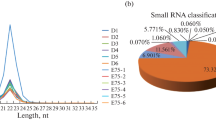
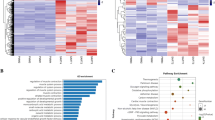
Abstract
The domestic pig is an important agricultural animal used as a source of meat worldwide. As an important resource, Laiwu pig has some special characteristics compared with Yorkshire pig. It is necessary to identify the differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) in skeletal muscle between two pig breeds. Therefore, we herein performed a comprehensive investigation for miRNA transcriptome of skeletal muscle from the two pig breeds. On average, we obtained approximately 13,493,607 clean reads in Laiwu pig and 12,938,257 clean reads in Yorkshire pig in this study. Totally, 265 known miRNAs were identified, and among these, 229 miRNAs were expressed in all the six pigs. From the 265 known miRNAs, 19 of these miRNAs were found significantly differentially expressed (q < 0.05). Of these significantly expressed miRNAs, seven miRNAs were significantly up-regulated and 12 miRNAs were down-regulated in Laiwu pig compared with Yorkshire pig. Among the significantly expressed miRNAs, ssc-miR-194-5p has the largest fold-change (6.35-fold). Ten differentially expressed miRNAs selected from high throughput sequencing were confirmed by real-time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR), and the results indicated that the expression patterns were consistent with sequencing results. Our results not only present a comprehensive miRNA transcriptome profile of skeletal muscle between two pig breeds with distinct phenotypes, but also could be useful for investigating the functions of differentially expressed miRNAs associated with the phenotype traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C, Leslie C (2010) Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol 11:R90
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) microRNA Functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:175–205
Carrington JC, Ambros V (2003) Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301:336–338
Chen J-F, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q, Callis TE, Hammond SM, Conlon FL, Wang D-Z (2006) The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet 38:228–233
Friedman RC, Farh KK-H, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Hossain M, Ghanem N, Hoelker M, Rings F, Phatsara C, Tholen E, Schellander K, Tesfaye D (2009) Identification and characterization of miRNAs expressed in the bovine ovary. BMC Genomics 10:443
Hou X, Tang Z, Liu H, Wang N, Ju H, Li K (2012) Discovery of microRNAs associated with myogenesis by deep sequencing of serial developmental skeletal muscles in pigs. PLoS ONE 7:e52123
Hu HY, Guo S, Xi J, Yan Z, Fu N, Zhang X, Menzel C, Liang H, Yang H, Zhao M et al (2011) MicroRNA expression and regulation in human, chimpanzee, and macaque brains. PLoS Genet 7:e1002327
Huang T-H, Zhu M-J, Li X-Y, Zhao S-H (2008) Discovery of porcine microRNAs and profiling from skeletal muscle tissues during development. PLoS ONE 3:e3225
Huang J, Ju Z, Li Q, Hou Q, Wang C, Li J, Li R, Wang L, Sun T, Hang S et al (2011) Solexa sequencing of novel and differentially expressed microRNAs in testicular and ovarian tissues in Holstein cattle. Int J Biol Sci 7(7):1016–1026
Hwang HW, Mendell JT (2006) MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer 94:776–780
Ji Z, Wang G, Xie Z, Zhang C, Wang J (2012) Identification and characterization of microRNA in the dairy goat (Capra hircus) mammary gland by Solexa deep-sequencing technology. Mol Biol Rep 39:9361–9371
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg S (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Li T, Wu R, Zhang Y, Zhu D (2011) A systematic analysis of the skeletal muscle miRNA transcriptome of chicken varieties with divergent skeletal muscle growth identifies novel miRNAs and differentially expressed miRNAs. BMC Genomics 12:186
Li H-Y, Xi Q-Y, Xiong Y-Y, Liu X-L, Cheng X, Shu G, Wang S-B, Wang L-N, Gao P, Zhu X-T et al (2012) Identification and comparison of microRNAs from skeletal muscle and adipose tissues from two porcine breeds. Anim Genet 43:704–713
Lian C, Sun B, Niu S, Yang R, Liu B, Lu C, Meng J, Qiu Z, Zhang L, Zhao Z (2012) A comparative profile of the microRNA transcriptome in immature and mature porcine testes using Solexa deep sequencing. FEBS J 279:964–975
Lin S, Li H, Mu H, Luo W, Li Y, Jia X, Wang S, Jia X, Nie Q, Li Y et al (2012) Let-7b regulates the expression of the growth hormone receptor gene in deletion-type dwarf chickens. BMC Genomics 13:306
Ma J, Yu S, Wang F, Bai L, Xiao J, Jiang Y, Chen L, Wang J, Jiang A, Li M et al (2013) MicroRNA transcriptomes relate intermuscular adipose tissue to metabolic risk. Int J Biol Sci 14:8611–8624
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L (2005) Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 21:3787–3793
Nielsen M, Hansen JH, Hedegaard J, Nielsen RO, Panitz F, Bendixen C, Thomsen B (2010) MicroRNA identity and abundance in porcine skeletal muscles determined by deep sequencing. Anim Genet 41:159–168
Podolska A, Anthon C, Bak M, Tommerup N, Skovgaard K, Heegaard P, Gorodkin J, Cirera S, Fredholm M (2012) Profiling microRNAs in lung tissue from pigs infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. BMC Genomics 13:459
Roush S, Slack FJ (2008) The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol 18:505–516
Sharbati S, Friedlander M, Sharbati J, Hoeke L, Chen W, Keller A, Stahler P, Rajewsky N, Einspanier R (2010) Deciphering the porcine intestinal microRNA transcriptome. BMC Genomics 11:275
Spurlock ME, Gabler NK (2008) The development of porcine models of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J Nutr 138:397–402
Trang P, Medina PP, Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, Omotola M, Homer R, Brown D, Bader AG, Weidhaas JB et al (2010) Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA. Oncogene 29:1580–1587
Xie S-S, Li X-Y, Liu T, Cao J-H, Zhong Q, Zhao S-H (2011) Discovery of porcine microRNAs in multiple tissues by a solexa deep sequencing approach. PLoS ONE 6:e16235
Ye L, Su X, Wu Z, Zheng X, Wang J, Zi C, Zhu G, Wu S, Bao W (2012) Analysis of differential miRNA expression in the duodenum of Escherichia coli F18-sensitive and -resistant weaned piglets. PLoS ONE 7:e43741
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11:R14
Zhou L, Chen J, Li Z, Li X, Hu X, Huang Y, Zhao X, Liang C, Wang Y, Sun L et al (2010) Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: microRNAs located on Xq27.3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 5:e15224
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Animal Breed Resource Preservation Project of China (2130135), the National Project for Breeding Transgenic Pigs of China (2013ZX08006-002), Shandong Province Modern Pig Technology and Industry System Project (SDAIT-08-02) and Shandong Province Agricultural Animal Breeding Project of China (2013LZ02-015, 2014LZ03-016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Wei Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Guo-Feng Fang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shou-Dong Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hui Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yong-Qing Zeng declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This work was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Ethics Committee of Shandong Agricultural University and carried out in accordance with the ‘‘Guidelines for Experimental Animals’’ of the Ministry of Science and Technology (Beijing, PR China).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Fang, GF., Wang, SD. et al. Characterization and differential expression of microRNA in skeletal muscle of Laiwu and Yorkshire pig breeds. Genes Genom 39, 173–182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0484-5