Abstract
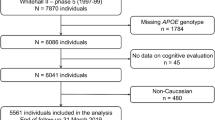
The ε4 allele of the apolipoprotein E (ApoE) gene may have important interactions with physical health and cognitive function among individuals with HIV disease. The purpose of this study is to examine the relationships between ε4, HIV disease, age, neuropsychological impairment, and death in a large, well-characterized study sample. A total of 2846 men participating in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study had ApoE genotyping and neuropsychological test data available for analysis. We found a significant association between HIV infection and time to death (from any cause), as well as older age, race, and education. But, ApoE status was not significantly associated with time to death. Similarly, we found a significant association between HIV infection and time to incident cognitive impairment, as well as age, education, and HIV serostatus; Apoε4 status was not related to incident cognitive impairment. There were no significant interactions between ApoE, HIV infection, and age on cognitive impairment. These data replicate and strengthen prior findings of the lack of association between ApoE ε4 and cognitive outcomes in HIV disease. We conclude that within the specific constraints of an exclusively male study in which the majority of participants were less than 65 years of age (range 22–87 years), it appears reasonable to conclude that the ε4 allele is not significantly interacting with HIV serostatus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres MA, Feger U, Nath A, Munsaka S, Jiang CS, Chang L (2010) APOE epsilon 4 allele and CSF APOE on cognition in HIV-infected subjects. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 6(3):389–398
Antinori A, Arendt G, Becker JT, Brew BJ, Byrd DA, Cherner M, Clifford DB, Cinque P, Epstein LG, Goodkin K, Gisslen M, Grant I, Heaton RK, Joseph J, Marder K, Marra CM, McArthur JC, Nunn M, Price RW, Pulliam L, Robertson KR, Sacktor N, Valcour V, Wojna VE (2007) Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology 69(18):1789–1799
Becker JT, Kingsley LA, Molsberry S, Reynolds S, Aronow A, Levine AJ, Martin E, Miller EN, Munro CA, Ragin A, Sacktor N, Selnes OA (2014) “Cohort profile: recruitment cohorts in the neuropsychological substudy of the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study.” Int J Epidemiol
Beydoun MA, Beydoun HA, Kaufman JS, An Y, Resnick SM, O'Brien R, Ferrucci L, Zonderman AB (2013) Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele interacts with sex and cognitive status to influence all-cause and cause-specific mortality in U.S. older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 61(4):525–534
Brayne C, Harrington CR, Wischik CM, Huppert FA, Chi LY, Xuereb JH, O'Connor DW, Paykel ES (1996) Apolipoprotein E genotype in the prediction of cognitive decline and dementia in a prospectively studied elderly population. Dementia 7(3):169–174
Burt TD, Agan BK, Marconi VC, He W, Kulkarni H, Mold JE, Cavrois M, Huang Y, Mahley RW, Dolan MJ, McCune JM, Ahuja SK (2008) Apolipoprotein (apo) E4 enhances HIV-1 cell entry in vitro, and the APOE epsilon4/epsilon4 genotype accelerates HIV disease progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(25):8718–8723
Chang L, Andres M, Sadino J, Jiang CS, Nakama H, Miller E, Ernst T (2011) Impact of apolipoprotein E epsilon4 and HIV on cognition and brain atrophy: antagonistic pleiotropy and premature brain aging. Neuroimage 58(4):1017–1027
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261(5123):921–923
Drenos F, Kirkwood TB (2010) Selection on alleles affecting human longevity and late-life disease: the example of apolipoprotein E. PLoS ONE 5(4):e10022
Guang-da X, You-ying L, Zhi-song C, Yu-sheng H, Xiang-jiu Y (2004) Apolipoprotein e4 allele is predictor of coronary artery disease death in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 175(1):77–81
Hoare J, Westgarth-Taylor J, Fouche JP, Combrinck M, Spottiswoode B, Stein DJ, Joska JA (2012) “Relationship between apolipoprotein E4 genotype and white matter integrity in HIV-positive young adults in South Africa.” Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci
Hoenig JM, Heisey DM (2001) “The abuse of power: the pervasive fallacy of power calculations in data analysis.” The American Statistician 55(19–24)
Jarvik GP (1997) Genetic predictors of common disease: apolipoprotein E genotype as a paradigm. Ann Epidemiol 7(5):357–362
Joska JA, Combrinck M, Valcour VG, Hoare J, Leisegang F, Mahne AC, Myer L, Stein DJ (2010) Association between apolipoprotein E4 genotype and human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia in younger adults starting antiretroviral therapy in South Africa. J Neurovirol 16(5):377–383
Kingsley LA, Cuervo-Rojas J, Munoz A, Palella FJ, Post W, Witt MD, Budoff M, Kuller L (2008) Subclinical coronary atherosclerosis, HIV infection and antiretroviral therapy: Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. AIDS 22(13):1589–1599
Kraemer HC, Mintz J, Noda A, Tinklenberg J, Yesavage JA (2006) Caution regarding the use of pilot studies to guide power calculations for study proposals. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63(5):484–489
Kulminski AM, Arbeev KG, Culminskaya I, Arbeeva L, Ukraintseva SV, Stallard E, Christensen K, Schupf N, Province MA, Yashin AI (2014) Age, gender, and cancer but not neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases strongly modulate systemic effect of the Apolipoprotein E4 allele on lifespan. PLoS Genet 10(1):e1004141
Lane KA, Gao S, Hui SL, Murrell JR, Hall KS, Hendrie HC (2003) Apolipoprotein E and mortality in African-Americans and Yoruba. J Alzheimers Dis JAD 5(5):383–390
Lee JH, Tang MX, Schupf N, Stern Y, Jacobs DM, Tycko B, Mayeux R (2001) Mortality and apolipoprotein E in Hispanic, African-American, and Caucasian elders. Am J Med Genet 103(2):121–127
Liu CC, Kanekiyo T, Xu H, Bu G (2013) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat Rev Neurol 9(2):106–118
Mahley RW (1988) Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 240(4852):622–630
Menzel HJ, Kladetzky RG, Assmann G (1983) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis 3(4):310–315
Miller EN, Selnes OA, McArthur MB (1990) Neuropsychological test performance in HIV1-infected homosexual men: the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS). Neurology 40:197–203
Miller EN, Satz P, Visscher B (1991) Computerized and conventional neuropsychological assessment of HIV1-infected homosexual men. Neurology 41(10):1608–1616
Moore CG, Carter RE, Nietert PJ, Stewart PW (2011) Recommendations for planning pilot studies in clinical and translational research. Clin Transl Sci 4(5):332–337
Morgan EE, Woods SP, Letendre SL, Franklin DR, Bloss C, Goate A, Heaton RK, Collier AC, Marra CM, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Morgello S, Simpson DM, McCutchan JA, Ellis RJ, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Smith DM, Grant I, Vaida F, Clifford DB (2013) “Apolipoprotein E4 genotype does not increase risk of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.” J Neurovirol
Panos SE, Hinkin CH, Singer EJ, Thames AD, Patel SM, Sinsheimer JS, Del Re AC, Gelman BB, Morgello S, Moore DJ, Levine AJ (2013) Apolipoprotein-E genotype and human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorder: the modulating effects of older age and disease severity. Neurobehav HIV Med 5:11–22
Radloff LS (1977) The CES-D Scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1:385–401
Rosvall L, Rizzuto D, Wang HX, Winblad B, Graff C, Fratiglioni L (2009) APOE-related mortality: effect of dementia, cardiovascular disease and gender. Neurobiol Aging 30(10):1545–1551
Selnes OA, Miller EN (1994) Development of a screening battery for HIV-related cognitive impairment: the MACS experience. Neuropsychology of HIV Infection. I. Grant and A. Martin. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 176–190
Sing CF, Davignon J (1985) Role of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism in determining normal plasma lipid and lipoprotein variation. Am J Hum Genet 37(2):268–285
Soontornniyomkij V, Moore DJ, Gouaux B, Soontornniyomkij B, Tatro ET, Umlauf A, Masliah E, Levine AJ, Singer EJ, Vinters HV, Gelman BB, Morgello S, Cherner M, Grant I, Achim CL (2012) Cerebral beta-amyloid deposition predicts HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders in APOE epsilon4 carriers. AIDS 26(18):2327–2335
Spector SA, Singh KK, Gupta S, Cystique LA, Jin H, Letendre S, Schrier R, Wu Z, Hong KX, Yu X, Shi C, Heaton RK (2010) APOE epsilon4 and MBL-2 O/O genotypes are associated with neurocognitive impairment in HIV-infected plasma donors. AIDS 24(10):1471–1479
Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS, Roses AD (1993) Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(5):1977–1981
Sun B, Abadjian L, Rempel H, Calosing C, Rothlind J, Pulliam L (2010) Peripheral biomarkers do not correlate with cognitive impairment in highly active antiretroviral therapy-treated subjects with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Neurovirol 16(2):115–124
Tiret L, de Knijff P, Menzel HJ, Ehnholm C, Nicaud V, Havekes LM (1994) ApoE polymorphism and predisposition to coronary heart disease in youths of different European populations. The EARS Study. European Atherosclerosis Research Study. Arterioscler Thromb J Vasc Biol Am Heart Assoc 14(10):1617–1624
Valcour V, Shiramizu B, Shikuma C (2008) Frequency of apolipoprotein E4 among older compared with younger HIV patients: support for detrimental effect of E4 on survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(41):E66, author reply E67-68
Wardell MR, Suckling PA, Janus ED (1982) Genetic variation in human apolipoprotein E. J Lipid Res 23(8):1174–1182
Woods SP, Rippeth JD, Frol AB, Levy JK, Ryan E, Soukup VM, Hinkin CH, Lazzaretto D, Cherner M, Marcotte TD, Gelman BB, Morgello S, Singer EJ, Grant I, Heaton RK (2004) Interrater reliability of clinical ratings and neurocognitive diagnoses in HIV. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 26(6):759–778
Zuo L, van Dyck CH, Luo X, Kranzler HR, Yang BZ, Gelernter J (2006) Variation at APOE and STH loci and Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Funct 2:13
Acknowledgments
Data in this manuscript were collected by the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS) with centers at Baltimore (U01-AI35042): The Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health: Joseph B. Margolick (PI), Barbara Crain, Adrian Dobs, Homayoon Farzadegan, Joel Gallant, Lisette Johnson-Hill, Cynthia Munro, Michael W. Plankey, Ned Sacktor, James Shepard, Chloe Thio; Chicago (U01-AI35039): Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, and Cook County Bureau of Health Services: John P. Phair, Sheila Badri, Maurice O’Gorman, David Ostrow, Frank Palella, Ann Ragin; Los Angeles (U01-AI35040): University of California, UCLA Schools of Public Health and Medicine: Roger Detels (PI), Otoniel Martínez-Maza (Co-P I), Aaron Aronow, Robert Bolan, Elizabeth Breen, Anthony Butch, Beth Jamieson, Eric N. Miller, John Oishi, Harry Vinters, Dorothy Wiley, Mallory Witt, Otto Yang, Stephen Young, Zuo Feng Zhang; Pittsburgh (U01-AI35041): University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health: Charles R. Rinaldo (PI), Lawrence A. Kingsley (Co-PI), James T. Becker, Ross D. Cranston, Jeremy J. Martinson, John W. Mellors, Anthony J. Silvestre, Ronald D. Stall; and the Data Coordinating Center (UM1-AI35043): The Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health: Lisa P. Jacobson (PI), Alvaro Munoz (Co-PI), Alison, Abraham, Keri Althoff, Christopher Cox, Jennifer Deal, Gypsyamber D’Souza, Priya Duggal, Janet Schollenberger, Eric C. Seaberg, Sol Su, Pamela Surkan. The MACS is funded primarily by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), with additional co-funding from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), and the National Institute on Deafness and Communication Disorders (NIDCD) also provided targeted supplemental funding for specific projects. MACS data collection is also supported by UL1-TR000424 (JHU CTSA). Website located at http://www.statepi.jhsph.edu/macs/macs.html. The contents of this publication are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Additional support for the analysis of these data and preparation of the manuscript was provided by funds from the NIH to J.T.B. (AG034852 and MH098745).
The members of the Neuropsychology Working Group include James T. Becker, Pim Brouwers, Christopher Cox, Jenna Fahey, Rebecca Godfrey, Karl Goodkin, Robin Huebner, Andrew J. Levine, Eileen M. Martin, Donna M. Martineck, Eric M. Miller, Ann Ragin, Sandra Reynolds, JoanaDarc Roe, Ned Sacktor, Janet Schollenberger, Eric Seaberg, Ola A. Selnes, and Matthew Wright. The authors are grateful to Dr. S. Wolinsky at Northwestern University for his assistance in the genetic analysis and the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Eric N. Miller is the author of the reaction time software used in this study (CalCAP) and has a financial interest in the software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
For the Neuropsychology Working Group of the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, J.T., Martinson, J.J., Penugonda, S. et al. No association between Apoε4 alleles, HIV infection, age, neuropsychological outcome, or death. J. Neurovirol. 21, 24–31 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-014-0290-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-014-0290-2