Abstract
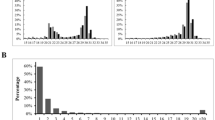
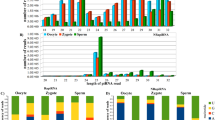
It has been shown that piRNA is the largest class of small non-coding RNA in germline cells of animals which plays key roles in transposons regulation and transcriptional activities. In the present study, piRNAs from two small RNA libraries including ovary and testis of Nile tilapia were identified and characterized. By length and k-mer based small RNA prediction algorithm, 279,059 and 583,230 small RNA reads were confirmed as piRNA from ovary and testis, respectively. The identified piRNAs showed evolutionarily conserved characterization, such as uridine bias in the 5′ ends. The 142,961 and 296,775 piRNAs from ovary and testis were mapped to the draft assembly of the tilapia genome, respectively. Both ovary and testis piRNAs were enriched from linkage (LG)6 and LG7. Meanwhile, the even distribution of +strand and −strand suggested the Ping–pong pathway (a double-displacement reaction of +strand and −strand) hypothesis. These piRNAs were derived from the upstream −2 kb and downstream +2 kb as well as gene regions which suggested a regulatory function on transcription activities. In gene regions, abundant piRNAs were derived from 5′UTR, 3′UTR and CDS. Furthermore, we characterized the differentially expressed piRNAs between ovary and testis. In total, 1979 and 2453 piRNAs were significantly higher and lower expressed in ovary compared to that in testis, respectively. Thereinto, the most concentrated up-regulate and down-regulate piRNAs were both from serine/threonine–protein kinase PIM genes of different transcripts. These findings will be helpful to facilitate studies on the piRNAs regulation on genes during gonad development of teleosts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravin AA, Hannon GJ, Brennecke J (2007) The Piwi–piRNA pathway provides an adaptive defense in the transposon arms race. Science 318:761–764
Baroiller JF, D’Cotta H (2001) Environment and sex determination in farmed fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 130:399–409
Bettegowda A, Wilkinson MF (2010) Transcription and post-transcriptional regulation of spermatogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365:1637–1651
Bukhari SIA, Vasquez-Rifo A, Gagne D, Paquet ER, Zetka M, Robert C, Masson JY, Simard MJ (2012) The microRNA pathway controls germ cell proliferation and differentiation in C. elegans. Cell Res 22:1034–1045
Cerutti L, Mian N, Bateman A (2000) Domains in gene silencing and cell differentiation proteins: the novel PAZ domain and redefinition of the Piwi domain. Trends Biochem Sci 25:481–482
Cnaani A, Lee BY, Zilberman N, Ozouf-Costaz C, Hulata G, Ron M, D’Hont A, Baroiller JF, D’Cotta H, Penman DJ, Tomasino E, Coutanceau JP, Pepey E, Shirak A, Kocher TD (2008) Genetics of sex determination in tilapiine species. Sexual development: genetics, molecular biology, evolution, endocrinology, embryology, and pathology of sex determination and differentiation. Sex Dev 2:43–54
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV, Deacon E, Salmon M, Lord JM (2000) Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 256:34–41
Deng W, Lin H (2002) miwi, a murine homolog of Piwi, encodes a cytoplasmic protein essential for spermatogenesis. Dev Cell 2:819–830
Edelman AM, Blumenthal DK, Krebs EG (1987) Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 56:567–613
Gan H, Lin X, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Liao S, Wang L, Han C (2011) piRNA profiling during specific stages of mouse spermatogenesis. RNA 17:1191–1203
Girard A, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ, Carmell MA (2006) A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 442:199–202
Grivna ST, Pyhtila B, Lin H (2006) MIWI associates with translational machinery and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) in regulating spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13415–13420
Houwing S, Kamminga LM, Berezikov E, Cronembold D, Girard A, van den Elst H, Filippov DV, Blaser H, Raz E, Moens CB, Plasterk RHA, Hannon GJ, Draper BW, Ketting RF (2007) A Role for Piwi and piRNAs in Germ Cell Maintenance and Transposon Silencing in Zebrafish. Cell 129:69–82
Houwing S, Berezikov E, Ketting RF (2008) Zili is required for germ cell differentiation and meiosis in zebrafish. EMBO J 27:2702–2711
Kim VN (2006) Small RNAs just got bigger: Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) in mammalian testes. Genes Dev 20:1993–1997
Klattenhoff C, Theurkauf W (2008) Biogenesis and germline functions of piRNAs. Development 135:3–9
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Kimura T, Yomogida K, Kuroiwa A, Tadokoro Y, Fujita Y, Sato M, Matsuda Y, Nakano T (2001) Two mouse Piwi-related genes: miwi and mili. Mech Dev 108:121–133
Le Thomas A, Rogers AK, Webster A, Marinov GK, Liao SE, Perkins EM, Hur JK, Aravin AA, Tóth KF (2013) Piwi induces piRNA-guided transcriptional silencing and establishment of a repressive chromatin state. Mech Dev 27:390–399
Levine M, Tjian R (2003) Transcription regulation and animal diversity. Nature 424:147–151
Lubzens E, Young G, Bobe J, Cerdà J (2010) Oogenesis in teleosts: how fish eggs are formed. Gen Comp Endocrinol 165:367–389
Ro S, Song R, Park C, Zheng H, Sanders KM, Yan W (2007) Cloning and expression profiling of small RNAs expressed in the mouse ovary. RNA 13:2366–2380
Robine N, Lau NC, Balla S, Jin Z, Okamura K, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Blower MD, Lai EC (2009) A Broadly Conserved Pathway Generates 3′UTR-Directed Primary piRNAs. Curr Biol 19:2066–2076
Ross RJ, Weiner MM, Lin H (2014) PIWI proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs in the soma. Nature 505:353–359
Schulz RW, de França LR, Lareyre JJ, LeGac F, Chiarini-Garcia H, Nobrega RH, Miura T (2010) Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 165:390–411
Shinkai Y, Satoh H, Takeda N, Fukuda M, Chiba E, Kato T, Kuramochi T, Araki Y (2002) A testicular germ cell-associated serine-threonine kinase, MAK, is dispensable for sperm formation. Mol Cell Biochem 22:3276–3280
Tahbaz N, Kolb FA, Zhang H, Jaronczyk K, Filipowicz W, Hobman TC (2004) Characterization of the interactions between mammalian PAZ PIWI domain proteins and Dicer. EMBO Rep 5:189–194
Tao W, Yuan J, Zhou L, Sun L, Sun Y, Yang S, Li M, Zeng S, Huang B, Wang D (2013) Characterization of gonadal transcriptomes from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reveals differentially expressed genes. PLoS ONE 8:e63604
Thomson T, Lin H (2009) The biogenesis and function of PIWI proteins and piRNAs: progress and prospect. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:355–376
Vagin VV, Sigova A, Li C, Seitz H, Gvozdev V, Zamore PD (2006) A Distinct Small RNA Pathway Silences Selfish Genetic Elements in the Germline. Science 313:320–324
Watanabe T, Takeda A, Tsukiyama T, Mise K, Okuno T, Sasaki H, Minami N, Imai H (2006) Identification and characterization of two novel classes of small RNAs in the mouse germline: retrotransposon-derived siRNAs in oocytes and germline small RNAs in testes. Genes Dev 20:1732–1743
Wilczynska A, Minshall N, Armisen J, Miska EA, Standart N (2009) Two Piwi proteins, Xiwi and Xili, are expressed in the Xenopus female germline. RNA 15:337–345
Xiao J, Zhong H, Zhou Y, Yu F, Gao Y, Luo Y, Tang Z, Guo Z, Guo E, Gan X, Zhang M, Zhang Y (2014) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in ovary and testis of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by using solexa sequencing technology. PLoS ONE 9:e86821
Yanagisawa M, Mukouyama Y, Watanabe T, Obinata M, Matsui Y (1996) A novel serine/threonine kinase gene, Gek1, is expressed in meiotic testicular germ cells and primordial germ cells. Mol Reprod Dev 45:411–420
Yi M, Chen F, Luo M, Cheng Y, Zhao H, Cheng H, Zhou R (2014) Rapid evolution of piRNA pathway in the teleost fish: implication for an adaptation to transposon diversity. Mol Biol Evol 6:1393–1407
Zhang Y, Wang X, Kang L (2011) A k-mer scheme to predict piRNAs and characterize locust piRNAs. Bioinformatics 27:771–776
Zhou Y, Wang F, Liu S, Zhong H, Liu Z, Tao M, Zhang C, Liu Y (2012) Human chorionic gonadotropin suppresses expression of Piwis in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) ovaries. Gen Comp Endocrinol 176:126–131
Zhou Y, Zhong H, Liu S, Yu F, Hu J, Zhang C, Tao M, Liu Y (2014) Elevated expression of Piwi and piRNAs in ovaries of triploid crucian carp. Mol Cell Endocrinol 383:1–9
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31302167, 31460688, 31260637, 31402281 and 31201984), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2014GXNSFBA118077 and 2015GXNSFBA139049), Public Welfare Special funds of Guangxi (GXIF-2014-13), Guangxi science and technology infrastructure project (15-235-10B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical compliance
This study was carried out with ethical approval from the ethical committee of Guangxi Academy of Fisheries Science.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yi Zhou and Huan Zhong have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhong, H., Xiao, J. et al. Identification and comparative analysis of piRNAs in ovary and testis of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Genes Genom 38, 519–527 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0400-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0400-z