Abstract
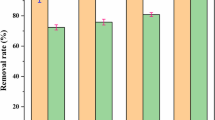
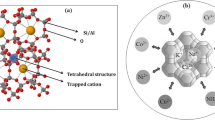
In this study, we used clinoptilolite-supported iron hydroxide NPs (\(\hbox {Fe(OH)}_{3}\)/Cp) for evaluating the simultaneous removal of \(\hbox {NO}_{3}^{-}\) and \(\hbox {PO}_{4}^{-3}\). Remediation was investigated in a range of initial concentrations of \(\hbox {NO}_{3}^{-}\) (0–25 mg/L) and \(\hbox {PO}_{4}^{-3}\) (0–25 mg/L) as a function of pH (2–8), nanoparticles concentration (1 and 0.5 g/L). To achieve the best result, the weight ratio of raw material in iron sulfate versus clinoptilolite (5:1, 2:1, 1:1, 2:1) was tested. The highest pollutant removal was obtained 93% for \(\hbox {PO}_{4}^{-3}\) in 5:1 ratio of Fe versus clinoptilolite and 81% for \(\hbox {NO}_{3}^{-}\) in 1:2 ratio of Fe versus clinoptilolite at the pH of 2. Kinetic data for \(\hbox {NO}_{3}^{-}\) and \(\hbox {PO}_{4}^{-3}\) were well fitted in the pseudo-first-order model and pseudo-second-order model, respectively. Based on the results, it may be concluded that \(\hbox {Fe(OH)}_{3}\)/Cp NPs can effectively be used for simultaneous removal of \(\hbox {NO}_{3}^{- }\) and \(\hbox {PO}_{4}^{-3 }\) from water resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malakouti, M.J.: Sustainable agriculture and increase performance by optimizing fertilizer use in Iran, The Agricultural Education Research, Sana Press, Tehran, Iran, 2005, pp. 220 (in Persian)
Elmi, A.A.; Chandra, M.; Egeh, M.; Liu, A.; Hamel, C.: Environmental and agronomic implications of water table and nitrogen fertilization management. J. Environ. Qual. 31, 1858–1867 (2002)
Boumans, L.J.; Fraters, D.; Van Drecht, G.: Nitrate leaching in agriculture to upper groundwater in the sandy regions of the Netherlands during the 1992–1995 period. Environ. Monit. Assess. 102, 225–241 (2005)
FAO: Current World Fertilizer Trends and Outlook to 2018, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome (2015)
Salome, G.P.; Soares, E.J.: Activated carbon supported metal catalysts for nitrate and nitrite reduction in water. Catal. Lett. 126, 253–260 (2008)
Fan, A.M.; Steinberg, V.E.: Health implications of nitrate and nitrite in drinking water: an update on methemoglobinemia occurrence and reproductive and developmental toxicity. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 23, 35–43 (1996)
Nolan, B.T.; Ruddy, B.C.; Hitt, K.J.; Helsel, D.R.: Risk of nitrate in ground waters of the United States a national perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2229–2236 (1997)
Xiong, Z.; Zhao, D.; Pan, G.: Rapid and controlled transformation of nitrate in water and brine by stabilized iron nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 11, 807–819 (2008)
Blaney, L.M.; Cinar, S.; Sen Gupta, A.K.: Hybrid anion exchanger for trace phosphate removal from water and wastewater. Water Res. 41, 1603–1613 (2007)
Barca, C.; Gérente, C.; Meyer, D.; Chazarenc, F.; Andrès, Y.: Phosphate removal from synthetic and real wastewater using steel slags produced in Europe. Water Res. 46, 2376–2384 (2012)
Bennion, H.; Juggins, S.; Anderson, N.J.: Predicting epilimnetic phosphorus concentrations using an improved diatom-based transfer function and its application to lake eutrophication management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 2004–2007 (1996)
Chapra, S.C.: Surface Water-Quality Modeling. McGraw-Hill Inc, Singapore (1997)
Park, J.K.; Wang, J.; Novotny, G.: Waste Water Characterization for Evaluation of Biological Phosphorus Removal. Wisconsin, USA (1997)
Taghipour, M.; Jalali, M.: Effect of nanoparticles on kinetics release and fractionation of phosphorus. J. Hazard. Mater. 283, 359–370 (2015)
Windolf, J.; Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Carstensen, J.; Kronvang, B.: Changes in nitrogen loads to estuaries following implementation of governmental action plans in Denmark: a paired catchment and estuary approach for analyzing regional responses. Environ. Sci. Policy. 24, 24–33 (2012)
Yang, Z.C.; Zhao, N.; Huang, F.; Lv, Y.Z.: Long-term effects of different organic and inorganic fertilizer treatments on soil organic carbon sequestration and crop yields on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 146, 47–52 (2015)
Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Luan, Z.; Peng, X.; Liang, Z.; Shi, L.: Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by red mud using a factorial design. J. Hazard. Mater. 165, 1193–1199 (2009)
Bekta, N.; Akbulut, H.; Inan, H.; Dimoglo, A.: Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by electro-coagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 106, 101–105 (2004)
Zhang, W.X.: Nanoscale Fe particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J. Nanopart. Res. 5, 323–332 (2003)
Narr, J.; Viraraghavan, T.; Jin, Y.C.: Applications of nanotechnology in water/wastewater treatment: a review. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 16, 320–329 (2007)
Theron, J.; Walker, J.A.; Cloete, T.E.: Nanotechnology and water treatment: applications and emerging opportunities. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 34, 43–69 (2008)
Chen, S.S.; Hsu, H.D.; Li, C.W.: A new method to produce nanoscale Fe for nitrate removal. J. Nanopart. Res. 6, 639–647 (2004)
Sun, Y.P.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, H.P.: Characterization of zero-valent Fe nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 120, 47–56 (2006)
Cumbal, L.; Greenleaf, J.; Leun, D.; SenGupta, A.K.: Polymer supported inorganic nanoparticles: characterization and environmental applications. React. Funct. Polym. 54, 167–180 (2003)
Nurmi, J.T.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Sarathy, V.; Baer, D.R.; Amonette, J.E.; Pecher, K.: Characterization and properties of metallic iron nanoparticles: spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 1221–1230 (2005)
Liu, R.; Zhao, D.: Reducing leachability and bioaccessibilty of lead in soils using a new class of stabilized iron phosphate nanoparticles. Water Res. 41, 2491 (2007)
Arai, Y.; Sparks, D.L.: ATR-FTIR spectroscopic investigation on phosphate adsorption mechanisms at the ferrihydrite-water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 241, 317–326 (2001)
Chitrakar, R.; Tezuka, S.; Sonoda, A.; Sakane, K.; Ooi, K.; Hirotsu, T.: Phosphate adsorption on synthetic goethite and akaganeite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 602–609 (2006)
Harvey, O.R.; Rhue, R.D.: Kinetics and energetics of phosphate sorption in a multi-component Al(III)–Fe(III) hydr(oxide) sorbent system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 322, 384–393 (2008)
Zhang, G.S.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, R.P.; Qu, J.H.: Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 335, 168–174 (2009)
Long, F.; Gong, J.L.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Deng, J.H.; Niu, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.R.: Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by magnetic Fe–Zr binary oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 171, 448–455 (2011)
Liu, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Yan, X.: Enhanced chitosan beads-supported \(\text{ Fe }^{0}\)-nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals from electroplating wastewater inpermeable reactive barriers. Water Res. 47, 6691–6700 (2013)
Lu, J.B.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, R.P.; Zhao, X.; Sun, L.P.; Qu, J.H.: Adsorptive removal of phosphate by a nanostructured Fe–Al–Mn trimetal oxide adsorbent. Powder Technol. 233, 146–154 (2013)
Moharami, S.; Jalali, M.: Effect of \(\text{ TiO }_{2}\), \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\), and \(\text{ Fe }_{3}\text{ O }_{4}\) nanoparticles on phosphorus removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 33, 1209–1219 (2014)
Li, G.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.: Enhanced adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by nanostructured Fe(III)–copper(II) binary oxides. Chem. Eng. J. 235, 124–131 (2014)
Liou, Y.H.; Lo, S.L.; Lin, C.J.; Kuan, W.H.: Size effect in reactivity of copper nanoparticles to carbon tetrachloride degradation. Water Res. 41, 1705–1712 (2007)
Lee, C.C.; Doong, R.A.: Dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene in aqueous solutions using metal-modified zerovalent silicon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 4752–4757 (2008)
Uzum, C.; Shahwan, T.; Eroglu, A.E.; Eroglu, K.R.; Scott, T.B.; Lieberwirth, I.: Synthesis and characterization of kaolinite-supported zero-valent Fe nanoparticles and their application for the removal of aqueous Cu \(^{2+}\) and Co\(^{2+}\) ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 43, 172–181 (2008)
Liu, F.; Yang, J.H.; Zuo, J.; Ma, D.; Gan, L.; Xie, B.; Wang, P.; Yang, B.: Graphene-supported nanoscale zero-valent Fe: removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution and mechanistic study. J. Environ. Sci. 26, 1751–1762 (2014)
Huang, Y.; Yang, J.K.; Keller, A.A.: Removal of arsenic and phosphate from aqueous solution by metal (hydr-)oxide coated sand. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 1128–1138 (2014)
Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, D.; Kong, H.: Synthesis and properties of zeolite/hydrated Fe oxide composite from coal fly ash as efficient adsorbent to simultaneously retain cationic and anionic pollutants from water. Fuel 116, 71–76 (2014)
Birks, L.; Friedman, H.: Particle size determination from X-ray line broadening. J. Appl. Phys. 17, 687–692 (1946)
Cucarella, V.; Renman, G.: Phosphorus sorption capacity of filter materials used for on-site wastewater treatment determined in batch experiments-a comparative study. J. Environ. Qual. 38, 381–392 (2009)
Violante, A.; Pigna, M.: Competitive sorption of arsenate and phosphate on different clay minerals and soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 66, 1788–1796 (2002)
Dang, Y.P.; Dalal, R.C.; Edwards, D.G.; Tiller, K.G.: Kinetics of zinc desorption from Vertisols. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 58, 1392–1399 (1994)
Kassaee, M.Z.; Motamedi, E.; Mikhak, A.; Rahnemaie, R.: Nitrate removal from water using iron nanoparticles produced by arc discharge vs. reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 166, 490–495 (2011)
Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, T.C.: Effects of low pH on nitrate reductionby Fe powder. Water Res. 38, 2631–2642 (2004)
Zhang, T.C.; Huang, Y.H.: Effects of selected good’s pH buffers on nitrate reduction by Fe powder. J. Environ. Eng. 131, 461–470 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikhak, A., Sohrabi, A., Kassaee, M.Z. et al. Removal of Nitrate and Phosphate from Water by Clinoptilolite-Supported Iron Hydroxide Nanoparticle. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 2433–2439 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2432-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2432-3