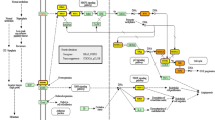
Abstract
There has been accumulative evidence that microRNAs (miRNAs) play essential roles in the tumorigenesis and progression of bladder cancer. However, individual studies and small sample size caused discrepant outcomes. Thus, the current study focused on a comprehensive profiling of all differentially expressed miRNAs in a total of 519 bladder cancer tissue samples, based on miRNA microarray data. Altogether, 11 prioritized miRNAs stated by 21 published microarray datasets, including five down-regulated (miR-133a-3p, miR-1-3p, miR-99a-5p, miR-490-5p, and miR-133b) and six up-regulated candidate miRNAs (miR-182-5p, miR-935, miR-518e-3p, miR-573, miR-100-3p, and miR-3171) were analyzed with vote-counting strategy and a Robust Rank Aggregation method. Subsequently, miRNA in silico target prediction and potential pathway enrichment analysis were performed to investigate the prospective molecular mechanism of miRNAs in the tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. We found that most of the relative pathways of the aberrantly expressed miRNAs found in the current study were closely correlated with different biological processes, cellular components, molecular functions, cancer pathogeneses, and some cell signalings, such as Wnt signaling, insulin/IGF, PI3 kinase, and FGF signaling pathways. Hence, a comprehensive overview on the miRNA expression pattern in bladder cancer tissues was gained by the current study. These miRNAs might be involved in the tumorigenesis and deterioration of bladder cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–86.
Miremami J, Kyprianou N. The promise of novel molecular markers in bladder cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(12):23897–908.
Scheffer AR, Holdenrieder S, Kristiansen G, von Ruecker A, Muller SC, Ellinger J. Circulating microRNAs in serum: novel biomarkers for patients with bladder cancer? World J Urol. 2014;32(2):353–8.
Wang Z, Cai Q, Jiang Z, Liu B, Zhu Z, Li C: Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res 2014, 20:1668–1674.
Chen QW, Zhu XY, Li YY, Meng ZQ. Epigenetic regulation and cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 2014;31(2):523–32.
Jin D, Fang Y, Li Z, Chen Z, Xiang J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitionassociated microRNAs in colorectal cancer and drug-targeted therapies (review). Oncol Rep. 2015;33(2):515–25.
Lyra-Gonzalez I, Flores-Fong LE, Gonzalez-Garcia I, Medina-Preciado D, Armendariz-Borunda J. MicroRNAs dysregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma: insights in genomic medicine. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(11):1530–40.
Zhu W, Xu B. MicroRNA-21 identified as predictor of cancer outcome: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103373.
Pan F, Mao H, Deng L, Li G, Geng P. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of microRNA-21 overexpression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(9):5622–33.
Zheng RL, Jiang YJ, Wang X. Role of microRNAs on therapy resistance in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(11):3818–32.
Kozomara A. Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D68–73.
Ding M, Li Y, Wang H, Lv Y, Liang J, Wang J, Li C. Diagnostic value of urinary microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):15432–40.
Chen L, Cui Z, Liu Y, Bai Y, Lan F. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnostics of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 2015;61(8):1101–8.
Ouyang H, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Shen G. Diagnostic value of MicroRNAs for urologic cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2015;94(37):e1272.
Cheng Y, Deng X, Yang X, Li P, Zhang X, Li P, Tao J, Lu Q, Wang Z. Urine microRNAs as biomarkers for bladder cancer: a diagnostic meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2015;8:2089–96.
Shi Z, Wei Q, Zhang M, She J. MicroRNAs in bladder cancer: expression profiles, biological functions, regulation, and clinical implications. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2014;24(1):55–75.
Zhou H, Tang K, Xiao H, Zeng J, Guan W, Guo X, Xu H, Ye Z. A panel of eight-miRNA signature as a potential biomarker for predicting survival in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. 2015;34:53.
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y, Kunimoto R, Chiyomaru T, Kawamoto K, Kawahara K, Toki K, Kawakami K, Nishiyama K, et al. Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2009;125(2):345–52.
Song T, Xia W, Shao N, Zhang X, Wang C, Wu Y, Dong J, Cai W, Li H. Differential miRNA expression profiles in bladder urothelial carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev: APJCP. 2010;11(4):905–11.
Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Kawakami K, Tatarano S, Nishiyama K, Nohata N, Seki N, Nakagawa M. The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;104(5):808–18.
Yamasaki T, Yoshino H, Enokida H, Hidaka H, Chiyomaru T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Fuse M, Seki N, Nakagawa M. Novel molecular targets regulated by tumor suppressors microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(6):1821–30.
Pignot G, Cizeron-Clairac G, Vacher S, Susini A, Tozlu S, Vieillefond A, Zerbib M, Lidereau R, Debre B. Amsellem-Ouazana D et al: microRNA expression profile in a large series of bladder tumors: identification of a 3-miRNA signature associated with aggressiveness of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2013;132(11):2479–91.
Wang T, Yuan J, Feng N, Li Y, Lin Z, Jiang Z, Gui Y. Hsa-miR-1 downregulates long non-coding RNA urothelial cancer associated 1 in bladder cancer. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2014;35(10):10075–84.
Du M, Shi D, Yuan L, Li P, Chu H, Qin C, Yin C, Zhang Z, Wang M. Circulating miR-497 and miR-663b in plasma are potential novel biomarkers for bladder cancer. Sci Report. 2015;5:10437.
Yoshino H, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, Tatarano S, Hidaka H, Yamasaki T, Gotannda T, Tachiwada T, Nohata N, Yamane T, et al. Tumor suppressive microRNA-1 mediated novel apoptosis pathways through direct inhibition of splicing factor serine/arginine-rich 9 (SRSF9/SRp30c) in bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417(1):588–93.
Feng Y, Kang Y, He Y, Liu J, Liang B, Yang P. Yu Z: microRNA-99a acts as a tumor suppressor and is down-regulated in bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2014;14:50.
Zhang DZ, Lau KM, Chan ES, Wang G, Szeto CC, Wong K, Choy RK, Ng CF. Cell-free urinary microRNA-99a and microRNA-125b are diagnostic markers for the non-invasive screening of bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e100793.
Xu Z, Yu YQ, Ge YZ, Zhu JG, Zhu M, Zhao YC, Xu LW, Yang XB, Geng LG, Dou QL, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: identification of a four-microRNA signature associated with patient survival. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2015;36(10):8159–66.
Wu D, Zhou Y, Pan H, Zhou J, Fan Y. Qu P: microRNA-99a inhibiting cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in bladder cancer. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(4):1219–24.
Lan G, Yang L, Xie X, Peng L, Wang Y. MicroRNA-490-5p is a novel tumor suppressor targeting c-FOS in human bladder cancer. Arch Med Sci AMS. 2015;11(3):561–9.
Li S, Xu X, Xu X, Hu Z, Wu J, Zhu Y, Chen H, Mao Y, Lin Y, Luo J, et al. MicroRNA-490-5p inhibits proliferation of bladder cancer by targeting c-Fos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441(4):976–81.
Han Y, Chen J, Zhao X, Liang C, Wang Y, Sun L, Jiang Z, Zhang Z, Yang R, Chen J, et al. MicroRNA expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep sequencing. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e18286.
Chen XN, Wang KF, Xu ZQ, Li SJ, Liu Q, Fu DH, Wang X, Wu B. MiR-133b regulates bladder cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting Bcl-w and Akt1. Cancer Cell Int. 2014;14:70.
Dyrskjot L, Ostenfeld MS, Bramsen JB, Silahtaroglu AN, Lamy P, Ramanathan R, Fristrup N, Jensen JL, Andersen CL, Zieger K, et al. Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro. Cancer Res. 2009;69(11):4851–60.
Zhou Y, Wu D, Tao J, Qu P, Zhou Z, Hou J. MicroRNA-133 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream effector proteins in bladder cancer. Scand J Urol. 2013;47(5):423–32.
Tao J, Wu D, Xu B, Qian W, Li P, Lu Q, Yin C. Zhang W: microRNA-133 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncol Rep. 2012;27(6):1967–75.
Kriebel S, Schmidt D, Holdenrieder S, Goltz D, Kristiansen G, Moritz R, Fisang C, Muller SC, Ellinger J. Analysis of tissue and serum microRNA expression in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0117284.
Hirata H, Ueno K, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y, Dahiya R. Oncogenic miRNA-182-5p targets Smad4 and RECK in human bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e51056.
Mengual L, Lozano JJ, Ingelmo-Torres M, Gazquez C, Ribal MJ, Alcaraz A. Using microRNA profiling in urine samples to develop a non-invasive test for bladder cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2013;133(11):2631–41.
Jiang X, Du L, Wang L, Li J, Liu Y, Zheng G, Qu A, Zhang X, Pan H, Yang Y, et al. Serum microRNA expression signatures identified from genome-wide microRNA profiling serve as novel noninvasive biomarkers for diagnosis and recurrence of bladder cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2015;136(4):854–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Yanping Wei and Rongquan He contributed equally as first authors, Xinggu Lin and Yingchun Chen contributed equally as corresponding authors.
The work was performed in the Center for Genomic and Personalized Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, 22 Shuangyong Road, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region 530,021, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., He, R., Wu, Y. et al. Comprehensive investigation of aberrant microRNA profiling in bladder cancer tissues. Tumor Biol. 37, 12555–12569 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5121-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5121-z