Abstract
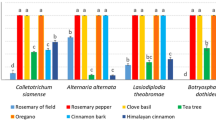
The antimicrobial effects of essential oils and pure oil compounds on mycelial growth of soilborne pathogens causing vegetable diseases in Australia was investigated. Fourteen essential oils and four pure oil compounds were evaluated using contact in vitro bioassays to determine optimum concentrations which can inhibit growth or kill pathogen mycelium. Three essential oils (thyme, clove bud and origanum) and all four pure oil compounds showed broad-spectrum and dose-dependant inhibitory and/or biocidal activity against mycelium of key soilborne pathogens. These treatments also showed antimicrobial activity against Trichoderma atroviride, which is a beneficial soil fungus. In pots, thyme, clove bud and origanum oils applied pre-planting as 5 % aqueous emulsions (5.0 ml/150 cm3) controlled Rhizoctonia solani AG2.1 infection on broccoli seedlings. However clove bud and origanum oils were phytotoxic at 10 % in soil. This study showed that essential oils have potential for controlling soilborne diseases by reducing the spread and viability of pathogen mycelium in soil. This information will be useful for the development of new and existing products which contain plant extracts for use to manage soilborne vegetable diseases in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abawi GS, Widmer TL (2000) Impact of soil health management practices on soil-borne pathogens, nematodes and root diseases of vegetable crops. App Soil Ecol 15:37–47
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D, Idaomar M (2008) Biological effects of essential oils-a review. Food Chem Toxicol 46:446–475
Barrera-Necha LL, Garduno-Pizana C, Garcia-Barrera LJ (2009) In vitro antifungal activity of essential oils and their compounds on mycelial growth of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. gladioli (Massey) Snyder and Hansen. Plant Path J 8(1):17–21
Cavanagh H (2007) Antifungal activity of the volatile phase of essential oils: a brief review. Nat Prod Commun 2(12):1297–1302
Donald C, Horlock C, Conde B, Villalta O, Porter I (2010) Towards sustainable integrated control of soilborne diseases in vegetable crops-a review of available and emerging chemical and non-chemical strategies and their potential compatibility with IPM programs. In: Donald C (ed) Best practice IPM strategies for control of major soilborne diseases of vegetable crops. Final Report for project VG 07125. Sydney, Horticulture Australia Limited, 13–82
Dorman HJD, Deans SG (2000) Antimicrobial agents from plants: antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils. J Appl Microbiol 88:308–316
Edris AE, Farrag ES (2003) Antifungal activity of peppermint and sweet basil essential oils and their major aroma constituents on some plant pathogenic fungi from the vapour phase. Food Nahrung 47(2):117–121
Kumar A, Shukla R, Singh P, Prasad CS, Dubey NK (2008) Assessment of Thymus vulgaris L. essential oil as a safe botanical preservative against post harvest fungal infestation on food commodities. Innovat Food Sci Emerg Tech 9:575–580
Lee SO, Choi GJ, Jang KS, Lim HK, Kwang YC, Kim J (2007) Antifungal activity of five plant essential oils as fumigant against postharvest and soilborne pathogenic fungi. Plant Path J 23(2):97–102
Letessier MP, Svoboda KP, Walters DR (2001) Antifungal activity of essential oil of hyssop (Hyssopus officinalis). J Phytopath 149:673–678
Montes-Belmont R, Prados-Ligero AM (2006) Influence of plant extracts on Sclerotium cepivorum development. Plant Path J 5(3):373–377
Muller-Riebau F, Berger B, Yegen O (1995) Chemical composition and fungitoxic properties to phytopathogenic fungi of essential oils of selected aromatic plants growing wild in Turkey. J Agric Food Chem 43:2262–2266
Porter I, Donald C, Minchinton E (2007) National vegetable industry IPM pathology gap analysis. Final Report for project VG 06092. Sydney, Horticulture Australia Limited, May 2007
Soylu EM, Soylu S, Kurt S (2006) Antimicrobial activities of the essential oils of various plants against tomato late blight agent Phytophthora infestans. Mycopathologia 161:119–128
Soylu S, Yigibas H, Soylu EM, Kurt S (2007) Antifungal effects of essential oils from oregano and fennel on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. J Appl Microbiol 103:1021–1030
Szczerbanik M, Jobling J, Morris S, Holford P (2007) Essential oil vapours control some common postharvest pathogens. Aust J Exp Agr 47:103–109
Tullio V, Nostro A, Mandras N, Dugo P, Banche G, Cannatelli MA, Cuffini AM (2007) Antifungal activity of essential oils against filamentous fungi determined by broth micro dilution and vapour contact methods. J Appl Microbiol 102:1544–1550
Vukovic N, Milosevic T, Sukdolak S, Solujic S (2007) Antimicrobial activities of essential oil and methanol extract of Teucrium montanum. Evid base Compl Alternative Med (eCAM) 4(S1):17–20
Wilson CL, Solar JM, El Ghauth A, Wisniewski ME (1997) Rapid evaluation of plant extracts and essential oils for antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea. Plant Dis 81(2):204–210
Zambonelli AZ, D’Aulerio A, Bianchi A, Albasini A (1996) Effects of essential oils on phytopathogenic fungi in vitro. J Phytopathology 144:491–494
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Victorian Department of Primary Industries and Horticulture Australia Ltd (HAL). We thank Dr Elizabeth Minchinton, Desmond Auer, Denise Wite, and Crop Health Services DPI Victoria for pathogen isolates, Agrimm Technologies Pty Ltd for the biocontrol product, and Sydney Essential Oils Company for chemical analysis. We also thank Dr Jacqueline Edwards, Dr Oscar Villalta and Damien McMaster for providing comments which improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMaster, C.A., Plummer, K.M., Porter, I.J. et al. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and pure oil compounds against soilborne pathogens of vegetables. Australasian Plant Pathol. 42, 385–392 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0216-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0216-0