Abstract
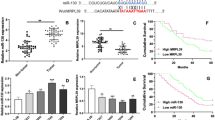
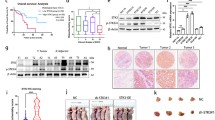
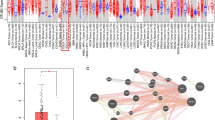
Transmembrane protein 45B (TMEM45B) is a member of TMEMs. Altered expression of TMEMs is frequently observed in a variety of human cancers, but the expression and functional roles of TMEM45B in lung cancer is not reported. In the present study, levels of mRNA expression of TMEM45B in lung cancer tissues were assessed using re-analyzing expression data of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) lung cancer cohort and real-time PCR analysis on our own cohort. Lung cancer cells, A549 and NCI-H1975, infected with TMEM45B short hairpin RNA were examined in cell proliferation, cell cycle, cell apoptosis, wound-healing, and cell invasion assays as well as mouse xenograft models. Here, we demonstrated that TMEM45B was overexpressed in lung cancer and its expression correlated with overall survival of patients. In addition, silencing of TMEM45B expression reduced cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo, induced cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis, and blocked cell migration and invasion. Moreover, knockdown of TMEM45B significantly suppressed G1/S transition, induced cell apoptosis, and inhibited cell invasion via regulating the expression of cell cycle-related proteins (CDK2, CDC25A, and PCNA), cell apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl2, Bax, and Cleaved Caspase 3), and metastasis-related proteins (MMP-9, Twist, and Snail), respectively. Thus, TMEM45B is a potential prognostic marker and cancer-selective therapeutic target in lung cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2015;65:87–108.
Longo-Sorbello GS, Chen B, Budak-Alpdogan T, Bertino JR. Role of pemetrexed in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Investig. 2007;25:59–66.
Wrzesinski T, Szelag M, Cieslikowski WA, Ida A, Giles R, Zodro E, et al. Expression of pre-selected tmems with predicted er localization as potential classifiers of ccrcc tumors. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:518.
Zhou X, Popescu NC, Klein G, Imreh S. The interferon-alpha responsive gene tmem7 suppresses cell proliferation and is downregulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007;177:6–15.
Hrasovec S, Hauptman N, Glavac D, Jelenc F, Ravnik-Glavac M. Tmem25 is a candidate biomarker methylated and down-regulated in colorectal cancer. Dis Markers. 2013;34:93–104.
Doolan P, Clynes M, Kennedy S, Mehta JP, Germano S, Ehrhardt C, et al. Tmem25, reps2 and meis 1: favourable prognostic and predictive biomarkers for breast cancer. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2009;30:200–9.
Qiu G, Sun W, Zou Y, Cai Z, Wang P, Lin X, et al. Rna interference against tmem97 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioma cells. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2015;36:8231–8.
Li B, Huang MZ, Wang XQ, Tao BB, Zhong J, Wang XH, et al. Tmem140 is associated with the prognosis of glioma by promoting cell viability and invasion. Journal of hematology & oncology. 2015;8:89.
Guo J, Chen L, Luo N, Yang W, Qu X, Cheng Z. Inhibition of tmem45a suppresses proliferation, induces cell cycle arrest and reduces cell invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2015;33:3124–30.
Cheng Z, Guo J, Chen L, Luo N, Yang W, Qu X. Overexpression of tmem158 contributes to ovarian carcinogenesis. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR. 2015;34:75.
Cuajungco MP, Podevin W, Valluri VK, Bui Q, Nguyen VH, Taylor K. Abnormal accumulation of human transmembrane (tmem)-176a and 176b proteins is associated with cancer pathology. Acta Histochem. 2012;114:705–12.
Qiao W, Han Y, Jin W, Tian M, Chen P, Min J, et al. Overexpression and biological function of tmem48 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2015.
Sponziello M, Lavarone E, Pegolo E, Di Loreto C, Puppin C, Russo MA, et al. Molecular differences between human thyroid follicular adenoma and carcinoma revealed by analysis of a murine model of thyroid cancer. Endocrinology. 2013;154:3043–53.
Molina-Pinelo S, Gutierrez G, Pastor MD, Hergueta M, Moreno-Bueno G, Garcia-Carbonero R, et al. Microrna-dependent regulation of transcription in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90524.
Kawana H, Tamaru J, Tanaka T, Hirai A, Saito Y, Kitagawa M, et al. Role of p27kip1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 in the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Pathol. 1998;153:505–13.
Blomberg I, Hoffmann I. Ectopic expression of cdc25a accelerates the g(1)/s transition and leads to premature activation of cyclin e- and cyclin a-dependent kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:6183–94.
Nguyen VN, Mirejovsky P, Mirejovsky T, Melinova L, Mandys V. Expression of cyclin d1, ki-67 and pcna in non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic significance and comparison with p53 and bcl-2. Acta Histochem. 2000;102:323–38.
Kroemer G. The proto-oncogene bcl-2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med. 1997;3:614–20.
Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 and bax function independently to regulate cell death. Nat Genet. 1997;16:358–63.
Davis ME, Hsieh PC, Takahashi T, Song Q, Zhang S, Kamm RD, et al. Local myocardial insulin-like growth factor 1 (igf-1) delivery with biotinylated peptide nanofibers improves cell therapy for myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:8155–60.
Rao JS, Gondi C, Chetty C, Chittivelu S, Joseph PA, Lakka SS. Inhibition of invasion, angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis by adenovirus-mediated transfer of antisense upar and mmp-9 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1399–408.
Paulo P, Ribeiro FR, Santos J, Mesquita D, Almeida M, Barros-Silva JD, et al. Molecular subtyping of primary prostate cancer reveals specific and shared target genes of different ets rearrangements. Neoplasia. 2012;14:600–11.
Wu W, Fan YH, Kemp BL, Walsh G, Mao L. Overexpression of cdc25a and cdc25b is frequent in primary non-small cell lung cancer but is not associated with overexpression of c-myc. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4082–5.
Ziegler A, Luedke GH, Fabbro D, Altmann KH, Stahel RA, Zangemeister-Wittke U. Induction of apoptosis in small-cell lung cancer cells by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeting the bcl-2 coding sequence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997;89:1027–36.
Kaliberov SA, Buchsbaum DJ, Gillespie GY, Curiel DT, Arafat WO, Carpenter M, et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of bax driven by the vascular endothelial growth factor promoter induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Molecular therapy: the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy. 2002;6:190–8.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Hung JJ, Yang MH, Hsu HS, Hsu WH, Liu JS, Wu KJ. Prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, twist1 and snail expression in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax. 2009;64:1082–9.
Authors’ contributions
RH, MSW, and HBX conceived and designed the experiments. RH, FQH, XX, and LW performed the experiments. RH and FQH analyzed the data. GQL and TQ contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. MSW and HBX wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Rui Hu and Fengqing Hu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, R., Hu, F., Xie, X. et al. TMEM45B, up-regulated in human lung cancer, enhances tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 12181–12191 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5063-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5063-5