Abstract
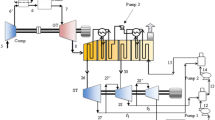
In this study, energy and exergy analyses for four configurations, simple gas turbine, steam bottoming cycle with heat recovery steam generator, heat exchanger and secondary bottoming cycle, are performed. The waste heat from the turbine exhaust is utilized in order to optimize the efficiency and output of a simple gas turbine cycle. The combined cycle efficiencies and exergy destruction for each configuration have been analyzed parametrically by using first and second laws of thermodynamics. The effects of the pressure ratio and turbine inlet temperatures on the specific fuel consumption, net output power, energy and exergy efficiencies and the exergy destruction of the plant are investigated in this study. It is demonstrated that the maximum output of the plant increases up to 32.1% when TIT \(=\) 1500 K and up to 19.3% when TIT \(=\) 2000 K as we go from conventional gas turbine cycle to SBC with HRSG, HX and secondary bottoming cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalina, A.I.: Combined-cycle system with novel bottoming cycle. Trans. ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 106(4), 737–742 (1984)
Frost, T.H.; Anderson, A.; Agnew, B.: A hybrid gas turbine cycle (Brayton/Ericsson): an alternative to conventional combined gas and steam turbine power plant. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A (J. Power Energy) 211(A2), 121–131 (1997)
Najjar, Yousef S.H.: Gas turbine cogeneration systems: a review of some novel cycles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 20(2), 179–197 (2000)
Ishida, M.; Hongguang, J.: Fundamental study on a novel gas turbine cycle. Trans. ASME J. Energy Resour. Technol. 123(1), 10–14 (2001)
Riaz, M.S.; Barb, K.J.; Engeda, A.: A novel technique for steam turbine exhaust pressure limitation using dynamic pressure sensors. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C (J. Mech. Eng. Sci.) 219(C9), 925–932 (2005)
Wu, C.; Tsai, J.-S.: Thermodynamic analysis of mirror gas turbine cycle. Int. J. Power Energy Syst. 26(2), 153–156 (2006)
Shalan, H.E.M.A.; Moustafa Hassan, M.A.; Bahgat, A.B.G.: Comparative study on modelling of gas turbines in combined cycle power plants. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON’10), December 19–21, 2010. Cairo University
Bassily, A.: The application of novel techniques for gas turbine inlet-cooling that improve both the power and efficiency of the modern commercial steam-air-cooled gas turbine combined cycle power plants in hot and humid climates. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A (J. Power Energy) 229(4), 406–430 (2015)
Kumar, A.; Kachhwaha, S.S.; Mishra, R.S.: Steady state thermal analysis of gas turbine power plant cycles at higher temperatures. Indian J. Sci. Ind. Res. 74, 52–57 (2015)
Dellenback, P.A.: Improved gas turbine efficiency through alternative regenerator configuration. Trans. ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 124(3), 441–446 (2002)
Ravi Kumar, N.; Rama Kirishna, K.; Sita Rama Raju, A.V.: Exergy analysis of gas turbine power plant with alternative configuration of regenerator. In: Proceedings 2nd International Exergy Energy Environment Symposium (IEEES2): VI-13. Kos (2005)
Kumar. R.N.; Raju. S.; Rama. A.V.: The study of the effects of gas turbine inlet cooling on plant and HRSG performance. In: Proceedings, National Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering (AIM-2005), Hyderabad (2005)
Ong’iro, A.; Ugursal, V.I.; A1 Taweel, A.M.; Walker, J.D.: Modeling of heat recovery steam generator performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 17(5), 427–446 (1997)
Nag, P.K.; De, S.: Design and operation of a heat recovery steam generator with minimum irreversibility. Appl. Therm. Eng. 17(4), 385–391 (1997)
Casarosa, C.; Franco, A.: Thermodynamic optimization of the operative parameters for the heat recovery in combined power plants. Int. J. Appl. Thermodyn. 4(1), 43–52 (2000)
Salvi, D.; Pierpaoli, P.: Optimization of inlet air cooling systems for steam injected gas turbines. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 41(9), 815–822 (2002)
Chuang, C.; Sue, D.: Performance effects of combined cycle power plant with variable condenser pressure and loading. Energy 30, 1793–1801 (2005)
AL-Hawaj, O.M.; AL-Mutairi, H.A.: combined work cycle with absorption air conditioning. Energy 32, 971–982 (2007)
Xiang, W.; Chen, Y.: Performance improvement of combined cycle work plant based on the optimization of the bottom cycle and heat recuperation. J. Therm. Sci. 16(1), 84–89 (2007)
Polyzakis, A.L.; Koroneos, C.; Xydis, G.: Optimum gas turbine cycle for combined cycle power plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 49(4), 551–563 (2008)
Khaliq, A.: Exergy analysis of gas turbine trigeneration system for combined production of power heat and refrigeration. Int. J. Refrig. 32(3), 534–545 (2009)
Khaliq, A.; Choudhary, K.; Dincer, I.: Exergy analysis of a gas turbine trigeneration system using the Brayton refrigeration cycle for inlet air cooling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A (J. Power Energy) 224(A4), 449–461 (2010)
Ashley, D.S.; Zubaidy, S.A.: Gas turbine performance at varying ambient temperature. Appl. Therm. Eng. 31, 2735–2739 (2011)
Ibrahim, T.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Abdalla, A.N.: Gas turbine configuration for improving the performance of combined cycle power plant. Procedia Eng. 15, 4216–4223 (2011)
Ibrahim, T.K.; Rahman, M.M.: Thermal impact of operating conditions on the performance of a combined cycle gas turbine. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 10, 567–577 (2012)
Kotas, T.J.: The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis. Butterworth Publishers, Stoneham (1985)
Dincer, Ibrahim; Rosen, Marc A.: Exergy, Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2007)
Zhu, S.; Deng, K.; Qu, S.: Energy and exergy analyses of a bottoming Rankine cycle for engine exhaust heat recovery. Energy 58, 448–457 (2013)
Bejan, A.: Fundamentals of exergy analysis, entropy generation minimization, and the generation of flow architecture. Int. J. Energy Res. 26, 545–565 (2002)
Sanjay, Prasad B.N.: Energy and exergy analysis of intercooled combustion-turbine based combined cycle power plant. Energy 59, 277–284 (2013)
Tiwari, A.K.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M.: Exergy analysis of combined cycle power plant: NTPC Dadri, India. Int. J. Thermodyn. (IJoT) 16(1), 36–42 (2013)
Ghazikhani, M.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Mousavi, M.: Two new high-performance cycles for gas turbine with air bottoming. Energy 36(1), 294–304 (2011)
Ghazikhani, M.; Khazaee, I.; Abdekhodaie, E.: Exergy analysis of gas turbine with air bottoming cycle. Energy 72, 599–607 (2014)
Carcasci, C.; Costanzi, F.; Pacifici, B.: Performance analysis in off-design condition of gas turbine air-bottoming combined system. Energy Procedia 45, 1037–1046 (2014)
Singh, S.; Agarwal, O.; Rajay, M.: Energy and exergy analysis of Brayton–Brayton hybrid cycle for power plant applications. Eng. Lett. 22(4), 215 (2014)
Naradasu, R.K.; Konijeti, R.K.; Raju, Venkata Alluru S.R.: Thermodynamic analysis of heat recovery steam generator in combined cycle power plant. Therm. Sci. 11(4), 143–156 (2007)
Tiwari, A.K.; Islam, Mohd; Khan, M.N.: Thermodynamic analysis of combined cycle power plant. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2(4), 480–491 (2010)
Chmielniak, T.; Czaja, D.; Lepszy, S.; Stępczyńska-Drygas, K.: Thermodynamic and economic comparative analysis of air and steam bottoming cycle. Energy 92(2), 189–196 (2015)
Bolland, O.; Forde, M.; Hande, B.: Air bottoming cycle: use of gas turbine waste heat for power generation. J Eng Gas Turbines Power 118(2), 359–368 (1996)
Alklaibi, A.M.; Khan, M.N.; Khan, W.A.: Thermodynamic analysis of gas turbine with air bottoming cycle. Energy 107(15), 603–611 (2016)
Moran, M.J.; Shapiro, H.N.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, 5th edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.N., Tlili, I. & Khan, W.A. Thermodynamic Optimization of New Combined Gas/Steam Power Cycles with HRSG and Heat Exchanger. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 4547–4558 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2549-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2549-4