Abstract
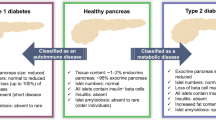
Although genetic factors are involved in the development of both type 1 (T1D) and type 2 (T2D) diabetes, a complete picture of those factors remains to be elucidated. T1D is an autoimmune disease in which the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) serves as a major genetic factor. By genetic analysis of an animal model of T1D, the Komeda diabetes-prone (KDP) rat, we identified the casitas B-lineage lymphoma b (Cblb) gene as another major genetic factor in this model. The Cblb mutation and MHC u haplotype determine autoimmune reaction and tissue specificity to pancreatic β cells, respectively. By mutation screening of the CBLB gene in Japanese patients with T1D, six missense mutations were found, among which Phe328Leu showed impaired suppression of T-cell activation. T2D is a metabolic disorder associated with insulin resistance and/or impaired insulin secretion. By genetic analysis of the spontaneously diabetic Torii (SDT) rat, an animal model of nonobese T2D, we identified several quantitative trait loci, among which a major locus, designated Dmsdt1, was involved in islet inflammation and fibrosis. Identification of the genes responsible should provide insight into the pathogenesis of diabetes. We recently established a novel model of obese T2D, the Zucker fatty diabetes mellitus (ZFDM) rat. In addition to severe insulin resistance and diminished insulin response to incretin, intrinsic fragility of islets in ZFDM rats is involved in the development of T2D. The ZFDM strain should be useful for studying the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of T2D, especially the mechanisms of incretin-induced insulin secretion and islet fragility.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makino S, Kunimoto K, Muraoka Y, Mizushima Y, Katagiri K, Tochino Y. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Exp Anim (Jikken Dobutsu). 1980;29:1–13.
Like AA, Butler L, Williams RM, Appel MC, Weringer EJ, Rossini AA. Spontaneous autoimmune diabetes mellitus in the BB rat. Diabetes. 1982;31:S7–13.
Chappel CI, Chappel WR. The discovery and development of the BB rat colony: an animal model of spontaneous diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1983;32:S8–10.
Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Saitoh Y, Kurosumi M, Natori T. New inbred strain of Long-Evans Tokushima lean rats with IDDM without lymphopenia. Diabetes. 1991;40:1375–81.
Komeda K, Noda M, Terao K, Kuzuya N, Kanazawa M, Kanazawa Y. Establishment of two substrains, diabetes-prone and non-diabetic, from Long-Evans Tokushima Lean (LETL) rats. Endocr J. 1998;45:737–44.
Yokoi N, Namae M, Fuse M, Wang HY, Hirata T, Seino S, Komeda K. Establishment and characterization of the Komeda diabetes-prone rat as a segregating inbred strain. Exp Anim. 2003;52:295–301.
Lenzen S, Tiedge M, Elsner M, Lortz S, Weiss H, Jorns A, Kloppel G, Wedekind D, Prokop CM, Hedrich HJ. The LEW.1AR1/Ztm-iddm rat: a new model of spontaneous insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2001;44:1189–96.
Goto Y, Kakizaki M, Masaki N. Spontaneous diabetes produced by selective breeding of normal Wistar rats. Proc Jpn Acad. 1975;51:80–5.
Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Saitoh Y, Kurosumi M, Natori T. Spontaneous long-term hyperglycemic rat with diabetic complications. Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) strain. Diabetes. 1992;41:1422–8.
Shinohara M, Masuyama T, Shoda T, Takahashi T, Katsuda Y, Komeda K, Kuroki M, Kakehashi A, Kanazawa Y. A new spontaneously diabetic non-obese Torii rat strain with severe ocular complications. Int J Exp Diabetes Res. 2000;1:89–100.
Masuyama T, Katsuda Y, Shinohara M. A novel model of obesity-related diabetes: introgression of the Lepr(fa) allele of the Zucker fatty rat into nonobese Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) rats. Exp Anim. 2005;54:13–20.
Ikeda H, Shino A, Matsuo T, Iwatsuka H, Suzuoki Z. A new genetically obese-hyperglycemic rat (Wistar fatty). Diabetes. 1981;30:1045–50.
Peterson RG, Shaw WN, Neel MA, Little LA, Eichberg J. Zucker diabetic fatty rat as a model for non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus. ILAR News. 1990;32:16–9.
Hummel KP, Dickie MM, Coleman DL. Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science. 1966;153:1127–8.
Nishimura M. Breeding of mice strains for diabetes mellitus. Jikken Dobutsu (Exp Anim). 1969;18:147–57.
Shibata M, Yasuda B. New experimental congenital diabetic mice (N.S.Y. mice). Tohoku J Exp Med. 1980;130:139–42.
Bielschowsky M, Goodall CM. Origin of inbred NZ mouse strains. Cancer Res. 1970;30:834–6.
Kim JH, Sen S, Avery CS, Simpson E, Chandler P, Nishina PM, Churchill GA, Naggert JK. Genetic analysis of a new mouse model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Genomics. 2001;74:273–86.
Suzuki W, Iizuka S, Tabuchi M, Funo S, Yanagisawa T, Kimura M, Sato T, Endo T, Kawamura H. A new mouse model of spontaneous diabetes derived from ddY strain. Exp Anim. 1999;48:181–9.
Yokoi N, Kanazawa M, Kitada K, Tanaka A, Kanazawa Y, Suda S, Ito H, Serikawa T, Komeda K. A non-MHC locus essential for autoimmune type I diabetes in the Komeda Diabetes-Prone rat. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:2015–21.
Yokoi N, Komeda K, Wang HY, Yano H, Kitada K, Saitoh Y, Seino Y, Yasuda K, Serikawa T, Seino S. Cblb is a major susceptibility gene for rat type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 2002;31:391–4.
Keane MM, Rivero-Lezcano OM, Mitchell JA, Robbins KC, Lipkowitz S. Cloning and characterization of cbl-b: a SH3 binding protein with homology to the c-cbl proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1995;10:2367–77.
Bachmaier K, Krawczyk C, Kozieradzki I, Kong YY, Sasaki T, Oliveira-dos-Santos A, Mariathasan S, Bouchard D, Wakeham A, Itie A, Le J, Ohashi PS, Sarosi I, Nishina H, Lipkowitz S, Penninger JM. Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cbl-b. Nature. 2000;403:211–6.
Chiang YJ, Kole HK, Brown K, Naramura M, Fukuhara S, Hu RJ, Jang IK, Gutkind JS, Shevach E, Gu H. Cbl-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature. 2000;403:216–20.
Yokoi N. Identification of a major gene responsible for type 1 diabetes in the Komeda diabetes-prone rat. Exp Anim. 2005;54:111–5.
Yokoi N, Hayashi C, Fujiwara Y, Wang HY, Seino S. Genetic reconstitution of autoimmune type 1 diabetes with two major susceptibility genes in the rat. Diabetes. 2007;56:506–12.
Awata T, Kuzuya T, Matsuda A, Iwamoto Y, Kanazawa Y. Genetic analysis of HLA class II alleles and susceptibility to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Japanese subjects. Diabetologia. 1992;35:419–24.
Ikegami H, Kawaguchi Y, Yamato E, Kuwata S, Tokunaga K, Noma Y, Shima K, Ogihara T. Analysis by the polymerase chain reaction of histocompatibility leucocyte antigen-DR9-linked susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992;75:1381–5.
Yasunaga S, Kimura A, Hamaguchi K, Ronningen KS, Sasazuki T. Different contribution of HLA-DR and -DQ genes in susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Tissue Antigens. 1996;47:37–48.
Kawabata Y, Ikegami H, Kawaguchi Y, Fujisawa T, Shintani M, Ono M, Nishino M, Uchigata Y, Lee I, Ogihara T. Asian-specific HLA haplotypes reveal heterogeneity of the contribution of HLA-DR and -DQ haplotypes to susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:545–51.
Ellerman KE, Like AA. Susceptibility to diabetes is widely distributed in normal class IIu haplotype rats. Diabetologia. 2000;43:890–8.
Yokoi N, Hidaka S, Tanabe S, Ohya M, Ishima M, Takagi Y, Masui N, Seino S. Role of major histocompatibility complex class II in the development of autoimmune type 1 diabetes and thyroiditis in rats. Genes Immun. 2012;13:139–45.
Masuyama T, Komeda K, Hara A, Noda M, Shinohara M, Oikawa T, Kanazawa Y, Taniguchi K. Chronological characterization of diabetes development in male Spontaneously Diabetic Torii rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;314:870–7.
Kakehashi A, Saito Y, Mori K, Sugi N, Ono R, Yamagami H, Shinohara M, Tamemoto H, Ishikawa SE, Kawakami M, Kanazawa Y. Characteristics of diabetic retinopathy in SDT rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2006;22:455–61.
Shinohara M, Masuyama T, Kakehashi A. The Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) rat with retinopathy lesions resembling those of humans. In: Shafrir E, editor. Animal Models of Diabetes: Frontiers in Research. 2nd ed. New York: Taylor and Francis Group; 2006. p. 311–21.
Masuyama T, Fuse M, Yokoi N, Shinohara M, Tsujii H, Kanazawa M, Kanazawa Y, Komeda K, Taniguchi K. Genetic analysis for diabetes in a new rat model of nonobese type 2 diabetes, Spontaneously Diabetic Torii rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;304:196–206.
Fuse M, Yokoi N, Shinohara M, Masuyama T, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Seino S. Identification of a major locus for islet inflammation and fibrosis in the spontaneously diabetic Torii rat. Physiol Genomics. 2008;35:96–105.
Zucker LM, Zucker TF. Fatty, a new mutation in the rat. J Hered. 1961;52:275–8.
Iida M, Murakami T, Ishida K, Mizuno A, Kuwajima M, Shima K. Phenotype-linked amino acid alteration in leptin receptor cDNA from Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;222:19–26.
Yokoi N, Hoshino M, Hidaka S, Yoshida E, Beppu M, Hoshikawa R, Sudo K, Kawada A, Takagi S, Seino S. A novel rat model of type 2 diabetes: the Zucker fatty diabetes mellitus ZFDM rat. J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:103731.
Gheni G, Yokoi N, Beppu M, Yamaguchi T, Hidaka S, Kawabata A, Hoshino Y, Hoshino M, Seino S. Characterization of the prediabetic state in a novel rat model of type 2 diabetes, the ZFDM rat. J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:261418.
Jones HB, Nugent D, Jenkins R. Variation in characteristics of islets of Langerhans in insulin-resistant, diabetic and non-diabetic-rat strains. Int J Exp Pathol. 2010;91:288–301.
Kosoy R, Yokoi N, Seino S, Concannon P. Polymorphic variation in the CBLB gene in human type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun. 2004;5:232–5.
Bergholdt R, Taxvig C, Eising S, Nerup J, Pociot F. CBLB variants in type 1 diabetes and their genetic interaction with CTLA4. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;77:579–85.
Payne F, Cooper JD, Walker NM, Lam AC, Smink LJ, Nutland S, Stevens HE, Hutchings J, Todd JA. Interaction analysis of the CBLB and CTLA4 genes in type 1 diabetes. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81:581–3.
Yokoi N, Fujiwara Y, Wang HY, Kitao M, Hayashi C, Someya T, Kanamori M, Oiso Y, Tajima N, Yamada Y, Seino Y, Ikegami H, Seino S. Identification and functional analysis of CBLB mutations in type 1 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368:37–42.
Fukushima M, Suzuki H, Seino Y. Insulin secretion capacity in the development from normal glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;66:S37–43.
Fukushima M, Usami M, Ikeda M, Nakai Y, Taniguchi A, Matsuura T, Suzuki H, Kurose T, Yamada Y, Seino Y. Insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity at different stages of glucose tolerance: a cross-sectional study of Japanese type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 2004;53:831–5.
Mitsui R, Fukushima M, Nishi Y, Ueda N, Suzuki H, Taniguchi A, Nakai Y, Kawakita T, Kurose T, Yamada Y, Inagaki N, Seino Y. Factors responsible for deteriorating glucose tolerance in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in Japanese men. Metabolism. 2006;55:53–8.
Yokoi N, Kanamori M, Horikawa Y, Takeda J, Sanke T, Furuta H, Nanjo K, Mori H, Kasuga M, Hara K, Kadowaki T, Tanizawa Y, Oka Y, Iwami Y, Ohgawara H, Yamada Y, Seino Y, Yano H, Cox NJ, Seino S. Association studies of variants in the genes involved in pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes in Japanese subjects. Diabetes. 2006;55:2379–86.
Acknowledgments
Parts of this review were presented as the Lilly Award Lecture at the Japan Diabetes Society 2015, Shimonoseki, Japan. The author thanks late Professor Kajuro Komeda and Professors Susumu Seino, Yutaka Seino, and Tadao Serikawa for their instruction and generous support. The author also thanks colleagues and collaborators, especially Drs. Kohtaro Minami, Tadao Shibasaki, Harumi Takahashi, Toshiya Matsubara, and Daisuke Yabe, for their significant contribution. The studies in this review were supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, and grants from the Takeda Science Foundation, the Ichiro Kanehara Foundation, the Kanae Foundation for the Promotion of Medical Science, the Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders, and the Suzuken Memorial Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no conflict of interest to declare.
Animal studies
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Human rights statement and informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Declaration of Helsinki of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoi, N. Elucidation of genetic factors in diabetes based on studies of animal models. Diabetol Int 6, 255–260 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0228-9