Abstract
The brain is protected by a tight barrier between the blood and parenchyma. This so-called blood–brain barrier protects the brain from invading pathogens, infiltrating immune cells, and the extravasation of serum proteins. Beside pericytes and astrocytes mainly endothelial cells form this barrier.
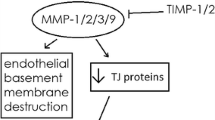
Inflammation leads to an increase in the permeability of the blood–brain barrier. NF-κB is activated during inflammation and is a key regulator of inflammatory processes. In brain endothelial cells NF-κB protects the blood–brain barrier. Loss of the NF-κB activating protein NEMO in brain endothelial cells leads to endothelial cell death, increased permeability, and epilepsy in mice as well as in humans with the hereditary disease incontinentia pigmenti. Therefore, inflammatory mediators are able to disturb but also to protect the blood–brain barrier.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrlich P (1885) Das Sauerstoff-Bedürfniss des Organismus. Hirschwald, Berlin
Yousif LF, Di Russo J, Sorokin L (2013) Laminin isoforms in endothelial and perivascular basement membranes. Cell Adhes Migr 7:101–110
Daneman R, Zhou L, Kebede AA, Barres BA (2010) Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 468:562–566
Proebstl D, Voisin MB, Woodfin A, Whiteford J, D’Acquisto F, Jones GE, Rowe D, Nourshargh S (2012) Pericytes support neutrophil subendothelial cell crawling and breaching of venular walls in vivo. J Exp Med 209:1219–1234
Baltimore D (2011) Nf-kappab is 25. Nat Immunol 12:683–685
Senegas A, Gautheron J, Maurin AG, Courtois G (2015) Ikk-related genetic diseases: Probing nf-kappab functions in humans and other matters. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:1275–1287
Schneider A, Martin-Villalba A, Weih F, Vogel J, Wirth T, Schwaninger M (1999) Nf-kappab is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 5:554–559
Herrmann O, Baumann B, de Lorenzi R, Muhammad S, Zhang W, Kleesiek J, Malfertheiner M, Kohrmann M, Potrovita I, Maegele I, Beyer C, Burke JR, Hasan MT, Bujard H, Wirth T, Pasparakis M, Schwaninger M (2005) Ikk mediates ischemia-induced neuronal death. Nat Med 11:1322–1329
Bell RD, Winkler EA, Singh I, Sagare AP, Deane R, Wu Z, Holtzman DM, Betsholtz C, Armulik A, Sallstrom J, Berk BC, Zlokovic BV (2012) Apolipoprotein e controls cerebrovascular integrity via cyclophilin a. Nature 485:512–516
Aveleira CA, Lin CM, Abcouwer SF, Ambrosio AF, Antonetti DA (2010) Tnf-alpha signals through pkczeta/nf-kappab to alter the tight junction complex and increase retinal endothelial cell permeability. Diabetes 59:2872–2882
Nenci A, Becker C, Wullaert A, Gareus R, van Loo G, Danese S, Huth M, Nikolaev A, Neufert C, Madison B, Gumucio D, Neurath MF, Pasparakis M (2007) Epithelial nemo links innate immunity to chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature 446:557–561
Ridder DA, Wenzel J, Müller K, Töllner K, Tong XK, Assmann JC, Stroobants S, Weber T, Niturad C, Fischer L, Lembrich B, Wolburg H, Grand’Maison M, Papadopoulos P, Korpos E, Truchetet F, Rades D, Sorokin L, Schmidt-Supprian M, Bedell BJ, Pasparakis M, Balschun D, D’Hooge R, Löscher W, Hamel E, Schwaninger M (2015) Brain endothelial tak1 and nemo safeguard the neurovascular unit. J Exp Med 212:1529–1549 (DA Ridder and J Wenzel contributed equally)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. Wenzel and M. Schwaninger state that there are no conflicts of interest.
The accompanying manuscript does not include studies on humans or animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenzel, J., Schwaninger, M. The blood–brain barrier and its regulation by NF-κB. e-Neuroforum 7, 23–30 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13295-016-0022-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13295-016-0022-6