Abstract
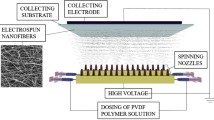
In this study, polyethylene glycol (PEG)-reinforced polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibrous membranes were fabricated by electrospinning technique. The PEG was incorporated into the PET matrix at fixed ratios (1/1, 2/1, 4/1, 6/1, 8/1, 10/1, w/w) to significantly improve the conductivity and reduce the viscosity of the solution, which would result in a novel morphology and high hydrophilicity of the composite fibrous membranes. Water contract angle tests show that the membranes exhibit super hydrophilic properties only when the ratio of PET/PEG is 10/1. The 6/1-PET fibrous membrane exhibits uniform and smooth morphology, while the flat fibers are formed in 4/1-PET fibrous membrane. Furthermore, incorporation of PEG can also significantly improve the mechanical properties of PET membranes. The tensile strength is increased about two times in 6/1-PET membrane compared with pure PET membrane. Additionally, the 6/1-PET membrane has the best porosity and NaCl rejection due to the uniform and thinner fibers. This work finds that PEG can effectively improve hydrophilic and mechanical properties of electrospun PET fibrous membranes, which plays a vital role in filtration field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai Y., Niu J., Yin L., Xu J., Xi Y.: Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on electrospun nanofibrous membranes: sorption kinetics and mechanism. J Hazard. Mater. 192, 1409–1417 (2011)
Liu Y., Wang R., Ma H., Hsiao B.S., Chu B.: High-flux microfiltration filters based on eletrospun polyvinylalcohol nanofibrous membranes. Polymer 54, 548–556 (2013)
Prince J.A., Anbharasi V., Shanmugasundaram T.S., Singh G.: Preparation and characterization of novel triple layer hydrophilic-hydrophobic composite membrane for desalination using air gap membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 118, 598–603 (2013)
Grafe T., Graham K.: Polymeric nanofibers and nanofiber webs: a new class of nonwovens. Int. Nonwovens J. 12, 51–55 (2003)
Yoon K., Hsiao B.S., Chu B.: Functional nanofibers for environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. 44, 5326–5334 (2008)
Wang Z., Ma H., Hsiao B.S., Chu B.: Nanofibrous ultrafiltration membranes containing cross-linked poly(ethylene glycol) and cellulose nanofiber composite barrier layer. Polymer 55, 366–372 (2014)
Ding B., Yu J.Y.: Electrospun Nanofibers for Energy and Environmental Applications, Nanostructure Science and Technology, pp. 355–369. Springer, Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London (2014)
Goh Y.F., Shakir I., Hussain R.: Electrospun fibers for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound dressing. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 3027–3054 (2013)
Ma H., Hsiao B.S., Chu B.: Thin-film nanofibrous composite membranes containing cellulose or chitin barrier layers fabricated by ionic liquids. Polymer 52, 2594–2599 (2011)
Zhang S., Shim W.S., Kim J.: Design of ultra-fine nonwovens via electrospinning of Nylon 6: spinning parameters and filtration efficiency. Mater. Des. 30, 3659–3666 (2009)
Chen J.C., Harrison I.R.: Modification of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) carbon fiber precursor via post-spinning plasticization and stretching in dimethyl formamide (DMF). Carbon 40, 25–45 (2002)
Ding B., Kim H.Y., Lee S.C., Shao C.L., Lee D.R., Park S.J., Kwag G.B., Choi K.J.: Preparation and characterization of a nanoscale poly(vinyl alcohol) fiber aggregate produced by an electrospinning method. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phy. 40, 1261–1268 (2002)
Nakata K., Hun K.S., Ohkoshi Y., Gotoh Y., Nagura M.: Electrospinning of poly (ether sulfone) and evaluation of the filtration efficiency. Sen’ i Gakkaishi 63, 307–312 (2007)
Moon S., Choi J., Farris R.J.: Preparation of aligned polyetherimide fiber by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 109, 691–694 (2008)
Chen H., Liu Z., Cebe P.: Chain confinement in electrospun nanofibers of PET with carbon nanotubes. Polymer 50, 872–880 (2009)
Meng X.F., Luo N., Cao S.L., Zhang S.M., Yang M.S., Hu X.: In-situ growth of titania nanoparticles in electrospun polymer nanofibers at low temperature. Mater. Lett. 63, 1401–1403 (2009)
Kim G.M., Lach R., Michler G.H., Pötschke P.: Relationships between phase morphology and deformation mechanisms in polymer nano-composite nanofibres prepared by an electrospinning process. Nanotechnology 17, 963–972 (2006)
Sui X., Wiesel E., Wagner H.D.: Mechanical properties of electrospun PMMA micro-yarns: Effects of NaCl mediation and yarn twist. Polymer 53, 5037–5044 (2012)
Fennessey S.F., Farris R.J.: Fabrication of aligned and molecularly oriented electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and the mechanical behavior of their twisted yarns. Polymer 45, 4217–4225 (2004)
Kołbuk D., Sajkiewicz P., Kowalewski T.A.: Optcrientation of electrospun polycaprolactone fibers by polarizing-interference microscopy. Eur. Polym. J. 48, 275–283 (2012)
Li Ai.D., Sun Z.Z., Zhou M., Xu X.X., Ma J.Y., Zheng W., Zhou H.M., Li L., Zheng Y.F.: Electrospun Chitosan-graft-PLGA nanofibres with significantly enhanced hydrophilicity and improved mechanical property. Colloid. Surf. B. 102, 674–681 (2013)
Ma Z., Kotaki M., Yong T., He W., Ramakrishna S.: Surface engineering ofelectrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers towards develop-ment of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials. 26, 2527–2536 (2005)
Li G.H., Zhao Y.M., Lv M.Q., Shi Y., Cao D.: Super hydrophilic poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/poly(vinylalcohol) (PVA) composite fibrous mats with improved mechanical properties prepared via electrospinning process. Colloid. Surf. A. 436, 417–424 (2013)
Bhattarai S.R., Bhattarai N., Viswanathamurthi P., Yi H.K., Hwang P.H., Kim H.Y.: Hydrophilic nanofibrous structure of polylactide; fabrication and cell affinity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 78(.), 247–257 (2006)
Sun M., Li X., Ding B., Yu J., Sun G.: Mechanical and wettable behavior of polyacrylonitr- ile reinforced fibrous polystyrene mats. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 347, 147–152 (2010)
Favaro S.L., Rubira A.F., Muniz E.C., Radovanovic E.: Surface modification of HDPE,PP and PET films with KMnO4/HCl solutions. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 92, 1219–1226 (2007)
Zhang H., Du Z., Jiang Y., Yu Q.: Preparation and characterization of grafting polyacrylamide from PET Films by SI-ATRP via sater-borne system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 126, 1941–1955 (2012)
Vasita R., Shanmugam K., Katti D.S.: Improved biomaterials for tissue engineering applications: Surface modification of polymers. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 8, 341–353 (2008)
Hao J., Lei G., Li Z., Wu L., Xiao Q., Wang L.: A novel polyethylene terephthalate nonwoven separator based on electrospinning technique for lithium ion battery. J. Membr. Sci. 428, 11–16 (2013)
Briscoe B., Luckham P., Zhu S.: The effects of hydrogen bonding upon the viscosity of aqueous poly(vinyl alcohol) solutions. Polymer 41, 3851–3860 (2000)
Uyar T., Besenbacher F.: Electrospinning of uniform polystyrene fibers: The effect of solvent conductivity. Polymer 49, 5336–5343 (2008)
Koski A., Yim K., Shivkumar S.: Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 58, 493–497 (2004)
Koombhongse S., Liu W., Reneker D.H.: Flat polymer ribbons and other shapes by electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. B. 39, 2598–2606 (2001)
Baji A., Mai Y.w., Wong S.C., Abtahia M., Chen P.: Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: Effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 703–718 (2010)
Zavareh S., Samandari G.: Polyethylene glycol as an epoxy modifier with extremely high toughening effect: Formation of nanoblend morphology. Polym. Eng. Sci. 54, 1833–1838 (2014)
Hadjizadeh A., Ajji A., Bureau M.N.: Nano/micro electro-spun polyethylene terephthalate fibrous mat preparation and characterization. J. mech. Behave. Biomed. 4, 340–351 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Based on 10th International Conference on Novel Materials and their Synthesis (NMS) - China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L.N., Xin, C.Z., Liu, W.T. et al. Electrospun PET/PEG Fibrous Membrane with Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Hydrophilicity for Filtration Applications. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 2889–2895 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1828-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1828-1