Abstract
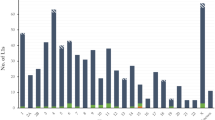
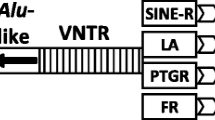
SVA (SINE/VNTR/Alu) transposable element, one of non-LTR retrotransposons, emerged in the primate genome about 25 million years ago. Currently, ~2,800 SVA copies exist in the human genome. Recently, a group of transposable elements named SVA2 is discovered. SVA2 elements share the VNTR region with the SVA element but do not contain the SINE-R region of the SVA elements. In this study, we studied the SVA2 evolution and the impact of the SVA2 elements on primate genomes. We first identified 144, 139, 136, 139, and 116 SVA2 elements in the human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan, and rhesus macaque genomes, respectively. To examine the evolutionary state and structure of the elements, we performed comparative genomics, comparing human SVA2 with its orthologous counterpart from non-human primates. The result suggests that SVA2 subfamily is not, at present, retrotranspositionally active in the primate genomes because none of the SVA2 elements identified in this study are species-specific. In addition, we found that four human SVA2 elements locate in human genes and two of them have miRNA target sites, indicating that they might regulate gene expression and involve in the gene-related human diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batzer MA, Deininger PL (2002) Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nat Rev Genet 3:370–379
Boeke JD (1997) LINEs and Alus—the polyA connection. Nat Genet 16:6–7
Callinan PA, Batzer MA (2006) Retrotransposable elements and human disease. Genome Dyn 1:104–115
Christensen SM, Eickbush TH (2005) R2 target-primed reverse transcription: ordered cleavage and polymerization steps by protein subunits asymmetrically bound to the target DNA. Mol Cell Biol 25:6617–6628
Cost GJ, Feng Q, Jacquier A, Boeke JD (2002) Human L1 element target-primed reverse transcription in vitro. EMBO J 21:5899–5910
Damert A, Raiz J, Horn AV, Löwer J, Wang H, Xing J, Batzer MA, Löwer R, Schumann GG (2009) 5′-Transducing SVA retrotransposon groups spread efficiently throughout the human genome. Genome Res 19:1992–2008
Goodier JL, Kazazian HH Jr (2008) Retrotransposons revisited: the restraint and rehabilitation of parasites. Cell 135:23–35
Han K, Konkel MK, Xing J, Wang H, Lee J, Meyer TJ, Huang CT, Sandifer E, Hebert K, Barnes EW et al (2007) Mobile DNA in Old World monkeys: a glimpse through the rhesus macaque genome. Science 316:238–240
Hancks DC, Mandal PK, Cheung LE, Kazazian HH Jr (2012) The minimal active human SVA retrotransposon requires only the 5’-hexamer and Alu-like domains. Mol Cell Biol 32:4718–4726
Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J (2005) Repbase update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:462–467
Kin T, Ono Y (2007) Idiographica: a general-purpose web application to build idiograms on-demand for human, mouse and rat. Bioinformatics 23:2945–2946
Luan DD, Korman MH, Jakubczak JL, Eickbush TH (1993) Reverse transcription of R2Bm RNA is primed by a nick at the chromosomal target site: a mechanism for non-LTR retrotranscription. Cell 72:595–605
Ostertag EM, Kazazian HH Jr (2001) Biology of mammalian L1 retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 35:501–538
Ostertag EM, Goodier JL, Zhang Y, Kazazian HH Jr (2003) SVA elements are nonautonomous retrotransposons that cause disease in humans. Am J Hum Genet 73:1444–1451
Ray DA, Xing J, Salem AH, Batzer MA (2006) SINEs of a nearly perfect character. Syst Biol 55:928–935
Shen L, Wu LC, Sanlioglu S, Chen R, Mendoza AR, Dangel AW, Carroll MC, Zipf WB, Yu CY (1994) structure and genetics of the partially duplicated gene RP located immediately upstream of the complement C4A and the C4B genes in the HLA class III region. Molecular cloning, exon-intron structure, composite retroposon, and breakpoint of gene duplication. J Biol Chem 269:8466–8476
Strichman-Almashanu LZ, Lee RS, Onyango PO, Perlman E, Flam F, Frieman MB, Feinberg AP (2002) A genome-wide screen for normally methylated human CpG islands that can identify novel imprinted genes. Genome Res 12:543–554
Wang H, Xing J, Grover D, Hedges DJ, Han K, Walker JA, Batzer MA (2005) SVA elements: a hominid-specific retroposon family. J Mol Biol 354:994–1007
Acknowledgments
The present work was conducted with funding from the Research Fund of Dankook University in 2013.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests exists in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwak, Y., Kim, Yj., Xing, J. et al. Evolutionary fate of SVA2 elements in primate genomes. Genes Genom 37, 153–159 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-014-0241-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-014-0241-6