Abstract
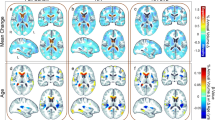
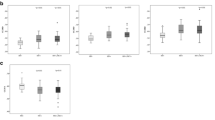
Controversy remains regarding the neurotoxicity of clade C human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-C). When examined in preclinical studies, a cysteine to serine substitution in the C31 dicysteine motif of the HIV-C Tat protein (C31S) results in less severe brain injury compared to other viral clades. By contrast, patient cohort studies identify significant neuropsychological impairment among HIV-C individuals independent of Tat variability. The present study clarified this discrepancy by examining neuroimaging markers of brain integrity among HIV-C individuals with and without the Tat substitution. Thirty-seven HIV-C individuals with the Tat C31S substitution, 109 HIV-C individuals without the Tat substitution (C31C), and 34 HIV− controls underwent 3T structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Volumes were determined for the caudate, putamen, thalamus, corpus callosum, total gray matter, and total white matter. DTI metrics included fractional anisotropy (FA), radial diffusivity (RD), and axial diffusivity (AD). Tracts of interest included the anterior thalamic radiation (ATR), cingulum bundle (CING), uncinate fasciculus (UNC), and corpus callosum (CC). HIV+ individuals exhibited smaller volumes in subcortical gray matter, total gray matter and total white matter compared to HIV− controls. HIV+ individuals also exhibited DTI abnormalities across multiple tracts compared to HIV− controls. By contrast, neither volumetric nor diffusion indices differed significantly between the Tat C31S and C31C groups. Tat C31S status is not a sufficient biomarker of HIV-related brain integrity in patient populations. Clinical attention directed at brain health is warranted for all HIV+ individuals, independent of Tat C31S or clade C status.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann C, Andronikou S, Laughton B, Kidd M, Dobbels E, Innes S et al (2014) White matter signal abnormalities in children with suspected HIV-related neurologic disease on early combination antiretroviral therapy. Pediatr Infect Dis J 33:e207–e212
Ananworanich J, Sacdalan CP, Pinyakorn S, Chomont N, de Souza M, Luekasemsuk T et al (2016) Virological and immunological characteristics of HIV-infected individuals at the earliest stage of infection. Journal of virus eradication 2:43–48
Ances BM, Ortega M, Vaida F, Heaps J, Paul R (2012) Independent effects of HIV, aging, and HAART on brain volumetric measures. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 59:469–477
Boivin MJ, Ruel TD, Boal HE, Bangirana P, Cao H, Eller LA et al (2010) HIV-subtype A is associated with poorer neuropsychological performance compared with subtype D in antiretroviral therapy-naive Ugandan children. AIDS 24:1163–1170
Catani M, de Schotten MT (2012) Atlas of human brain connections
Chan PA, Reitsma MB, DeLong A, Boucek B, Nunn A, Salemi M et al (2014) Phylogenetic and geospatial evaluation of HIV-1 subtype diversity at the largest HIV center in Rhode Island. Infect Genet Evol 28:358–366
Chen Y, An H, Zhu H, Stone T, Smith KJ, Hall C et al (2009) White matter abnormalities revealed by diffusion tensor imaging in non-demented and demented HIV+ patients. NeuroImage 47:1154–1162
Cohen RA, Harezlak J, Schifitto G, Hana G, Clark U, Gongvatana A et al (2010) Effects of nadir CD4 count and duration of human immunodeficiency virus infection on brain volumes in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era. J Neurovirol 16:25–32
Constantino AA, Huang Y, Zhang H, Wood C, Zheng JC (2011) HIV-1 clade B and C isolates exhibit differential replication: relevance to macrophage-mediated neurotoxicity. Neurotox Res 20:277–288
Correia S, Lee SY, Voorn T, Tate DF, Paul RH, Zhang S et al (2008) Quantitative tractography metrics of white matter integrity in diffusion-tensor MRI. NeuroImage 42:568–581
de Almeida S, Ribeiro C, de Pereira A, Badiee J, Cherner M, Smith D et al (2013) Neurocognitive impairment in HIV-1 clade C- versus B-infected individuals in Southern Brazil. Journal of NeuroVirology 19:550–556
Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D et al (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 31:968–980
Filippi CG, Ulug AM, Ryan E, Ferrando SJ, van Gorp W (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging of patients with HIV and normal-appearing white matter on MR images of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:277–283
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11050–11055
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C et al (2002) Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33:341–355
Gamaldo CE, Gamaldo A, Creighton J, Salas RE, Selnes OA, David PM et al (2013) Evaluating sleep and cognition in HIV. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 63:609–616
Gandhi N, Saiyed Z, Thangavel S, Rodriguez J, Rao KV, Nair MP (2009) Differential effects of HIV type 1 clade B and clade C Tat protein on expression of proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines by primary monocytes. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 25:691–699
Ghate M, Narkhede H, Rahane G, Nirmalkar A, Gaikwad N, Kadam D (2014) Cognitive function among HIV infected children in Pune. Indian J Pediatr 82:515–518
Gongvatana A, Schweinsburg BC, Taylor MJ, Theilmann RJ, Letendre SL, Alhassoon OM et al (2009) White matter tract injury and cognitive impairment in human immunodeficiency virus–infected individuals. Journal of Neurovirology 15:187–195
Gupta JD, Satishchandra P, Gopukumar K, Wilkie F, Waldrop-Valverde D, Ellis R et al (2007) Neuropsychological deficits in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade C-seropositive adults from South India. J Neurovirol 13:195–202
Hawkins CP, McLaughlin JE, Kendall BE, McDonald WI (1993) Pathological findings correlated with MRI in HIV infection. Neuroradiology 35:264–268
He JGJ, Mui K, Aminipour S, Kim J, Fuller R, Rataj E, Lentz M, Sehgal P, Westmoreland S, de Crespigny A, Gonzalex R (2003) Diffusion MR detection of early white matter changes in the SIV primate model of neuroaids. Intl Soc Mag Reson Med:2536
Heaps JM, Joska J, Hoare J, Ortega M, Agrawal A, Seedat S et al (2012) Neuroimaging markers of human immunodeficiency virus infection in South Africa. Journal of NeuroVirology 18:151–156
Heaps JM, Sithinamsuwan P, Paul R, Lerdlum S, Pothisri M, Clifford D et al (2015) Association between brain volumes and HAND in cART-naïve HIV+ individuals from Thailand. Journal of NeuroVirology 21:105–112
Hemelaar J, Gouws E, Ghys PD, Osmanov S (2011) Isolation W-UNfH, characterisation. Global trends in molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 during 2000–2007. AIDS 25:679–689
Hoare J, Fouche J-P, Spottiswoode B, Sorsdahl K, Combrinck M, Stein DJ et al (2011) White-matter damage in clade C HIV-positive subjects: a diffusion tensor imaging study. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 23:308315
Hoare J, Fouche JP, Spottiswoode B, Donald K, Philipps N, Bezuidenhout H et al (2012) A diffusion tensor imaging and neurocognitive study of HIV-positive children who are HAART-naive “slow progressors”. J Neurovirol 18:205–212
Hoare J, Fouche J-P, Phillips N, Joska JA, Donald KA, Thomas K et al (2015a) Clinical associations of white matter damage in cART-treated HIV-positive children in South Africa. Journal of NeuroVirology 21:120–128
Hoare J, Fouche J-P, Phillips N, Joska JA, Paul R, Donald KA, et al. (2015b) White matter micro-structural changes in ART-naive and ART-treated children and adolescents infected with HIV in South Africa. AIDS, Publish Ahead of Print
Huang W, Eshleman SH, Toma J, Fransen S, Stawiski E, Paxinos EE et al (2007) Coreceptor tropism in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype D: high prevalence of CXCR4 tropism and heterogeneous composition of viral populations. J Virol 81:7885–7893
Jenkinson M, Smith S (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5:143–156
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) FSL. NeuroImage 62:782–790
Jernigan TL, Archibald SL, Fennema-Notestine C, Taylor MJ, Theilmann RJ, Julaton MD et al (2011) Clinical factors related to brain structure in HIV: the CHARTER study. J Neurovirol 17:248–257
Joska JA, Westgarth-Taylor J, Myer L, Hoare J, Thomas KGF, Combrinck M et al (2011) Characterization of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders among individuals starting antiretroviral therapy in South Africa. AIDS Behav 15:1197–1203
Kaleebu P, French N, Mahe C, Yirrell D, Watera C, Lyagoba F et al (2002) Effect of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 envelope subtypes A and D on disease progression in a large cohort of HIV-1-positive persons in Uganda. The Journal of infectious diseases 185:1244–1250
Kaleebu P, Nankya IL, Yirrell DL, Shafer LA, Kyosiimire-Lugemwa J, Lule DB et al (2007) Relation between chemokine receptor use, disease stage, and HIV-1 subtypes A and D: results from a rural Ugandan cohort. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 45:28–33
Kallianpur KJ, Shikuma C, Kirk GR, Shiramizu B, Valcour V, Chow D et al (2013) Peripheral blood HIV DNA is associated with atrophy of cerebellar and subcortical gray matter. Neurology 80:1792–1799
Kallianpur KJC, Donn Jahanshad, Neda Fletcher, James L Ananworanich, Jintanat Clifford, Katherine Benjapornpong, Khunthalee Adams, Collin Spudich, Serena S. Valcour (2016) Victor. for the The RV254/SEARCH010 Study Group. Brain Volumetric Changes After 2 Years of ART Initiated During Acute HIV Infection | CROI Conference. In: CROI. Boston, MA
Kiwanuka N, Laeyendecker O, Robb M, Kigozi G, Arroyo M, McCutchan F et al (2008) Effect of human immunodeficiency virus Type 1 (HIV-1) subtype on disease progression in persons from Rakai, Uganda, with incident HIV-1 infection. The Journal of infectious diseases 197:707–713
Kiwanuka N, Robb M, Laeyendecker O, Kigozi G, Wabwire-Mangen F, Makumbi FE et al (2010) HIV-1 viral subtype differences in the rate of CD4+ T-cell decline among HIV seroincident antiretroviral naive persons in Rakai district, Uganda. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 54:180–184
Leemans A, Jones DK (2009) The B-matrix must be rotated when correcting for subject motion in DTI data. Magn Reson Med 61:1336–1349
Leite SCB, Corrêa DG, Doring TM, Kubo TTA, Netto TM, Ferracini R et al (2013) Diffusion tensor MRI evaluation of the corona radiata, cingulate gyri, and corpus callosum in HIV patients. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI 38:1488–1493
Mbugua KK, Holmes MJ, Cotton MF, Ratai EM, Little F, Hess AT, et al. (2016) HIV-associated CD4/8 depletion in infancy is associated with neurometabolic reductions in the basal ganglia at age 5 years despite early antiretroviral therapy. Aids
McCutchan FE (2006) Global epidemiology of HIV. J Med Virol 78(Suppl 1):S7–s12
Mishra M, Vetrivel S, Siddappa NB, Ranga U, Seth P (2008) Clade-specific differences in neurotoxicity of human immunodeficiency virus-1 B and C Tat of human neurons: significance of dicysteine C30C31 motif. Ann Neurol 63:366–376
Mori S, van Zijl PC (2002) Fiber tracking: principles and strategies—a technical review. Biomedicine 15:468–480
Oishi K, Faria AV, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2010) MRI atlas of human white matter.: Academic Press
Ortega M, Heaps JM, Joska J, Vaida F, Seedat S, Stein DJ et al (2013) HIV clades B and C are associated with reduced brain volumetrics. Journal of NeuroVirology 19:479–487
Osmanov S, Pattou C, Walker N, Schwardlander B, Esparza J, Isolation W-UNH et al (2002) Estimated global distribution and regional spread of HIV-1 genetic subtypes in the year 2000. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 29:184–190
Ostrosky-Solis F, Ramirez M, Ardila A (2004) Effects of culture and education on neuropsychological testing: a preliminary study with indigenous and nonindigenous population. Appl Neuropsychol 11:188–195
Paul R, Cohen R, Navia B, Tashima K (2002) Relationships between cognition and structural neuroimaging findings in adults with human immunodeficiency virus type-1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:353–359
Paul RH, Ernst T, Brickman AM, Yiannoutsos CT, Tate DF, Cohen RA et al (2008) Relative sensitivity of magnetic resonance spectroscopy and quantitative magnetic resonance imaging to cognitive function among nondemented individuals infected with HIV. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 14:725–733
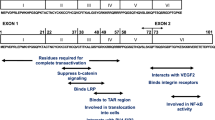
Paul RH, Joska JA, Woods C, Seedat S, Engelbrecht S, Hoare J et al (2014) Impact of the HIV Tat C30C31S dicysteine substitution on neuropsychological function in patients with clade C disease. Journal of NeuroVirology 20:627–635
Radloff LS (1977) The CES-D scale: a self report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurements 1:385–401
Ranga U, Shankarappa R, Siddappa NB, Ramakrishna L, Nagendran R, Mahalingam M et al (2004) Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C strains is a defective chemokine. J Virol 78:2586–2590
Rao VR, Sas AR, Eugenin EA, Siddappa NB, Bimonte-Nelson H, Berman JW et al (2008) HIV-1 clade-specific differences in the induction of neuropathogenesis. J Neurosci 28:10010–10016
Rao VR, Neogi U, Talboom JS, Padilla L, Rahman M, Fritz-French C et al (2013) Clade C HIV-1 isolates circulating in Southern Africa exhibit a greater frequency of dicysteine motif-containing Tat variants than those in Southeast Asia and cause increased neurovirulence. Retrovirology 10:61
Rosselli M, Ardila A (2003) The impact of culture and education on non-verbal neuropsychological measurements: a critical review. Brain Cogn 52:326–333
Sacktor N, Nakasujja N, Skolasky RL, Rezapour M, Robertson K, Musisi S et al (2009) HIV subtype D is associated with dementia, compared with subtype A, in immunosuppressed individuals at risk of cognitive impairment in Kampala, Uganda. Clin Infect Dis 49:780–786
Sacktor N, Nakasujja N, Redd AD, Manucci J, Laeyendecker O, Wendel SK et al (2014) HIV subtype is not associated with dementia among individuals with moderate and advanced immunosuppression in Kampala, Uganda. Metab Brain Dis 29:261–268
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E et al (1998) The mini-international neuropsychiatric interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. The Journal of clinical psychiatry 59(Suppl 20):22
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155
Stern RA, Silva SG, Chaisson N, Evans DL (1996) Influence of cognitive reserve on neuropsychological functioning in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Arch Neurol 53:148–153
Valcour V, Chalermchai T, Sailasuta N, Marovich M, Lerdlum S, Suttichom D et al (2012) Central nervous system viral invasion and inflammation during acute HIV infection. J Infect Dis 206:275–282
Vasan A, Renjifo B, Hertzmark E, Chaplin B, Msamanga G, Essex M et al (2006) Different rates of disease progression of HIV type 1 infection in Tanzania based on infecting subtype. Clin Infect Dis 42:843–852
Yepthomi T, Paul R, Vallabhaneni S, Kumarasamy N, Tate DF, Solomon S et al (2006) Neurocognitive consequences of HIV in southern India: a preliminary study of clade C virus. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 12:424–430
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC et al (2006) User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 31:1116–1128
Zhang SDC, Laidlaw DH (2003) Visualizing diffusion tensor MR images using streamtubes and streamsurfaces. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 9:454–462
Zhang H, Yushkevich PA, Alexander DC, Gee JC (2006) Deformable registration of diffusion tensor MR images with explicit orientation optimization. Med Image Anal 10:764–785
Zhang H, Avants BB, Yushkevich PA, Woo JH, Wang S, McCluskey LF et al (2007) High-dimensional spatial normalization of diffusion tensor images improves the detection of white matter differences: an example study using amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:1585–1597
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This work was supported by a NIH grant (MH085604).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, R.H., Phillips, S., Hoare, J. et al. Neuroimaging abnormalities in clade C HIV are independent of Tat genetic diversity. J. Neurovirol. 23, 319–328 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-016-0503-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-016-0503-y