Abstract
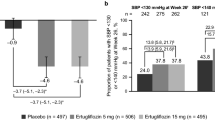
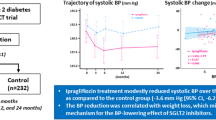
Our aim was to examine the effects of ipragliflozin, a selective sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, on blood pressure in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We conducted a pooled analysis of double-blind trials of Japanese T2DM patients, randomized to 50 mg ipragliflozin or placebo, with patient-level data for the change in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) from baseline to end of treatment (12–24 weeks). Data from six trials were analyzed: ipragliflozin was administered as monotherapy in two; in combination with metformin, pioglitazone, or sulfonylurea in one each; and in combination with prior therapy in patients with renal impairment in one. Overall, 628 and 368 patients were treated with ipragliflozin and placebo, respectively. The placebo-adjusted mean changes (95 % confidence interval) in SBP and DBP (mmHg) were −2.8 (−4.4, −1.3, P < 0.001) and −1.6 (−2.7, −0.6, P < 0.002), respectively, in all patients. The reductions in SBP and DBP were significantly greater in patients with baseline SBP ≥140 mmHg [−5.5 (−9.1, −1.8) and −2.9 (−5.3, −0.5), respectively] than in patients with SBP <140 mmHg [−2.1 (−3.8, −0.4) and −1.3 (−2.5, −0.1), respectively]. The reductions in SBP and DBP were also significantly greater in the ipragliflozin group than in the placebo group in patients treated with [−2.8 (−5.1, −0.4) and −2.4 (−4.0, −0.8), respectively] or without [−3.0 (−5.0, −1.0) and −1.0 (−2.4, 0.4), respectively] concomitant antihypertensive therapy. In conclusion, this pooled analysis showed that ipragliflozin was associated with significant reductions in SBP and DBP compared with placebo.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colosia AD, Palencia R, Khan S. Prevalence of hypertension and obesity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in observational studies: a systematic literature review. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2013;6:327–38. doi:10.2147/dmso.s51325.
Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Japan. Patient Survey 2011 (Disease and Injury). Available at: http://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/kanja/10syoubyo/dl/h23syobyo.pdf. Last accessed, April 2015. [In Japanese].
Emdin CA, Rahimi K, Neal B, Callender T, Perkovic V, Patel A. Blood pressure lowering in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2015;313:603–15. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.18574.
Shimamoto K, Ando K, Fujita T, Hasebe N, Higaki J, Horiuchi M, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2014). Hypertens Res. 2014;37:253–390. doi:10.1038/hr.2014.20.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ. 1998;317:703–13.
Katsuya T, Ishikawa K, Sugimoto K, Rakugi H, Ogihara T. Salt sensitivity of Japanese from the viewpoint of gene polymorphism. Hypertens Res. 2003;26:521–5.
Agabiti-Rosei E. From macro- to microcirculation: benefits in hypertension and diabetes. J Hypertens Suppl. 2008;26:S15–9.
Brillante DG, O’Sullivan AJ, Howes LG. Arterial stiffness in insulin resistance: the role of nitric oxide and angiotensin II receptors. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009;5:73–8.
Kozakova M, Morizzo C, Bianchi C, Di Filippi M, Miccoli R, Paterni M, et al. Glucose-related arterial stiffness and carotid artery remodeling: a study in normal subjects and type 2 diabetes patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:E2362–6. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-2028.
Hansen TW, Jeppesen J, Rasmussen S, Ibsen H, Torp-Pedersen C. Relation between insulin and aortic stiffness: a population-based study. J Hum Hypertens. 2004;18:1–7. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001620.
Bakris GL, Fonseca VA, Sharma K, Wright EM. Renal sodium-glucose transport: role in diabetes mellitus and potential clinical implications. Kidney Int. 2009;75:1272–7. doi:10.1038/ki.2009.87.
Jurczak MJ, Lee HY, Birkenfeld AL, Jornayvaz FR, Frederick DW, Pongratz RL, et al. SGLT2 deletion improves glucose homeostasis and preserves pancreatic β-cell function. Diabetes. 2011;60:890–8. doi:10.2337/db10-1328.
Kanai Y, Lee WS, You G, Brown D, Hediger MA. The human kidney low affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT2. Delineation of the major renal reabsorptive mechanism for D-glucose. J Clin Investig. 1994;93:397–404. doi:10.1172/jci116972.
Oliva RV, Bakris GL. Blood pressure effects of sodium-glucose co-transport 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8:330–9. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2014.02.003.
Lambers Heerspink HJ, de Zeeuw D, Wie L, Leslie B, List J. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:853–62. doi:10.1111/dom.12127.
Tikkanen I, Narko K, Zeller C, Green A, Salsali A, Broedl UC, et al. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:420–8. doi:10.2337/dc14-1096.
Kashiwagi A, Kazuta K, Yoshida S, Nagase I. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind glycemic control trial of novel sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor ipragliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5:382–91. doi:10.1111/jdi.12156.
Kashiwagi A, Takahashi H, Ishikawa H, Yoshida S, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on long-term efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: results of the long-term ASP1941 safety evaluation in patients with type 2 diabetes with renal impairment (LANTERN) study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:152–60. doi:10.1111/dom.12403.
Kashiwagi A, Kazuta K, Takinami Y, Yoshida S, Utsuno A, Nagase I. Ipragliflozin improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the BRIGHTEN study. Diabetol Int. 2014;6:8–18. doi:10.1007/s13340-014-0164-0.
Kashiwagi A, Kazuta K, Goto K, Yoshida S, Ueyama E, Utsuno A. Ipragliflozin in combination with metformin for the treatment of Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: ILLUMINATE, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;17:304–8. doi:10.1111/dom.12331.
Kashiwagi A, Shiga T, Akiyama N, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, Yoshida S, et al. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to pioglitazone in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (the SPOTLIGHT study). Diabetol Int. 2014;6:104–16. doi:10.1007/s13340-014-0182-y.
Kashiwagi A, Akiyama N, Shiga T, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, Yoshida S, et al. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to a sulfonylurea in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase III EMIT study. Diabetol Int. 2014;6:125–38. doi:10.1007/s13340-014-0184-9.
Baker WL, Smyth LR, Riche DM, Bourret EM, Chamberlin KW, White WB. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8(262–75):e9. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2014.01.007.
Imprialos KP, Sarafidis PA, Karagiannis AI. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and blood pressure decrease: a valuable effect of a novel antidiabetic class? J Hypertens. 2015;33:2185–97. doi:10.1097/hjh.0000000000000719.
Sinclair A, Bode B, Harris S, Vijapurkar U, Mayer C, Fung A, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin compared with placebo in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis of clinical studies. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014;14:37. doi:10.1186/1472-6823-14-37.
Liakos A, Karagiannis T, Athanasiadou E, Sarigianni M, Mainou M, Papatheodorou K, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:984–93. doi:10.1111/dom.12307.
Zhang M, Zhang L, Wu B, Song H, An Z, Li S. Dapagliflozin treatment for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014;30:204–21. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2479.
Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Wanner C, Ferrari R, Fitchett D, Hantel S, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk: proposed pathways and review of ongoing outcome trials. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2015;12:90–100. doi:10.1177/1479164114559852.
Maliha G, Townsend RR. SGLT2 inhibitors: their potential reduction in blood pressure. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015;9:48–53. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2014.11.001.
Majewski C, Bakris GL. Blood pressure reduction: an added benefit of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:429–30. doi:10.2337/dc14-1596.
Sha S, Polidori D, Heise T, Natarajan J, Farrell K, Wang SS, et al. Effect of the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin on plasma volume in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:1087–95. doi:10.1111/dom.12322.
Bolinder J, Ljunggren Ö, Kullberg J, Johansson L, Wilding J, Langkilde AM, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:1020–31. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-2260.
Lin B, Koibuchi N, Hasegawa Y, Sueta D, Toyama K, Uekawa K, et al. Glycemic control with empagliflozin, a novel selective SGLT2 inhibitor, ameliorates cardiovascular injury and cognitive dysfunction in obese and type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:148. doi:10.1186/s12933-014-0148-1.
Cherney DZ, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Har R, Fagan N, Johansen OE, et al. The effect of empagliflozin on arterial stiffness and heart rate variability in subjects with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:28. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-13-28.
Wilding JP, Ferrannini E, Fonseca VA, Wilpshaar W, Dhanjal P, Houzer A. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a dose-finding study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:403–9. doi:10.1111/dom.12038.
Sufiun A, Rafiq K, Fujisawa Y, Rahman A, Mori H, Nakano D, et al. Effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition on circadian blood pressure during the development of salt-dependent hypertension in rats. Hypertens Res. 2015;38:237–43. doi:10.1038/hr.2014.173.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all of the investigators involved in each trial. This study was sponsored by Astellas Pharma Inc., Japan. Medical writing and editorial support was funded by Astellas and provided by Dr. Nicholas D. Smith (Edanz Group Ltd.) and Elsevier/ELMCOM™.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
AK has acted as a consultant for Astellas Pharma Inc. and has received consulting fees/honoraria from Astellas Pharma Inc. TO has acted as a consultant for Kotobuki Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and has received consulting fees/honoraria from Kotobuki Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. YK is an employee of Kotobuki Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The other authors are employees of Astellas Pharma Inc., Japan.
Human rights statement and informed consent
All included studies in this analysis were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or a substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the studies.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Kashiwagi, A., Yoshida, S., Kawamuki, K. et al. Effects of ipragliflozin, a selective sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, on blood pressure in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis of six randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Diabetol Int 8, 76–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-016-0283-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-016-0283-x