Abstract
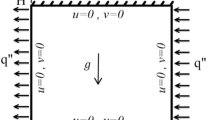
In this paper, Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in a square cavity with a linearly heated wall which is filled by nanofluid has been investigated. The fluid in the cavity is a water-based nanofluid containing various nanoparticles such as copper (Cu), cupric oxide (CuO) or alumina (Al2O3). This study has been conducted for Rayleigh numbers of 103 to 105, while solid volume fraction (φ)varied from 0 to 16 %. The effects of nanopartcles are displayed on streamlines, isotherms counters, local and average Nusselt number. Copper nanoparticle enhances heat transfer more than other nanoparticles, while the lowest heat transfer is demonstrated by alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles. In addition, the increment of Rayleigh number causes the effect of the nanoparticles to increase.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Lattice speed
- c i :
-
Discrete particle speeds
- c p :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- F :
-
External forces
- f :
-
Density distribution functions
- f eq :
-
Equilibrium density distribution functions
- g :
-
Internal energy distribution functions
- g eq :
-
Equilibrium internal energy distribution functions
- G :
-
Gravity
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- L :
-
Enclosure height
- M :
-
Lattice numbers
- Ma :
-
Mach number
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- R :
-
Constant of the gases
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- T :
-
Temperature
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- ω i :
-
Weighted factor for flow (D2Q9)
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- φ :
-
Volume fraction
- τ c :
-
Relaxation time for temperature
- τ v :
-
Relaxation time for flow
- ρ :
-
Density
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- ϑ :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- Δx :
-
Lattice spacing
- Δt :
-
Time increment
- \({\omega^{ '} _{i}}\) :
-
Weighted factor for temperature (D2Q4)
- avg:
-
Average
- C:
-
Cold
- f:
-
Fluid
- H:
-
Hot
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- s:
-
Solid
- *:
-
Normalized
References
Chen S., Doolen G.: Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 329–364 (1998)
Alexander, F.J.; Chen, S.; Sterling, J.D.: Lattice Boltzmann thermohydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. E 47, 2249–2252 (1993)
Qian, Y.: Simulating thermohydrodynamics with lattice BGK models. J. Sci. Comput. 8, 231–241 (1993)
Chen, Y.; Ohashi, H.; Akiyama, M.: Thermal lattice Bhatnagar–Gross–Krook model without nonlinear deviations in macrodynamic equations. Phys. Rev. E 50, 2776 –2783 (1994)
Bartoloni, A.; Battista, C.: LBE simulations of Rayleigh–Bernard convection on the APE100 parallel processor. Int. J. Modul. Phys. C 4, 993–1006 (1993)
Eggles, G.J.M.; Somers, J.A.: Numerical simulation of free convective flow using the lattice-Boltzmann scheme. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 16, 357–364 (1995)
Shan, X.: Simulation of Rayleigh–Bernard convection using a lattice-Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 55, 2780–2788 (1997)
Filippova, O.; Hanel, D.: A novel BGK approach for low Mach number combustion. J. Comput. Phys. 158, 139–160 (2000)
Mei, R.; Shyy, W.; Yu, D.; Luo, L.S.: Lattice Boltzmann method for 3-D flows with curved boundary. J. Comput. Phys. 161, 680–699 (2000)
Succi, S.: The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond. Clarendon Press, Oxford, London (2001)
Mohamad, A.A.: Applied Lattice Boltzmann Method for Transport Phenomena, Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer. Sure, Calgary (2007)
Aghajani, D.M.; Farhadi, M.; Sedighi, K.: Effect of discrete heater at the vertical wall of the cavity over the heat transfer and entropy generation using LBM. Thermal Sci. 14, 469–477 (2010)
Mohamad, A.A.; Kuzmin, A.: A critical evaluation of force term in lattice Boltzmann method, natural convection problem. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53, 990–996 (2010)
Mohamad, A.A.; Bennacer, R.; El-Ganaoui, M.: Double dispersion, natural convection in an open end cavity simulation via Lattice Boltzmann Method. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 49, 1944–1953 (2010)
Mussa, M.A.; Abdullah, S.; Nor Azwadi, C.S.; Muhamad, N.: Simulation of natural convection heat transfer in an enclosure by the lattice-Boltzmann method. Comp. Fluids 44, 162–168 (2011)
Sajjadi, H.; Gorji, M.; Kefayati, GH.R.; Ganji, D.D.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of MHD mixed convection in two sided lid-driven square cavity. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 41(2), 179–195 (2012)
Sajjadi, H.; Gorji, M.; Hosseinizadeh, S.F.; Kefayati, GH.R.; Ganji, D.D.: Numerical analysis of turbulent natural convection in square cavity using large-Eddy simulation in Lattice Boltzmann method. Iran J. Sci. Tech. Trans. B/Eng. 35, 133–142 (2011)
Sarris, I.E.; Lekakis, I.; Vlachos, N.S.: Natural convection in a 2D enclosure with sinusoidal upper wall temperature. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A 42, 513–530 (2002)
Roy, S.; Basak, T.: Finite element analysis of natural convection flows in a square cavity with nonuniformly heated wall(s). Int. J. Eng. Sci. 43, 668–680 (2005)
Sathiyamoorthy, M.; Basak, T.; Roy, S.; Pop, I.: Steady natural convection flows in a square cavity with linearly heated side wall(s). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 766–775 (2007)
Choi, U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Fluids Eng. Div. 231, 99–105 (1995)
Lee, S.; Choi, S.U.S.; Li, S.; Eastman, J.A.: Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles. ASME J. Heat Trans. 121, 280–289 (1999)
Eastman, J.A.; Choi, S.U.S.; Yu, W.; Thompson, L.J.: Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 718–720 (2001)
Das, S.K.; Putra, N.; Thiesen, P.; Roetzel, W.: Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 125, 567–574 (2003)
Jang, S.P.; Choi, S.U.S.: The role of Brownian motion in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4316–4318 (2004)
Das, S.K.; Putra, N.; Roetzel, W.: Pool boiling characteristics of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 851–862 (2003)
Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Grulke, E.A.; Anderson, W.B.; Wu, G.: Heat transfer properties of nanoparticle-in-fluid dispersions (nanofluids) in laminar flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 1107–1116 (2005)
Xuan, Y.; Li, Q.: Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. ASME Trans. J. Heat Transf. 125, 151–155 (2003)
Wen, D.; Ding, Y.: Experimental investigation into convective heat transfer of nanofluid at the entrance region under laminar flow conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 5181–5188 (2004)
Heris, S.Z.; Etemad, S.G.; Esfahany, M.N.: Experimental investigation of oxide nanofluids laminar flow convective heat transfer. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 33, 529–535 (2006)
Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K.; Lightstone, M.: Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 3639–3653 (2003)
Putra, N.; Roetzel, W.; Das, S.K.: Natural convection of nano-fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 39, 775–784 (2003)
Hwang, K.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, S.P.: Buoyancy-driven heat transfer of water-based Al2O3 nanofluids in a rectangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 4003–4010 (2007)
Santra, A.K.; Sen, S.; Chakraborty, N.: Study of heat transfer augmentation in a differentially heated square cavity using copper–water nanofluid. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 47, 1113–1122 (2008)
Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E.: Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 29, 1326–1336 (2008)
Abu-Nada, E.; Masoud, Z.; Hijazi, A.: Natural convection heat transfer enhancement in horizontal concentric annuli using nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 35(5), 657–665 (2008)
Jahanshahi, M.; Hosseinizadeh, S.F.; Alipanah, M.; Dehghani, A.; Vakilinejad, G.R.: Numerical simulation of free convection based on experimental measured conductivity in a square cavity using water/SiO2 nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37, 687–694 (2010)
Moraveji, K.M.; Darabi, M.; Haddad, S.M.H.; Davarnejad, R.: Modeling of convective heat transfer of a nanofluid in the developing region of tube flow with computational fluid dynamics. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 1291–1295 (2011)
Mahmoodi, M.; Hashemi, S.M.: Numerical study of natural convection of a nanofluid in C-shaped enclosures. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 55, 76–89 (2012)
Mahmoodi, M.: Numerical simulation of free convection of a nanofluid in L-shaped cavities, Int. J. Thermal Sci. 50, 1731–1740 (2011)
Arefmanesh, A.; Amini, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Najafi, M.: Buoyancy-driven heat transfer analysis in two-square duct annuli filled with a nanofluid. European J. Mech. B/Fluids 33, 95–104 (2012)
Mahmoodi, M.: Numerical simulation of free convection of nanofluid in a square cavity with an inside heater. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 50, 2161–2175 (2011)
Kefayati, GH.R.; Hosseinizadeh, S.F.; Gorji, M.; Sajjadi, H.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in an open enclosure subjugated to water/copper nanofluid, Int. J. Thermal Sci. 52, 91–101 (2012)
Kefayati, GH.R.; Hosseinizadeh, S.F.; Gorji, M.; Sajjadi, H.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in tall enclosures using water/ SiO2 nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 798–80 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kefayati, G.R. Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Natural Convection in a Square Cavity with a Linearly Heated Wall Using Nanofluid. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 2143–2156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0748-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0748-1