Abstract
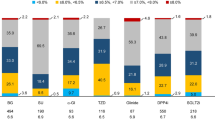
The Japan Diabetes Complication and its Prevention prospective (JDCP) study is a large-scale observational study conducted to investigate the current status of the management of people with diabetes, and to clarify the risk factors for the onset and progression of diabetes complications. The study includes 6338 patients aged 40 to <75 years who had received regular outpatient treatment from 2007–2009 at medical facilities nationwide specializing in diabetes. The primary endpoints for the study include occurrence and/or progression of nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, macroangiopathy, and periodontal disease; the secondary endpoints include occurrence of malignancy and mortality. This report gives an outline of the study and a summary of the baseline data for participating patients with type 2 diabetes (n = 5944). The baseline characteristics were: men, 60.1 %; mean age, 61.4 years; duration of diabetes, 10.8 years; family history of diabetes, 52.8 %; BMI, 24.5 kg/m2; HbA1c, 7.4 % (achievement of <7.0, 40.6 %); blood pressure, 129.8/74.8 mmHg; and non-HDL-C, 137.6 mg/dL. Treatments included: diet therapy alone, 10.4 %, oral hypoglycemic agents, 62.1 %; and insulin therapy, 27.5 %. The cohort is to be followed up for at least 5 years, with a high follow-up rate. The focus of the study is to develop a clinical registry that is reliable and versatile and to bring the research findings and insights to bear on the society’s Treatment Guide for Diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tajima N, Nishimura R, Izumi K, et al. A large-scale, observational study to investigate the current state of diabetes complications and their prevention in Japan: research outline and baseline data for type 2 diabetes—JDCP study 1—a report of the diabetes registry configuration committee, Japan diabetes society (JDS) (in Japanese). J Jpn Diabet Soc. 2015;58:346–357.
Tajima N (Principal investigator). A large-scale, prospective, registry-based study aimed at investigating the status of diabetes complications, including blindness, periodontal disease, nephropathy and macroangiopathy and their treatment (H21-Diabetes etc-designated-005). In: Integrated research report 2009–2010. A ministry of health, labour and welfare grant-in-aid. A research project for control of lifestyle-related diseases (e.g., cardiovascular disease, diabetes), March 2011 (in Japanese).
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Ethical guidelines for epidemiological studies (in Japanese) http://www.niph.go.jp/wadai/ekigakurinri/rinrishishin.htm. Accessed 29 July 2015.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Survey on the Status of Diabetes 2011 (in Japanese) http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/eiyou/h23-houkoku.html. Accessed 29 July 2015.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Survey on the Status of Diabetes 2013 (in Japanese) http://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/04-Houdouhappyou-10904750-Kenkoukyoku-Gantaisakukenkouzoushinka/0000068070.pdf. Accessed 29 July 2015.
Seino Y, Nanjo K, Tajima N, et al. Report of the committee on the classification of diabetes and diagnostic criteria (global standard version). J Japan Diabetes Soc. 2012;55:485–504 (in Japanese).
Ishibashi T. Research survey on atrophy of choroid and retina/optical nerve. In: A 2005 ministry of health, labour and welfare research project. Report from the research project for the conquest of intractable diseases (in Japanese).
Fujishima M, Kiyohara Y, Kato I, et al. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease in a population survey in Japan: the Hisayama study. Diabetes. 1996;45(Suppl 3):S14–6.
Doi Y, Ninomiya T, Hata J, et al. Impact of glucose tolerance status on development of ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama study. Stroke. 2010;41:203–209.
Sone H, Katagiri A, Ishibashi S, et al. JDC Study Group. Effect of lifestyle modification on patients with type 2 diabetes: The Japan diabetes complication study (JDCS) study design, baseline analysis and three year-interim report. Horm Metab Res. 2002;34:509–15.
Sone H, Tanaka S, Iimuro S, et al. for the Japan Diabetes Complications Study Group. Long-term lifestyle intervention lowers the incidence of stroke in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide multicentre randomised controlled trial (the Japan diabetes complications study). Diabetologia. doi:10.1007/s00125-009-1622-2.
Kobayashi M, Yamazaki K, Hirano K, et al. Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management Study Group. The status of diabetes control and antidiabetic drug therapy in Japan—a cross-sectional survey of 17,000 patients with diabetes mellitus (JDDM 1). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;73:198–204.
Berkowitz SA, Meigs JB, Wexler D. Age at type 2 diabetes onset and glycaemic control: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005–2010. Diabetologia. 2013;56:2593–600.
Braga MFB, Casanova A, Teoh H, et al. On behalf of Diabetes Registry to Improve Vascular Events (DRIVE) Investigators. treatment gaps in the management of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes in Canada. Can J Cardiol. 2010;26:297–302.
Kasuga M, Ueki K, Tajima N, et al. Report of the Committee on Diabetes and Cancer. J Japan Diabetes Soc. 2013;56:374–90 (in Japanese).
Acknowledgments
The JDCP study is a Japan Diabetes Society (JDS)-initiated research project. The study was supported by a Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare grant-in-aid during the 2009–2010 period and then by JDS grants-in-aid from 2011 onwards. The project also has received research grants from the Manpei Suzuki Diabetes Foundation since 2006 to provide support in registry configuration that had to do with the data collection. The JDCP study investigators believe that the JDCP study will have relevant contributions to make toward preventing the onset or progression of diabetic complications only when they have completed the study with a high follow-up rate as a prospective observational study. The JDCP study investigators would like to thank all physicians and their staff at the 464 participating institutions for their cooperation and assistance in the conduct of the study. The JDCP study investigators also wish to extend their heartfelt thanks to diabetic patients from all parts of Japan for their participation in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Naoko Tajima has served as a speaker for MSD, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd.. Rimei Nishimura has served as a speaker for Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd.. Mitsuhiko Noda has served as a speaker for Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. Kohjiro Ueki has served as a speaker for MSD, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd, received clinical research grants from AstraZeneca and Sanofi, and was endowed lectures by MSD, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., and Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd..
Ethical considerations
In this study, the Declaration of Helsinki and the “Ethical Guidelines in Epidemiological Research” compiled by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (as applicable in the study period) [3] were followed to obtain informed consent from study participants, to protect their rights and welfare, and to protect them against any potential harm and risk associated with the conduct of the study. The informed consent form as part of the study protocol clearly stated that ophthalmologic and dental examinations were to be conducted as appropriate in routine care settings to ensure no additional time or financial burden on the part of the patient being examined. This study, currently registered with the University Hospital Medical Information Network Center (UMIN000016519), was approved by the JDS Ethics Review Committee for Scientific Surveys and Studies and by the ethics committee of each participating institution. An ad hoc ethics committee was convened at the request of the principal investigator if the required review process was not feasible at any participating institution. Care was also taken to ensure that all data obtained from the study was anonymized in a linkable fashion to protect the privacy of all study participants.
Additional information
The Japan Diabetes Society launched the Diabetes Registry Configuration Committee to conduct the Japan Diabetes Complication and its Prevention prospective (JDCP) study, which reported, in Japanese, the results of a large-scale observational study to investigate the current status of diabetes complications and their prevention in Japan [1]. This is an English version of that report.
Appendix
Appendix
-
1.
JDCP Study Investigators
-
JDCP Study Working Groups (representatives shown with an asterisk [*])
-
Nephropathy: Kazunori Utsunomiya, Daisuke Koya, Kenichi Shikata*
-
Retinopathy: Shigehiko Kitano*, Yukihiro Sato, Hidetoshi Yamashita
-
Neuropathy: Jiro Nakamura*, Masayuki Baba
-
Microvascular disease: Hitoshi Shimano, Yoshimitsu Yamazaki*, Naruhito Yoshioka
-
Diet therapy: Satoshi Sasaki, Jo Sato, Kinsuke Tsuda*, Nobuo Yoshiike
-
Exercise therapy: Yoshiharu Oshida, Hirohito Sone*.
-
Epidemiology/statistics: Kazuo Izumi, Hideki Origasa, Rimei Nishimura*, Yasuaki Hayashino
-
Periodontal disease: Kouji Inagaki*, Fusanori Nishimura, Hidetoshi Noguchi
-
-
JDCP Study Regional Leaders
-
Hokkaido Chapter: Naruhito Yoshioka
-
Tohoku Chapter: Jo Sato
-
Kanto-Koshinetsu Chapter: Naoko Tajima (Principal Investigator)
-
Chubu Chapter: Jiro Nakamura
-
Kinki Chapter: Nobuya Inagaki
-
Chugoku-Shikoku Chapter: Yukio Tanizawa
-
Kyushu Chapter: Eiichi Araki
-
-
-
2.
JDCP Study Coordination Committee
-
Objective: To make key decisions relating to the research project to ensure appropriate and smooth conduct of the study.
-
Members of the Committee: Eiichi Araki, Kazuo Izumi, Nobuya Inagaki, Kohjiro Ueki, Hirohito Sone, Naoko Tajima (Chair), Yukio Tanizawa Rimei Nishimura (Secretariat), Mitsuhiko Noda, Yasuaki Hayashino.
-
-
3.
JDCP Study Steering Committee (SSC)
-
Objective: To provide guidance on key issues in the conduct of the study, with the committee set up within the JDS; to receive reports from the SCC; to make recommendations to the SCC as required; and to assess the progress of the study as well as its outcomes and report to the JDS as to whether the study is being conducted appropriately.
-
Members of the Committee
-
(First-termers, 2009–2012): Yasuhiko Iwamoto, Masato Kasuga, Kishio Nanjo (Chair), Masakazu Haneda, Nigishi Hotta.
-
(Second-termers, 2013–): Masato Kasuga (Chair), Yasuhiro Iso, Hiroshi Kiyohara, Masakazu Haneda, Toshimasa Yamauchi, Tsutomu Yamazaki.
-
-
About this article
Cite this article
Tajima, N., Nishimura, R., Izumi, K. et al. A large-scale, observational study to investigate the current status of diabetes complications and their prevention in Japan: research outline and baseline data for type 2 diabetes—JDCP study 1. Diabetol Int 6, 243–251 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0223-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-015-0223-1