Abstract
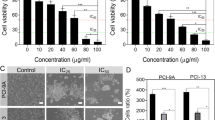
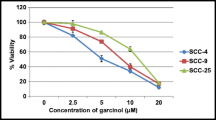
The present study was performed to investigate the effect of resveratrol (trans-3,4′,5-trihydroxystilbene) present as a natural phytoalexin in grapes, peanuts, and red wine on oral squamous cancer cell lines, SCC-VII, SCC-25, and YD-38. MTS assay and flow cytometry, respectively, were used for the analysis of inhibition of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Western blot analysis was performed to examine the effect of resveratrol on the expression of proteins associated with cell cycle regulation. The results revealed a concentration- and time-dependent inhibition of proliferation in all the three tested cell lines on treatment with resveratrol. The IC50 of resveratrol for SCC-VII, SCC-25, and YD-38 cell lines was found to be 0.5, 0.7, and 1.0 μg/ml, respectively, after 48-h treatment. Examination of the cell cycle analysis showed that resveratrol treatment induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase and enhanced the expression of phospho-cdc2 (Tyr 15), cyclin A2, and cyclin B1 in the oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells. It also caused a marked increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells as revealed by the fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. Thus, resveratrol exhibits inhibitory effect on the proliferation of OSCC oral cancer cells through the induction of apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch WM, Stafford E, Bajaj G. Cancer of the oral cavity. Part A: general principles and management. In: Harrison LB, Sessions RB, Hong WK, editors. Head and neck cancer: a multidisciplinary approach. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2009. p. 250–65.
Feller L, Lemmer J. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: epidemiology, clinical presentation and treatment. J Cancer Ther. 2012;3:263–8.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Garavello W, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Lucchini F, Bosetti C, Malvezzi M, et al. The oral cancer epidemic in central and eastern Europe. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:160–71.
Raff MC, Barres BA, Burne JF, Coles HS, Ishizaki Y, Jacobson MD. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993;262:695–700.
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306.
Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC. Induction of apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 2000;256:42–9.
King KL, Cidlowski JA. Cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:601–17.
Gusman J, Malonne H, Atassi G. A reappraisal of the potential chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic properties of resveratrol. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:1111–7.
Yang CS, Landau JM, Huang MT, Newmark HL. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Annu Rev Nutr. 2001;21:381–406.
Loe AK, Liu H, Suzui M, Vural ME, Xiao D, Weinstein IB. Resveratrol induces growth inhibition, S-phase arrest, apoptosis and changes in biomarker expression in several human cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:893–903.
Jiang H, Zhang L, Kuo J, et al. Resveratrol-induced apoptotic death in human U251 glioma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:554–61.
Shen M, Wu RX, Zhao L, et al. Resveratrol attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury in neonatal cardiomyocytes and its underlying mechanism. PLoS One. 2012;7:e51223.
Ku CR, Lee HJ, Kim SK, et al. Resveratrol prevents streptozotocin-induced diabetes by inhibiting the apoptosis of pancreatic β-cell and the cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Endocr J. 2012;59:103–9.
Robb EL, Page MM, Wiens BE, Stuart JA. Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress resistance induced by resveratrol: specific and progressive induction of MnSOD. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367:406–12.
Bo S, Ciccone G, Castiglione A, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of resveratrol in healthy smokers a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Curr Med Chem. 2013;20:1323–31.
Athar M, Back JH, Kopelovich L, et al. Multiple molecular targets of resveratrol: anti-carcinogenic mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009;486:95–102.
Simão F, Matté A, Breier AC, et al. Resveratrol prevents global cerebral ischemia-induced decrease in lipid content. Neurol Res. 2013;35:59–64.
Li Z, Pang L, Fang F, et al. Resveratrol attenuates brain damage in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia via up-regulation of hippocampal Bcl-2. Brain Res. 2012;1450:116–24.
Wu Z, Xu Q, Zhang L, et al. Protective effect of resveratrol against kainate-induced temporal lobe epilepsy in rats. Neurochem Res. 2009;34:1393–400.
Pasinetti GM, Wang J, Marambaud P, et al. Neuroprotective and metabolic effects of resveratrol: therapeutic implications for Huntington’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Exp Neurol. 2011;232:1–6.
Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ishrat T, et al. Resveratrol attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage and dopamine depletion in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2010;1328:139–51.
Li F, Gong Q, Dong H, Shi J. Resveratrol, a neuroprotective supplement for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:27–33.
Booher RN, Holman PS, Fattaey A. Human Myt1 is a cell cycle-regulated kinase that inhibits Cdc2 but not Cdk2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22300–6.
Liu F, Stanton JJ, Wu Z, Piwnica-Worms H. The human Myt1 kinase preferentially phosphorylates Cdc2 on threonine 14 and localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:571–83.
Parker LL, Piwnica-Worms H. Inactivation of the p34cdc2-cyclin B complex by the human WEE1 tyrosine kinase. Science. 1992;257:1955–7.
Conflicts of interest
None
Authors’ contributions
Dong-Xu Liu and Xiao-Dong Yu designed the study. Dong-Xu Liu and Jing-lei Yang wrote the manuscript. Dong-Xu Liu and Jing-lei Yang performed out the experiments and the related statistical analysis. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiao-Dong Yu and Jing-lei Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, XD., Yang, Jl., Zhang, WL. et al. Resveratrol inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma through induction of apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. Tumor Biol. 37, 2871–2877 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3793-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3793-4