Abstract
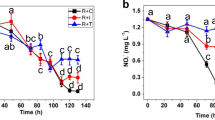
The marine microalga Chlorella sp. (PSDK01) was cultured in shrimp-cultured effluent under different initial population densities (IPDs) ranging from 0.25 to 12.0 g L−1 for dual purpose (excess nutrient consumption and biomass productivity). It was found that the IPD had affected the nutrient consumption and biomass significantly (P < 0.001). A higher biomass productivity compared to that of other IPDs was achieved in 0.5 g L−1 IPD, and the concentration had reached 0.78 g L−1 d−1. In the same time, higher IPD derived higher biomass concentration (up to 5.5 g L−1) in 6 days growth, but at the end of the experiment (9th day), the biomass was slightly decreased (2 %). In the current observation, while starting IPDs 0.25–0.5 g L−1, with the increase in IPD, the biomass productivity also increased, when IPD exceed the 0.5 g L−1, the biomass productivity reversely decreased. The maximum nutrients consumption was recorded in 0.5 g L−1 IPD at the end of the experiment (9th day) as 96, 69, and 67 % for phosphate, nitrate, and nitrite, respectively. However, the highest \({{\rm NH}_{3}^{-}}\) consumption (63 %) was observed in 0.25 g L−1 on 9th day. Maximum ammonia consumption in other IPDs was resulted at 6th day, after that ammonia concentration was slightly increased from the previous concentration due to the decay of microalgae. Based on these results, to obtain the maximum nutrient consumption and biomass productivity of Chlorella sp. (PSDK01) in diverse wastewater on large-scale level, it is necessary to select a suitable IPD at around 0.5 g L−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pillay, T.V.R: Aquaculture: Principles and Practices. Fishing New Books, Englands (1990)
Tovar, A.; Moreno, C.; Manuel-Vez, M.P.; Garcia-Vargas, M.: Environmental impacts of intensive aquaculture in marine waters. Water Res. 34, 334–342 (2000)
Tovar, A.; Moreno, C.; Manuel-Vez, M.P.; Garcia-Vargas, M.: Environmental implications of intensive marine aquaculture in earthen ponds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 40, 981–988 (2000)
Peuhkuri, T.: Knowledge and interpretation in environmental conflict: Fish farming and eutrophication in the Archipelago Sea, SW Finland. Landsc. Urban Plan. 61, 157–168 (2002)
Hazourli, S.; Ziati, M.; Benredjem, Z.; Delimi, R.; Boudiba, L.: Analysis of wastewater loaded with paint before and after treatment of coagulation–flocculation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37, 897–903 (2012)
Olguıin, E.J.: Phycoremediation: key issues for cost-effective nutrient removal processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 22, 81–91 (2003)
Mulbry, W.; Kondrad, S.; Pizarro, C.; Kebede-Westhead, E.: Treatment of dairy manure effluent using freshwater algae: Algal productivity and recovery of manure nutrients using pilot-scale algal turf scrubbers. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 8137–9142 (2008)
Patel, A.; Barrington, S.; Lefsrud, M.: Microalgae for phosphorus removal and biomass production: A six species screen for dual-purpose organisms. GCB Bioenergy 4, 485–495 (2012)
Munoz, R.; Guieysse, B.: Algal-bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: a review. Water Res. 40, 2799–2815 (2006)
Pizarro, C.; Mulbry, W.; Blersch, D.; Kangas, P.: An economic assessment of algal turf scrubber technology for treatment of dairy manure effluent. Ecol. Eng. 26, 321–327 (2006)
Kumar, S.D.; Santhanam, P.; Jayalakshmi, T.; Nandakumar, R.; Ananth, S.; Devi, A.S.; Prasath, B.B.: Ex-situ studies on excessive nutrients and heavy metals removal efficacy of marine microalga Chlorella marina (Butcher) for wastewater treatment. Indian J. Geomarine Sci. (2014, in press)
Guillard, R.R.L.: Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith, W.L.; Chanley, M.H. (eds.) Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals, pp. 29–60. Plenum Press, New York (1975)
Ip, P.F.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, F.: Enhanced production of astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in mixotrophic culture. Process Biochem. 39, 1761–1766 (2004)
Hirata, S.; Hayashitani, M.; Taya, M.; Tone, S.: Carbon dioxide fixation in batch culture of Chlorella sp. using a photobioreactor with a sunlight-collection device. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 81, 470–472 (1996)
Hirano, A.; Ueda, R.; Hirayama, S.; Ogushi, Y.: \({{\rm CO}_{2}}\) fixation and ethanol production with microalgal photosynthesis and intracellular anaerobic fermentation. Energy 22, 137–142 (1997)
Craggs, R.J.; McAuley, P.J.; Smith, V.J.: Wastewater nutrient removal by marine microalgae grown on a corrugated raceway. Water Res. 31, 1701–1707 (1997)
Lee, K.; Lee, C.G.: Effect of light/dark cycles on wastewater treatment by microalgae. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 6, 194–199 (2001)
Singh, R.P.; Fu, D.; Fu, D.; Juan, H.: Pollutant removal efficiency of vertical sub-surface upward flow constructed wetlands for highway runoff treatment. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39, 3571–3578 (2014)
Venkatesan, R.; Vasagam, K.P.K.; Balasubramanian, T.: Culture of marine microalgae in shrimp farm discharge water: a sustainable approach to reduce the cost production and recovery of nutrients. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1, 262–269 (2006)
Ahmad, F.; Khan, A.U.; Yasar, A.: The potential of Chlorella vulgaris for wastewater treatment and biodiesel production. Pak. J. Bot. 45, 461–465 (2013)
Knuckey, R.M.; Brown, M.R.; Barrett, S.M.; Hallegraeff, G.M.: Isolation of new nanoplanktonic diatom strains and their evaluation as diets for juvenile Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Aquaculture 211, 253–274 (2002)
Walne, P.R.: Studies on the food value of nineteen genera of algae to juvenile bivalves of the genera Ostrea, Crassostrea, Mercenaria and Mytilis. Fish. Investig. 26, 1–62 (1970)
Strickland, S.C.; Parsons, T.R.: A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analyses, pp. 185. Bulletin of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa (1972)
Jenkins, D.; Medsken, L.: A brucine method for the determination of nitrate in ocean, estuarine, and fresh waters. Anal. Chem. 36, 61 (1964)
Richmond, A.; Zhang, C.W.; Zarmi, Y.: Efficient use of strong light for high photosynthetic productivity: Interrelationships between the optical path, the optimal population density and cell-growth inhibition. Biomol. Eng. 20, 229–236 (2003)
Zar, J.H.: Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1999)
Jones, A.B.; Preston, N.P.; Dennison, W.C.: Integrated treatment of shrimp effluent by sedimentation, oyster filtration and macroalga absorption: a laboratory scale study. Aquaculture 193, 155–178 (2001)
Teicchert-Coddington, D.R.; Rouse, D.B.; Potss, A.; Boyd, C.E.: Treatment of harvest discharge from intensive shrimp ponds by settling. Aquac. Eng. 19, 147–161 (1999)
Jackson, C.J.; Preston, N.; Buford, M.A.; Thompson, J.P.: Managing the development of sustainable shrimp farming in Australia: The role of sedimentation ponds in treatment of farm discharge water. Aquaculture 146, 113–118 (2003)
Chrismadha, T.; Borowitzka, M.A.: Effect of cell-density and irradiance on growth, proximate composition and eicosapentaenoic acid production of Phaeodactylum tricornutum grown in a tubular photobioreactor. J. Appl. Phycol. 6, 67–74 (1994)
Richmond, A.; Zou, N.: Efficient utilization of high photon irradiance for mass production of photoautotrophic micro-organisms. J. Appl. Phycol. 11, 123–127 (1999)
Hu, Q.; Guterman, H.; Richmond, A.: A flat inclined modular photobioreactor for outdoor mass cultivation of photoautotrophs. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 51, 51–60 (1996)
Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Gao, L.: Effects of initial population density (IPD) on growth and lipid composition of Nannochloropsis sp. J. Appl. Phycol. 24, 1623–1627 (2012)
de Viçose, G.C.; Porta, A.; Viera, M.P.; Fernández-Palacios, H.; Izquierdo, M.S.: Effects of density on growth rates of four benthic diatoms and variations in biochemical composition associated with growth phase. J. Appl. Phycol. 24, 1427–1437 (2012)
Rekha, V.; Gurusamy, R.; Santhanam, P.; Devi, A.S.; Ananth, S.: Culture and biofuel production efficiency of marine microalgae Chlorella marina and Skeletonema costatum. Indian J. Geo-marine Sci. 41, 152–158 (2012)
Devi, A.S.: Effect of Salinity, Illumination and Nitrogen Concentration on Growth and Pigment Production of Marine Phytoplankton Dunaliella sp. for Exploration of Carotene. M. Phil.; Thesis, Bharathidasan University, India (2011)
Devi, A.S.; Santhanam, P.; Rekha, V.; Ananth, S.; Prasath, B.B.; Nandakumar, R.; Jeyanthi, S.; Kumar, S.D.: Culture and biofuel producing efficacy of marine microalgae Dunaliella salina and Nannochloropsis sp. J. Algal Biomass Util. 3, 38–44 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S.D., Santhanam, P., Lewis-Oscar, F. et al. A Dual Role of Marine Microalga Chlorella sp. (PSDK01) in Aquaculture Effluent with Emphasis on Initial Population Density. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 29–35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1498-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1498-4