Abstract
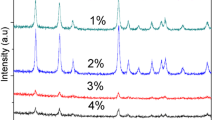
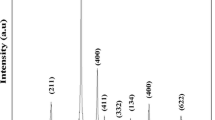
This paper reports the properties of p-type oxide semiconductor Sn1−x Mn x O2 (MTO) nanoparticles with a low doping concentration of Mn (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.05) prepared with a sol-gel method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results show that single-phase rutile MTO was obtained for x up to 0.03. The samples have particle average size of about 100 nm, which was confirmed with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The compositional changes and electrical properties of the MTO nanoparticles were characterized by using x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Hall effect measurements. Mn3+ cations are incorporated into the rutile SnO2 lattice. P-type conduction which is arisen from the substitution of Mn3+ to Sn4+ lattice was demonstrate by Hall data. These compositions have hole carrier concentrations in the range 2.26∼8.53 × 1016 cm−3 and exhibit Hall mobilities in the range 0.8∼4.1 cm2/Vs. The mobility of MTO decreases as the Mn content increases due to the doping effect. A transparent, ptype TFT device can be fabricated with this composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. A. Chaudhary, I. S. Mulla, K. Vijayamohanan, S. G. Hegde, and D. J. Srinivas, J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 2565 (2001).
D. Kotsikau, M. Ivanovskaya, D. Orlik, and M. Falasconi, Sensor Actuat. B-Chem. 101, 199 (2004).
T. Hayakawa and M. Nogami, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 6, 66 (2005).
S. Ferrere, A. Zaban, and B. A. Gsegg, J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 4490 (1997).
V. Subramanian, K. I. Gnanasekar, and B. Rambabu, Solid State Ionics 175, 181 (2004).
S. R. Stampfl, Y. Chen, J. A. Dumesis, Ch. Niu, and C. G. Hill, J. Catal. 105, 445 (1987).
J. Y. Kwon, D. J. Lee, and K. B. Kim, Electron. Mater. Lett. 7, 1 (2011).
O’Mara and C. William, Liquid Crystal Flat Panel Display: Manufacturing Science and Technology, Van Nostrand Reinhold (1993).
C. H. Lee, B. A. Nam, W. K. Choi, J. K. Lee, D. J. Choi, and Y. J. Oh, Mater. Lett. 65, 722 (2011).
Y. Xiao, S. Ge, L. Xi, Y. Zuo, X. Zhou, B. Zhang, L. Zhang, C. Li, X. Han, and Z. Wen, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 7459 (2008).
B. Sathyaseelan, K. Senthilnathan, T. Alagesan, R. Jayavel, and K. Sivakumar, Mater. Chem. Phys. 124, 1046 (2010).
S. Saravanakumar, M. Pattammal, S. Israel, R. A. J. R. Sheeba, and R. Saravanan, Physica B: Condensed Matter 407, 302 (2012).
A. F. Lamrani, M. Belaiche, A. Benyoussef, A. E. Kenz, and E. H. Saidi, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2982 (2011).
A. C. Bose, P. Thangadurai, and S. Ramasamy, Mater. Chem. Phys. 95, 72 (2006).
M. Mehdi, B. Mohagheghi, and M. S. Saremi, J. Appl. Phys. 37, 1248 (2004).
M. Mehdi, B. Mohagheghi, and M. S. Saremi, Semicond. Sci. Tech. 19, 764 (2004).
Z. Ji, Z. He, Y. Song, K. Liu, and Z. Ye, J. Cryst. Growth 259, 282 (2003).
D. J. Kong, H. Deng, P. Yang, and J. Chu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 854 (2009).
S. S. Chee and J. H. Lee, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8, 587 (2012).
D. C. Kundaliya, S. B. Ogale, S. E. Lofland, S. Dhar, C. J. Metting, S. R. Shinde, Z. Ma, B. Varughese, K. V. Ramanujachary, L. Salamanca-Riba, and T. Venkatesan, Nat. Mater. 3, 709 (2004).
W. K. Choi, H. Jin Jung, and S. K. Koh, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 14, 359 (1996).
M. K. Yang, J. W. Park, T. K. Ko, and J. K. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 042105 (2009).
H. W. Nesbitt and D. Banerjee, Am. Mineral. 83, 305 (1998).
L. Romano, A. M. Piro, M. G. Grimaldi, G. Bisognin, E. Napolitani, and D. De Salvador, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 136605 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Choi, DJ. & Oh, YJ. Characterization of the p-type Sn1−x Mn x O2 oxide semiconductor nanoparticles by Sol-Gel method. Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 283–286 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-012-2140-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-012-2140-9