Abstract
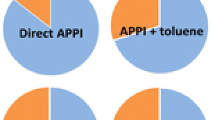
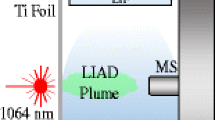
A novel, gas-tight API interface for gas chromatography–mass spectrometry was used to study the ionization mechanism in direct and dopant-assisted atmospheric pressure photoionization (APPI) and atmospheric pressure laser ionization (APLI). Eight analytes (ethylbenzene, bromobenzene, naphthalene, anthracene, benzaldehyde, pyridine, quinolone, and acridine) with varying ionization energies (IEs) and proton affinities (PAs), and four common APPI dopants (toluene, acetone, anisole, and chlorobenzene) were chosen. All the studied compounds were ionized by direct APPI, forming mainly molecular ions. Addition of dopants suppressed the signal of the analytes with IEs above the IE of the dopant. For compounds with suitable IEs or Pas, the dopants increased the ionization efficiency as the analytes could be ionized through dopant-mediated gas-phase reactions, such as charge exchange, proton transfer, and other rather unexpected reactions, such as formation of [M + 77]+ in the presence of chlorobenzene. Experiments with deuterated toluene as the dopant verified that in case of proton transfer, the proton originated from the dopant instead of proton-bound solvent clusters, as in conventional open or non-tight APPI sources. In direct APLI using a 266 nm laser, a narrower range of compounds was ionized than in direct APPI, because of exceedingly high IEs or unfavorable two-photon absorption cross-sections. Introduction of dopants in the APLI system changed the ionization mechanism to similar dopant-mediated gas-phase reactions with the dopant as in APPI, which produced mainly ions of the same form as in APPI, and ionized a wider range of analytes than direct APLI.

ᅟ







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robb, D.B., Covey, T.R., Bruins, A.P.: Atmospheric pressure photoionization: an ionisation method for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 72, 3653–3659 (2000)
Syage, J.A., Evans, M.D., Hanold, K.A.: Photoionization mass spectrometry. Am. Lab. 32, 24–29 (2000)
Marchi, I., Rudaz, S., Veuthey, J.-L.: Atmospheric pressure photoionization for coupling liquid-chromatography to mass spectrometry: a review. Talanta 78, 1–18 (2009)
Núñez, O., Gallart-Ayala, H., Martins, C.P.B., Moyano, E., Galceran, M.T.: Atmospheric pressure photoionization mass spectrometry of fullerenes. Anal. Chem. 84, 5316–5326 (2012)
Raffaelli, A., Saba, A.: Atmospheric pressure photoionization mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 22, 318–331 (2003)
Kersten, H., Funcke, V., Lorenz, M., Brockmann, K.J., Benter, T., O’Brien, R.: Evidence of neutral radical induced analyte ion transformations in APPI and near-VUV APLI. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20, 1868–1880 (2009)
Klee, S., Albrecht, S., Derpmann, V., Kersten, H., Benter, T.: Generation of ion-bound solvent clusters as reactant ions in dopant-assisted APPI and APLI. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 405, 6933–6951 (2013)
Kauppila, T.J., Kuuranne, T., Meurer, E.C., Eberlin, M.N., Kotiaho, T., Kostiainen, R.: Atmospheric pressure photoionization. The ionization mechanism and the effect of the solvent on ionization of naphthalenes. Anal. Chem. 74, 5470–5479 (2002)
Revelsky, I.A., Yashin, Y.S., Sobolevsky, T.G., Revelsky, A.I., Miller, B., Oriedo, V.: Electron ionization and atmospheric pressure photochemical ionization in gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of amino acids. J. Mass Spectrom. 9, 497–507 (2003)
Haapala, M., Luosujärvi, L., Saarela, V., Kotiaho, T., Ketola, R.A., Franssila, S., Kostiainen, R.: Microchip for combining gas chromatography or capillary liquid chromatography with atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 4994–4999 (2007)
Luosujärvi, L., Haapala, M., Thevis, M., Saarela, V., Franssila, S., Ketola, R.A., Kostiainen, R., Kotiaho, T.: Analysis of selective androgen receptor modulators by gas chromatography-microchip atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 21, 310–316 (2010)
Luosujärvi, L., Karikko, M.-M., Haapala, M., Saarela, V., Huhtala, S., Franssila, S., Kostiainen, R., Kotiaho, T., Kauppila, T.J.: Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry of polychlorinated biphenyls using atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization microchips. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 22, 425–431 (2008)
Hintikka, L., Haapala, M., Franssila, S., Kuuranne, T., Leinonen, A., Kostiainen, R.: Feasibility of gas chromatography-microchip atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry in analysis of anabolic steroids. J. Chromatogr. A 217, 8290–8297 (2010)
Kersten, H., Derpmann, V., Barnes, I., Brockmann, K.J., O’Brien, R., Benter, T.: A novel APPI-MS setup for in situ degradation product studies of atmospherically relevant compounds: capillary atmospheric pressure photo ionization (cAPPI). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 2070–2081 (2011)
Revelsky, I.A., Yashin, Y.S.: New approach to complex organic compounds mixtures analysis based on gas chromatography–atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry. Talanta 102, 110–113 (2012)
Hintikka, L., Haapala, M., Kuuranne, T., Leinonen, A., Kostiainen, R.: Analysis of anabolic steroids in urine by gas chromatography-microchip atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry with chlorobenzene as dopant. J. Chromatogr. A 1312, 111–117 (2013)
Suominen, T., Haapala, M., Takala, A., Ketola, R.A., Kostiainen, R.: Neurosteroid analysis by gas chromatography–atmospheric pressure photoionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 794, 76–81 (2013)
Haapala, M., Suominen, T., Kostiainen, R.: Capillary photoionization: a high sensitivity ionization method for mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 85, 5715–5719 (2013)
Kersten, H., Haberer, K., Kroll, K., Benter, T.: Progress in the development of a GC-APPI source with femtogram sensitivity. Proceedings of the 62nd ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Baltimore, MD, 4–9 June 2014
Peterson, A.C., Kersten, H., Krumwiede, D., Quarmby, S., D’Silva, K., Kroll, K., Haberer, K., Bromirski, M., Makarov, A., Benter, T.: Analytical performance of a novel, dopant-free GC-APPI source with femtogram-level sensitivity for quadrupole-Orbitrap GC/MS. Presented at the 62nd ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Baltimore, MD, 15–19 June 2014
Constapel, M., Schellentraeger, M., Schmitz, O.J., Gaeb, S., Brockmann, K.J., Giese, R., Benter, T.: Atmospheric-pressure laser ionization: a novel ionization method for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 19, 326–336 (2005)
Schiewek, R., Schellenträger, M., Mönnikes, R., Lorenz, M., Giese, R., Brockmann, K.J., Gäb, S., Benter, T., Schmitz, O.J.: Ultrasensitive determination of polycyclic aromatic compounds with atmospheric-pressure laser ionization as an interface for GC/MS. Anal. Chem. 79, 4135–4140 (2007)
Schrader, W., Panda, S.K., Brockmann, K.J., Benter, T.: Characterization of non-polar aromatic hydrocarbons in crude oil using atmospheric pressure laser ionization and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (APLI FT-ICR MS). Analyst 133, 867–869 (2008)
Panda, S.K., Brockmann, K.-J., Benter, T., Schrader, W.: Atmospheric pressure laser ionization (APLI) coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry applied to petroleum samples analysis: comparison with electrospray ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization methods. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 25, 2317–2326 (2011)
Stader, C., Beer, F.T., Achten, C.: Environmental PAH analysis by gas chromatography-atmospheric pressure laser ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-APLI-MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 405, 7041–7052 (2013)
Dion, C.F., Bernstein, E.R.: On the low‐lying Rydberg states of azabenzenes. J. Chem. Phys. 103, 4907–4913 (1995)
Tsubouchi, M., Suzuki, T.: Femtosecond photoelectron imaging on pyridine: ultrafast electronic dephasing from the S1(nπ*) state and Rydberg state energetics. J. Phys. Chem. A 107, 10897–10903 (2003)
Streibel, T., Hafner, K., Mühlberger, F., Adam, T., Zimmermann, R.: Resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for detection of nitrogen containing aliphatic and aromatic compounds: resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization spectroscopic investigation and on-line analytical application. Appl. Spectrosc. 60, 72–79 (2006)
Tubaro, M., Marotta, E., Seraglia, R., Traldi, P.: Atmospheric pressure photoionization mechanisms. 2. The case of benzene and toluene. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 17, 2423–2429 (2003)
Robb, D.B., Blades, M.W.: Effects of solvent flow, dopant flow, and lamp current on dopant-assisted atmospheric pressure photoionization (DA-APPI) for LC-MS. Ionization via proton transfer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 16, 1275–1290 (2005)
Tzeng, W.B., Wei, S., Castleman, A.W.: Multiphoton ionization of acetone clusters: metastable unimolecular decomposition of acetone cluster ions and the influence of solvation on intracluster ion-molecule reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 6035–6040 (1989)
Kadi, M., Davidsson, J., Tarnovsky, A.N., Rasmusson, M., Åkesson, E.: Photodissociation of aryl halides in the gas phase studied with femtosecond pump-probe spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 350, 93–98 (2001)
Laor, U., Ludwig, P.K.: Fluorescence lifetimes of vibronic states of naphthalene vapor in the region of excitation from 3080–2150 Å. J. Chem. Phys. 54, 1054–1057 (1971)
Haefliger, O.P., Zenobi, R.: Laser mass spectrometric analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with wide wavelength range laser multiphoton ionization spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 70, 2660–2665 (1998)
Mühlberger, F., Hafner, K., Kaesdorf, S., Ferge, T., Zimmermann, R.: Comprehensive on-line characterization of complex gas mixtures by quasi-simultaneous resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization, vacuum-UV single-photon ionization, and electron impact ionization in a time-of-flight mass spectrometer: setup and instrument characterizatio. Anal. Chem. 76, 6753–6764 (2004)
Haapala, M., Pol, J., Saarela, V., Arvola, V., Kotiaho, T., Ketola, R.A., Franssila, S., Kauppila, T.J., Kostiainen, R.: Desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization. Anal. Chem. 79, 7867–7872 (2007)
Luosujärvi, L., Arvola, V., Haapala, M., Pól, J., Saarela, V., Franssila, S., Kotiaho, T., Kostiainen, R., Kauppila, T.J.: Desorption and ionization mechanisms in desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization. Anal. Chem. 80, 7460–7466 (2008)
Vaikkinen, A., Kotiaho, T., Kostiainen, R., Kauppila, T.J.: Desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization with PDMS as extraction phase and sample plate material. Anal. Chim. Acta. 682, 1–8 (2010)
Harrison, A.G.: Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (1992)
McCollum, J., Meyerson, S.: Organic ions in gas phase. X. Decomposition of benzaldehyde under electron impact. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85, 1739–1741 (1963)
Robb, D.B., Smith, D.R., Blades, M.W.: Investigation of substituted-benzene dopants for charge exchange ionization of nonpolar compounds by atmospheric pressure photoionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 19, 955–963 (2008)
Brutschy, B., Eggert, J., Janes, C., Baumgärtel, H.: Nucleophilic substitution reactions in molecular clusters following photoionization. J. Phys. Chem. 95, 5041–5050 (1991)
Kauppila, T.J., Kostiainen, R., Bruins, A.P.: Anisole, a new dopant for atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry of low proton affinity, low ionization energy compounds. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 18, 808–815 (2004)
Brulik, J., Simek, Z., de Voogt, P.: A new liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method using atmospheric pressure photo ionization for the simultaneous determination of azaarenes and azaarones in Dutch river sediments. J. Chromatogr. A 1294, 33–40 (2013)
Lintelmann, J., França, M.H., Hübner, E., Matuschek, G.: A liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure photoionization tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of azaarenes in atmospheric particulate matter. J. Chromatogr. A 1217, 1636–1646 (2010)
Syage, J.A.: Mechanism of [M + H] + formation in photoionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 15, 1521–1533 (2004)
Lorenz, M., Schiewek, R., Brockmann, K.J., Schmitz, O.J., Gäb, S., Benter, T.: The distribution of ion acceptance in atmospheric pressure ion sources: spatially resolved APLI measurements. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 19, 400–410 (2008)
Kersten, H., Lorenz, M., Brockmann, K.J., Benter, T.: Evaluation of the performance of small diode pumped UV solid state (DPSS) Nd:YAG lasers as new radiation sources for atmospheric pressure laser ionization mass spectrometry (APLI-MS). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 1063–1069 (2011)
Linstrom, P.J., Mallard, W.G. Eds.: NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, July 2001, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD, 20899. Available at: http://webbook.nist.gov. Accessed 15 June 2014
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support by the Academy of Finland (projects 218150, 255559, and 268757), and Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation and iGenTrax. Thermo Scientific is acknowledged for supplying the Orbitrap, the GC, and the consumables, and Morpho Detection for supplying the APPI source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kauppila, T.J., Kersten, H. & Benter, T. The Ionization Mechanisms in Direct and Dopant-Assisted Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization and Atmospheric Pressure Laser Ionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25, 1870–1881 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0988-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0988-7