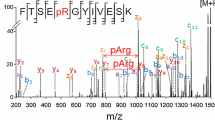
Abstract
The carboxyl groups of tryptic peptides were derivatized with a tertiary or quaternary amine labeling reagent to generate more highly charged peptide ions that fragment efficiently by electron transfer dissociation (ETD). All peptide carboxyl groups—aspartic and glutamic acid side-chains as well as C-termini—were derivatized with an average reaction efficiency of 99 %. This nearly complete labeling avoids making complex peptide mixtures even more complex because of partially-labeled products, and it allows the use of static modifications during database searching. Alkyl tertiary amines were found to be the optimal labeling reagent among the four types tested. Charge states are substantially higher for derivatized peptides: a modified tryptic digest of bovine serum albumin (BSA) generates ~90% of its precursor ions with z > 2, compared with less than 40 % for the unmodified sample. The increased charge density of modified peptide ions yields highly efficient ETD fragmentation, leading to many additional peptide identifications and higher sequence coverage (e.g., 70 % for modified versus only 43 % for unmodified BSA). The utility of this labeling strategy was demonstrated on a tryptic digest of ribosomal proteins isolated from yeast cells. Peptide derivatization of this sample produced an increase in the number of identified proteins, a >50 % increase in the sequence coverage of these proteins, and a doubling of the number of peptide spectral matches. This carboxyl derivatization strategy greatly improves proteome coverage obtained from ETD-MS/MS of tryptic digests, and we anticipate that it will also enhance identification and localization of post-translational modifications.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, L.M., Kelleher, N.L.: Proteoform: a single term describing protein complexity. Nat. Methods 10, 186–187 (2013)
Krusemark, C.J., Frey, B.L., Smith, L.M., Belshaw, P.J.: Complete chemical modification of amine and acid functional groups of peptides and small proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 753, 77–91 (2011)
Syka, J.E., Coon, J.J., Schroeder, M.J., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D.F.: Peptide and protein sequence analysis by electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 9528–9533 (2004)
Pitteri, S.J., Chrisman, P.A., Hogan, J.M., McLuckey, S.A.: Electron transfer ion/ion reactions in a three-dimensional quadrupole ion trap: reactions of doubly and triply protonated peptides with SO2*. Anal. Chem. 77, 1831–1839 (2005)
Good, D.M., Wirtala, M., McAlister, G.C., Coon, J.J.: Performance characteristics of electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6, 1942–1951 (2007)
Wiesner, J., Premsler, T., Sickmann, A.: Application of electron transfer dissociation (ETD) for the analysis of post-translational modifications. Proteomics 8, 4466–4483 (2008)
Swaney, D.L., McAlister, G.C., Coon, J.J.: Decision tree-driven tandem mass spectrometry for shotgun proteomics. Nat. Methods 5, 959–964 (2008)
Xia, Y., Gunawardena, H.P., Erickson, D.E., McLuckey, S.A.: Effects of cation charge-site identity and position on electron-transfer dissociation of polypeptide cations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 12232–12243 (2007)
Xia, Y., Han, H., McLuckey, S.A.: Activation of intact electron-transfer products of polypeptides and proteins in cation transmission mode ion/ion reactions. Anal. Chem. 80, 1111–1117 (2008)
Madsen, J.A., Brodbelt, J.S.: Simplifying fragmentation patterns of multiply charged peptides by n-terminal derivatization and electron transfer collision activated dissociation. Anal. Chem. 81, 3645–3653 (2009)
Ledvina, A.R., Beauchene, N.A., McAlister, G.C., Syka, J.E.P., Schwartz, J.C., Griep-Raming, J., Westphall, M.S., Coon, J.J.: Activated-ion electron transfer dissociation improves the ability of electron transfer dissociation to identify peptides in a complex mixture. Anal. Chem. 82, 10068–10074 (2010)
Iavarone, A.T., Jurchen, J.C., Williams, E.R.: Supercharged protein and peptide ions formed by electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 73, 1455–1460 (2001)
Lomeli, S.H., Yin, S., Loo, R.R.O., Loo, J.A.: Increasing charge while preserving noncovalent protein complexes for ESI-MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20, 593–596 (2009)
Kjeldsen, F., Giessing, A.M.B., Ingrell, C.R., Jensen, O.N.: Peptide sequencing and characterization of post-translational modifications by enhanced ion-charging and liquid chromatography electron-transfer dissociation tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 9243–9252 (2007)
Thompson, A., Schafer, J., Kuhn, K., Kienle, S., Schwarz, J., Schmidt, G., Neumann, T., Johnstone, R., Mohammed, A.K., Hamon, C.: Tandem mass tags: a novel quantification strategy for comparative analysis of complex protein mixtures by MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 75, 1895–1904 (2003)
Ross, P.L., Huang, Y.N., Marchese, J.N., Williamson, B., Parker, K., Hattan, S., Khainovski, N., Pillai, S., Dey, S., Daniels, S., Purkayastha, S., Juhasz, P., Martin, S., Bartlet-Jones, M., He, F., Jacobson, A., Pappin, D.J.: Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 3, 1154–1169 (2004)
Mirzaei, H., Regnier, F.: Enhancing electrospray ionization efficiency of peptides by derivatization. Anal. Chem. 78, 4175–4183 (2006)
Chamot-Rooke, J., van der Rest, G., Dalleu, A., Bay, S., Lemoine, J.: The combination of electron capture dissociation and fixed charge derivatization increases sequence coverage for O-glycosylated and O-phosphorylated peptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18, 1405–1413 (2007)
Xiang, F., Ye, H., Chen, R.B., Fu, Q., Li, L.J.: N, N-dimethyl leucines as novel isobaric tandem mass tags for quantitative proteomics and peptidomics. Anal. Chem. 82, 2817–2825 (2010)
Lu, Y.L., Zhou, X., Stemmer, P.M., Reid, G.E.: Sulfonium ion derivatization, isobaric stable isotope labeling and data dependent CID- and ETD-MS/MS for enhanced phosphopeptide quantitation, identification and phosphorylation site characterization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23, 577–593 (2012)
Wuhr, M., Haas, W., McAlister, G.C., Peshkin, L., Rad, R., Kirschner, M.W., Gygi, S.P.: Accurate multiplexed proteomics at the MS2 level using the complement reporter ion cluster. Anal. Chem. 84, 9214–9221 (2012)
Hennrich, M.L., Boersema, P.J., van den Toorn, H., Mischerikow, N., Heck, A.J., Mohammed, S.: Effect of chemical modifications on peptide fragmentation behavior upon electron transfer induced dissociation. Anal. Chem. 81, 7814–7822 (2009)
Hsu, J.L., Huang, S.Y., Chow, N.H., Chen, S.H.: Stable-isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Anal. Chem. 75, 6843–6852 (2003)
Hsu, J.-L., Huang, S.-Y., Shiea, J.-T., Huang, W.-Y., Chen, S.-H.: Beyond quantitative proteomics: signal enhancement of the a1 ion as a mass tag for peptide sequencing using dimethyl labeling. J. Proteome Res. 4, 101–108 (2005)
Fu, Q., Li, L.: De novo sequencing of neuropeptides using reductive isotopic methylation and investigation of ESI QTOF MS/MS fragmentation pattern of neuropeptides with N-terminal dimethylation. Anal. Chem. 77, 7783–7795 (2005)
Melanson, J.E., Avery, S.L., Pinto, D.M.: High-coverage quantitative proteomics using amine-specific isotopic labeling. Proteomics 6, 4466–4474 (2006)
Boersema, P.J., Raijmakers, R., Lemeer, S., Mohammed, S., Heck, A.J.R.: Multiplex peptide stable isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 4, 484–494 (2009)
Krusemark, C.J., Ferguson, J.T., Wenger, C.D., Kelleher, N.L., Belshaw, P.J.: Global amine and acid functional group modification of proteins. Anal. Chem. 80, 713–720 (2008)
Kulevich, S.E., Frey, B.L., Kreitinger, G., Smith, L.M.: Alkylating tryptic peptides to enhance electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis. Anal. Chem. 82, 10135–10142 (2010)
Gygi, S.P., Rist, B., Gerber, S.A., Turecek, F., Gelb, M.H., Aebersold, R.: Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 994–999 (1999)
Ren, D.Y., Julka, S., Inerowicz, H.D., Regnier, F.E.: Enrichment of cysteine-containing peptides from tryptic digests using a quaternary amine tag. Anal. Chem. 76, 4522–4530 (2004)
Yi, E.C., Li, X.J., Cooke, K., Lee, H., Raught, B., Page, A., Aneliunas, V., Hieter, P., Goodlett, D.R., Aebersold, R.: Increased quantitative proteome coverage with (13)C/(12)C-based, acid-cleavable isotope-coded affinity tag reagent and modified data acquisition scheme. Proteomics 5, 380–387 (2005)
Williams Jr., D.K., Meadows, C.W., Bori, I.D., Hawkridge, A.M., Comins, D.L., Muddiman, D.C.: Synthesis, characterization, and application of iodoacetamide derivatives utilized for the ALiPHAT strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 2122–2123 (2008)
Wang, J., Zhang, J., Arbogast, B., Maier, C.S.: Tandem mass spectrometric characterization of thiol peptides modified by the chemoselective cationic sulfhydryl reagent (4-iodobutyl)triphenylphosphonium. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 1771–1783 (2011)
Ueberheide, B.M., Fenyo, D., Alewood, P.F., Chait, B.T.: Rapid, sensitive analysis of cysteine rich peptide venom components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 6910–6915 (2009)
Vasicek, L., Brodbelt, J.S.: Enhanced electron transfer dissociation through fixed charge derivatization of cysteines. Anal. Chem. 81, 7876–7884 (2009)
Reid, G.E., Roberts, K.D., Simpson, R.J., O'Hair, R.A.: Selective identification and quantitative analysis of methionine containing peptides by charge derivatization and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 16, 1131–1150 (2005)
Xu, Y.W., Zhang, L.J., Lu, H.J., Yang, P.Y.: Mass spectrometry analysis of phosphopeptides after peptide carboxy group derivatization. Anal. Chem. 80, 8324–8328 (2008)
Zhang, L.J., Xu, Y.W., Lu, H.J., Yang, P.Y.: Carboxy group derivatization for enhanced electron-transfer dissociation mass spectrometric analysis of phosphopeptides. Proteomics 9, 4093–4097 (2009)
Qiao, X.Q., Sun, L.L., Chen, L.F., Zhou, Y.A., Yang, K.G., Liang, Z., Zhang, L.H., Zhang, Y.K.: Piperazines for peptide carboxyl group derivatization: effect of derivatization reagents and properties of peptides on signal enhancement in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 25, 639–646 (2011)
Zhang, J.M., Al-Eryani, R., Ball, H.L.: Mass spectrometry analysis of 2-nitrophenylhydrazine carboxy derivatized peptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 1958–1967 (2011)
Ko, B.J., Brodbelt, J.S.: Enhanced electron transfer dissociation of peptides modified at C-terminus with fixed charges. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23, 1991–2000 (2012)
Frey, B.L., Krusemark, C.J., Ledvina, A.R., Coon, J.J., Belshaw, P.J., Smith, L.M.: Ion–ion reactions with fixed-charge modified proteins to produce ions in a single, very high charge state. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 276, 136–143 (2008)
Krusemark, C.J., Frey, B.L., Belshaw, P.J., Smith, L.M.: Modifying the charge state distribution of proteins in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry by chemical derivatization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20, 1617–1625 (2009)
Inada, T., Winstall, E., Tarun, S.Z., Yates, J.R., Schieltz, D., Sachs, A.B.: One-step affinity purification of the yeast ribosome and its, associated proteins and mRNAs. RNA 8, 948–958 (2002)
Simons, S.P., McLellan, T.J., Aeed, P.A., Zaniewski, R.P., Desbonnet, C.R., Wondrack, L.M., Marr, E.S., Subashi, T.A., Dougherty, T.J., Xu, Z.Y., Wang, I.K., LeMotte, P.K., Maguire, B.A.: Purification of the large ribosomal subunit via its association with the small subunit. Anal. Biochem. 395, 77–85 (2009)
Krokhin, O.V., Spicer, V.: Peptide retention standards and hydrophobicity indexes in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of peptides. Anal. Chem. 81, 9522–9530 (2009)
Schnier, P.D., Gross, D.S., Williams, E.R.: On the Maximum charge-state and proton-transfer reactivity of peptide and protein ions formed by electrospray-ionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 6, 1086–1097 (1995)
Coon, J.J., Ueberheide, B., Syka, J.E.P., Dryhurst, D.D., Ausio, J., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D.F.: Protein identification using sequential ion/ion reactions and tandem mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 9463–9468 (2005)
Cooper, H.J., Hudgins, R.R., Hakansson, K., Marshall, A.G.: Characterization of amino acid side chain losses in electron capture dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 13, 241–249 (2002)
Rumachik, N.G., McAlister, G.C., Russell, J.D., Bailey, D.J., Wenger, C.D., Coon, J.J.: Characterizing peptide neutral losses induced by negative electron-transfer dissociation (NETD). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23, 718–727 (2012)
Iavarone, A.T., Paech, K., Williams, E.R.: Effects of charge state and cationizing agent on the electron capture dissociation of a peptide. Anal. Chem. 76, 2231–2238 (2004)
Jones, A.W., Cooper, H.J.: Dissociation techniques in mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Analyst 136, 3419–3429 (2011)
Huang, Y.Y., Triscari, J.M., Tseng, G.C., Pasa-Tolic, L., Lipton, M.S., Smith, R.D., Wysocki, V.H.: Statistical characterization of the charge state and residue dependence of low-energy CID peptide dissociation patterns. Anal. Chem. 77, 5800–5813 (2005)
Jones, J.W., Sasaki, T., Goodlett, D.R., Turecek, F.: Electron capture in spin-trap capped peptides. An experimental example of ergodic dissociation in peptide cation-radicals. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18, 432–444 (2007)
Li, X.J., Cournoyer, J.J., Lin, C., O'Connor, P.B.: The effect of fixed charge modifications on electron capture dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 19, 1514–1526 (2008)
Chung, T.W., Turecek, F.: Amplified histidine effect in electron-transfer dissociation of histidine-rich peptides from histatin 5. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 306, 99–107 (2011)
Chung, T.W., Turecek, F.: Selecting fixed-charge groups for electron-based peptide dissociations—a computational study of pyridinium tags. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 276, 127–135 (2008)
Chung, T.W., Moss, C.L., Zimnicka, M., Johnson, R.S., Moritz, R.L., Turecek, F.: Electron-capture and -transfer dissociation of peptides tagged with tunable fixed-charge groups: structures and dissociation energetics. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 13–30 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Amelia (Mia) Zutz for performing labeling reactions on the neurotensin peptide standards, M. Violet Lee for compiling the precursor charge state data, and A. J. Bureta for help with figure illustrations. The authors are grateful to Professor Toshifumi Inada at Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan for the gift of the YIT613 FLAG-tagged yeast strain. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health: NIGMS Program Project P01GM081629, R01 GM080148, and NHGRI Center of Excellence in Genomic Science 1P50HG004952.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frey, B.L., Ladror, D.T., Sondalle, S.B. et al. Chemical Derivatization of Peptide Carboxyl Groups for Highly Efficient Electron Transfer Dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24, 1710–1721 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0701-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0701-2