunohistochemical characterization of primitive neuroectodermal tumors and their possible relationship to the stepwise ontogenetic development of the central nervous system. 1.Ontogenetic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 82, 502–507 (1991)
R. Huang, N.K. Cheung, J. Vider, I.Y. Cheung, W.L. Gerald, S.K. Tickoo, E.C. Holland, R.G. Blasberg, MYCN and MYC regulate tumor proliferation and tumorigenesis directly through BMI1 in human neuroblastomas. FASEB J. 25, 4138–4149 (2011)
C. Zhang, V. Richon, X. Ni, R. Talpur, M. Duvic, Selective induction of apoptosis by histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells: relevance to mechanism of therapeutic action. J. Invest. Dermatol. 125, 1045–1052 (2005)
A. Muhlethaler-Mottet, R. Meier, M. Flahaut, K.B. Bourloud, K. Nardou, J.M. Joseph, N. Gross, Complex molecular mechanisms cooperate to mediate histone deacetylase inhibitors anti-tumour activity in neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cancer (2008). doi:10.1186/1476-4598-7-55
J. Ribas, X. Gomez-Arbones, J. Boix, Caspase 8/10 are not mediating apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells treated with CDK inhibitory drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 524, 49–52 (2005)
W. Lutz, M. Stohr, J. Schurmann, A. Wenzel, A. Lohr, M. Schwab, Conditional expression of N-myc in human neuroblastoma cells increases expression of alpha-prothymosin and ornithine decarboxylase and accelerates progression into S-phase early after mitogenic stimulation of quiescent cells. Oncogene 13, 803–812 (1996)
M.Y. Chen, W.S. Liao, Z. Lu, W.G. Bornmann, V. Hennessey, M.N. Washington, G.L. Rosner, Y. Yu, A.A. Ahmed, R.C. Bast Jr., Decitabine and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) inhibit growth of ovarian cancer cell lines and xenografts while inducing expression of imprinted tumor suppressor genes, apoptosis, G2/M arrest, and autophagy. Cancer 117, 4424–4438 (2011)
A. Slack, J.M. Shohet, MDM2 as a critical effector of the MYCN oncogene in tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle 4, 857–860 (2005)
V.H. Cowling, M.D. Cole, Mechanisms of transcriptional activation by the Myc oncoproteins. Semin Cancer Biol 16, 242–252 (2006)
K. Zhang, F. Faiola, E. Martinez, Six lysine residues on c-Myc are direct substrates for acetylation by p300. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336, 274–280 (2005)
J. Vervoots, J. Lüscher-Firzlaff, B. Lüscher, The ins and outs of MYC regulation by posttranslational mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 34725–34729 (2006)
F. Westermann, D. Muth, A. Bennet, T. Bauer, K.O. Henrich, A. Oberthuer, B. Brors, T. Beissbarth, J. Vandesompele, F. Pattyn, B. Hero, R. König, M. Fischer, M. Schwab, Distinct transcriptional MYCN/c-MYC activities are associated with spontaneous regression or malignant progression in neuroblastomas. Genome Biol. 9, R150–R150.14 (2008)
MYCN oncogene targets, http://mellfire.ugent.be/public/mycnot/, Accessed 21 November (2014)
M. Alaminos, J. Mora, N.K.V. Cheung, A. Smith, J. Qin, L. Chen, W.L. Gerald, Genome-wide analysis of gene expression associated with MYCN in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 63, 4538–4546 (2003)
U. Galderisi, G. Di Bernardo, M. Cipollaro, G. Peluso, A. Cascino, R. Cotrufo, M.A. Melone, Differentiation and apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells: role of N-Myc gene product. J. Cell. Biochem. 73, 97–105 (1999)
R. Janardhanan, N.L. Banik, S.K. Ray, N-Myc down regulation induced differentiation, early cell cycle exit, and apoptosis in human malignant neuroblastoma cells having wild type or mutant p53. Biochem. Pharmacol. 78, 1105–1114 (2009)
S. Fulda, W. Lutz, M. Schwab, K.M. Debatin, MycN sensitizes neuroblastoma cells for drug-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 18, 1479–1485 (1999)
R. Cotterman, V.X. Jin, S.R. Krig, J.M. Lemen, A. Wey, P.J. Farnham, P.S. Knoepfler, N-Myc regulates a widespread euchromatic program in the human genome partially independent of its role as a classical transcription factor. Cancer Res. 68, 9654–9662 (2008)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Megumi Iisasa for correcting the English language. This work was supported by Dirección General de Investigación Científica y Técnica, BFU2009-09933 to A.T. and BFU2012-38867 to S.C.K. and A.T., as well as by Red Temática de Investigación Cooperativa en Cáncer, RD12/0036/0049 to A.T. and S.C.K. and RD12/0036/0029 to S.A. Constanza Cortés was recipient of a fellowship from Universitat de Barcelona.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortés, C., Kozma, S.C., Tauler, A. et al. MYCN concurrence with SAHA-induced cell death in human neuroblastoma cells. Cell Oncol. 38, 341–352 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-015-0233-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-015-0233-9