Abstract
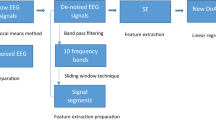
This paper presents a new method to apply timing characteristics of electroencephalograph (EEG) beta frequency bands to assess the depth of anaesthesia (DoA). Firstly, the measured EEG signals are denoised and decomposed into 20 different frequency bands. The Mobility (M), permutation entropy (PE) and Lempel–Ziv complexity (LCZ) of each frequency band are calculated. The M, PE and LCZ values of beta frequency bands (21.5–30 Hz) are selected to derive a new index. The new index is evaluated and compared with measured bispectral (BIS). The results show that there is a very close correlation between the proposed index and the BIS during different anaesthetic states. The new index also shows a 25–264 s earlier time response than BIS during the transient period of anaesthetic states. In addition, the proposed index is able to continuously assess the DoA when the quality of signal is poor and the BIS does not have any valid outputs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowdle TA (2006) Depth of anesthesia monitoring. Anesthesiol Clin 24(4):793
Chen D, Li D, Xiong M, Bao H, Li X (2010) GPGPU-aided ensemble empirical-mode decomposition for EEG analysis during anesthesia. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 14(6):1417–1427
Wei Q, Liu Q, Fan SZ, Lu CW, Lin TY, Abbod MF, Shieh JS (2013) Analysis of EEG via multivariate empirical mode decomposition for depth of anesthesia based on sample entropy. Entropy 15(9):3458–3470
Nguyen-Ky T, Wen P, Li Y (2010) An improved detrended moving-average method for monitoring the depth of anesthesia. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(10):2369–2378
Kortelainen J, Vayrynen E, Seppanen T (2011) Depth of anesthesia during multidrug infusion: separating the effects of propofol and remifentanil using the spectral features of EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(5):1216–1223
Nguyen-Ky T, Wen P, Li Y (2013) Consciousness and depth of anesthesia assessment based on Bayesian analysis of EEG signals. IEEE J Mag 60(6):1488–1498
Olofsen E, Sleigh J, Dahan A (2008) Permutation entropy of the electroencephalogram: a measure of anaesthetic drug effect. Br J Anaesth 101(6):810–821
Jordan D, Stockmanns G, Kochs EF, Pilge S, Schneider G (2008) Electroencephalographic order pattern analysis for the separation of consciousness and unconsciousness: an analysis of approximate entropy, permutation entropy, recurrence rate, and phase coupling of order recurrence plots. Anesthesiology 109(6):1014–1022
Silva A, Campos S, Monteiro J, Venâncio C, Costa B, de Pinho PG, Antunes L (2011) Performance of anesthetic depth indexes in rabbits under propofol anesthesia: prediction probabilities and concentration-effect relations. Anesthesiology 115(2):303–314
Ferenets R, Lipping T, Anier A, Jantti V, Melto S, Hovilehto S (2006) Comparison of entropy and complexity measures for the assessment of depth of sedation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(6):1067–1077
Musizza B, Ribaric S (2010) Monitoring the depth of anaesthesia. Sensors 10(12):10896–10935
McBride JC, Zhao X, Munro NB, Smith CD, Jicha GA, Hively L, Broster LS, Schmitt FA, Kryscio RJ, Jiang Y (2014) Spectral and complexity analysis of scalp EEG characteristics for mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 114(2):153–163
Jordan D, Stockmanns G, Kochs EF, Pilge S, Schneider G (2008) Electroencephalographic order pattern analysis for the separation of consciousness and unconsciousness. An analysis of approximate entropy, permutation entropy, recurrence rate, and phase coupling of order recurrence plots. J Am Soc Anesthesiol 109(6):1014–1022
Snaedal J, Johannesson GH, Gudmundsson TE, Gudmundsson S, Pajdak T, Johnsen K (2010) The use of EEG in Alzheimer’s disease, with and without scopolamine—a pilot study. Clin Neurophysiol 121(6):836–841
Li T, Wen P, Jayamaha S (2014) Anaesthetic EEG signal denoise using improved nonlocal mean methods. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 37(2):431–437
Rampil IJ (1998) A primer for EEG signal processing in anesthesia. J Am Soc Anesthesiol 89(4):980–1002
Shalbaf R, Behnam H, Sleigh JW, Steyn-Ross DA, Steyn-Ross ML (2015) Frontal-temporal synchronization of EEG signals quantified by order patterns cross recurrence analysis during propofol anesthesia. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 23(3):468–474
Palendeng ME, Wen P, Li Y (2014) Real-time depth of anaesthesia assessment using strong analytical signal transform technique. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 37(4):723–730
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Wen, P. Depth of anaesthesia assessment based on adult electroencephalograph beta frequency band. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 39, 773–781 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0459-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0459-5