Abstract
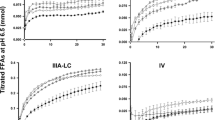
In vitro lipolysis studies are the most common approach to investigate digestion profiles and microstructure breakdown of emulsion-based functional foods after ingestion. This study investigated the difference between two static mono-compartmental models, the pH stat titration and a jar digestion model, as tools to evaluate lipolysis in vitro. Two oil-in-water emulsions, consisting of long- or medium-chain triglycerides, were used in the study. Factors essential to the pH-stat model were evaluated, including calcium concentration and mode of addition, i.e. initial or continuous. Continuous addition of calcium resulted in improved control of free fatty acid release kinetics. Results also indicated that titration at pH 9 alleviates the underestimation of free fatty acid release with the pH-stat model. The research clearly highlighted the differences between the models, and the results will help researchers identify the most appropriate model to use for in vitro digestion of emulsions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla A, Klein S, Mäder K (2008) A new self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for poorly soluble drugs: characterization, dissolution, in-vitro digestion and incorporation into solid pellets. Eur J Pharm Sci 35:457–464
Alvarez F, Stella V (1989) The role of calcium ions and bile salts on the pancreatic lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of triglyceride emulsions stabilized with lecithin. Pharm Res 6:449–457
Armand M, Borel P, Ythier P, Dutot G, Melin C, Senft M, Lafont H, Lairon D (1992) Effects of droplet size, triacylglycerol composition, and calcium on the hydrolysis of complex emulsions by pancreatic lipase: an in vitro study. J Nutr Biochem 3:333–341
Beisson F, Tiss A, Riviere C, Verger R (2000) Methods for lipase detection and assay: a critical review. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 102:133–153
Benzonana G, Desnuelle P (1968) Action of some effectors on the hydrolysis of long-chain triglycerides by pancreatic lipase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)/Lipids and Lipid Metabolism 164:47–58
Bonnaire L, Sandra S, Helgason T, Decker EA, Weiss J, McClements DJ (2008) Influence of lipid physical state on the in vitro digestibility of emulsified lipids. J Agric Food Chem 56:3791–3797
Bronner F (2003) Mechanisms of intestinal calcium absorption. J Cell Biol 88:387–393
Carriere F, Barrowman JA, Verger R, Laugier R (1993) Secretion and contribution to lipolysis of gastric and pancreatic lipases during a test meal in humans. Gastroenterology 105:876–888
Carriere F, Renou C, Lopez V, de Caro J, Ferrato F, Lengsfeld H, de Caro A, Laugier R, Verger R (2000) The specific activities of human digestive lipases measured from the in vivo and in vitro lipolysis of test meals. Gastroenterology 119:949–960
Carriere F, Grandval P, Gregory PC, Renou C, Henniges F, Sander-Struckmeier S, Laugier R (2005) Does the pancreas really produce much more lipase than required for fat digestion? JOP 6:206–215
Ceccarelli B, Clemente F, Meldolesi J (1975) Secretion of calcium in pancreatic juice. J Physiol Lond 245:617–638
Dahan A, Hoffman A (2008) Rationalizing the selection of oral lipid based drug delivery systems by an in vitro dynamic lipolysis model for improved oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. J Control Release 129:1–10
Devraj R, Williams HD, Warren DB, Mullertz A, Porter CJH, Pouton CW (2013) In vitro digestion testing of lipid-based delivery systems: calcium ions combine with fatty acids liberated from triglyceride rich lipid solutions to form soaps and reduce the solubilization capacity of colloidal digestion products. Int J Pharm 441:323–333
Fernandez S, Jannin V, Rodier J, Ritter N, Mahler B, Carrière F (2007) Comparative study on digestive lipase activities on the self emulsifying excipient Labrasol®, medium chain glycerides and PEG esters. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1771:633–640
Fernandez S, Rodier J, Ritter N, Mahler B, Demarne F, Carrière F, Jannin V (2008) Lipolysis of the semi-solid self-emulsifying excipient Gelucire® 44/14 by digestive lipases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1781:367–375
Friedman HI, Nylund B (1980) Intestinal fat digestion, absorption, and transport. A review. Am J Clin Nutr 33:1108–1139
Guerra A, Etienne-Mesmin L, Livrelli V, Denis S, Blanquet-Diot S, Alric M (2012) Relevance and challenges in modeling human gastric and small intestinal digestion. Trends Biotechnol 30:591–600
Helbig A, Silletti E, Timmerman E, Hamer RJ, Gruppen H (2012) In vitro study of intestinal lipolysis using pH-stat and gas chromatography. Food Hydrocoll 28:10–19
Hernell O, Staggers JE, Carey MC (1990) Physical-chemical behavior of dietary and biliary lipids during intestinal digestion and absorption. 2. Phase analysis and aggregation states of luminal lipids during duodenal fat digestion in healthy adult human beings. Biochemistry 29:2041–2056
Hu M, Li Y, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2010) Role of calcium and calcium-binding agents on the lipase digestibility of emulsified lipids using an in vitro digestion model. Food Hydrocoll 24:719–725
Hur SJ, Lim BO, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2011) In vitro human digestion models for food applications. Food Chem 125:1–12
Irina RM, Buckley CL, Poppenga RH (2004) Detection of nonesterified (Free) fatty acids in bovine serum: comparative evaluation of two methods. J Vet Diagn Investig 16:139–144
Jenab E, Temelli F, Curtis JM (2013) Lipase-catalysed interesterification between canola oil and fully hydrogenated canola oil in contact with supercritical carbon dioxide. Food Chem 141:2220–2228
Johnson LR (1977) Gastrointestinal hormones and their functions. Annu Rev Physiol 39:135–158
Kimura H, Futami Y, Tarui S, Shinomiya T (1982) Activation of human pancreatic lipase activity by calcium and bile salts. J Biochem 92:243–251
Klinkesorn U, McClements DJ (2010) Impact of lipase, bile salts, and polysaccharides on properties and digestibility of tuna oil multilayer emulsions stabilized by lecithin–chitosan. Food Biophys 5:73–81
Larsen AT, Sassene P, Müllertz A (2011) In-vitro lipolysis models as a tool for the characterization of oral lipid and surfactant based drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm 417:245–255
Lesmes U, Baudot P, McClements DJ (2010) Impact of interfacial composition on physical stability and in vitro lipase digestibility of triacylglycerol oil droplets coated with lactoferrin and/or caseinate. J Agric Food Chem 58:7962–7969
Li Y, McClements DJ (2010) New mathematical model for interpreting pH-stat digestion profiles: impact of lipid droplet characteristics on in vitro digestibility. J Agric Food Chem 58:8085–8092
Li Y, Hu M, McClements DJ (2011) Factors affecting lipase digestibility of emulsified lipids using an in vitro digestion model: proposal for a standardised pH-stat method. Food Chem 126:498–505
Lin X, Wang Q, Li W, Wright AJ (2014) Emulsification of algal oil with soy lecithin improved DHA bioaccessibility but did not change overall in vitro digestibility. Food Funct 5:2913–2921
MacGregor KJ, Embleton JK, Lacy JE, Perry EA, Solomon LJ, Seager H, Pouton CW (1997) Influence of lipolysis on drug absorption from the gastro-intestinal tract. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 25:33–46
Malaki Nik A, Wright AJ, Corredig M (2011) Impact of interfacial composition on emulsion digestion and rate of lipid hydrolysis using different in vitro digestion models. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 83:321–330
McClements DJ, Li Y (2010) Review of in vitro digestion models for rapid screening of emulsion-based systems. Food Funct 1:32–59
McClements DJ, Decker EA, Park Y (2008) Controlling lipid bioavailability through physicochemical and structural approaches. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 49:48–67
Miled N, Canaan S, Dupuis L, Roussel A, Riviere M, Carriere F, de Caro A, Cambillau C, Verger R (2000) Digestive lipases: from three-dimensional structure to physiology. Biochimie 82:973–986
Minekus M, Alminger M, Alvito P, Ballance S, Bohn T, Bourlieu C, Carrière F, Boutrou R, Brodkorb A (2014) A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—an international consensus. Food Funct 5:1113–1124
Mun S, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2007) Influence of emulsifier type on in-vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase. Food Res Int 40:770–781
Nik AM, Corredig M, Wright AJ (2010) Changes in WPI-stabilized emulsion interfacial properties in relation to lipolysis and ß-carotene transfer during exposure to simulated gastric–duodenal fluids of variable composition. Food Dig 1:14–27
Ogawa S, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2003) Influence of environmental conditions on the stability of oil in water emulsions containing droplets stabilized by lecithin-chitosan membranes. J Agric Food Chem 51:5522–5527
Oomen AG, Hack A, Minekus M, Zeijdner E, Cornelis C, Schoeters G, Verstraete W, Van de Wiele T, Wragg J, Rompelberg CJ (2002) Comparison of five in vitro digestion models to study the bioaccessibility of soil contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 36:3326–3334
Parada J, Aguilera JM (2007) Food microstructure affects the bioavailability of several nutrients. J Food Sci 72:R21–R32
Patton JS, Carey MC (1979) Watching fat digestion. Science 204:145–148
Porter CJ, Kaukonen AM, Taillardat-Bertschinger A, Boyd BJ, O'Connor JM, Edwards GA, Charman WN (2004) Use of in vitro lipid digestion data to explain the in vivo performance of triglyceride-based oral lipid formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs: studies with halofantrine. J Pharm Sci 93:1110–1121
Reis P, Raab T, Chuat J, Leser M, Miller R, Watzke H, Holmberg K (2008) Influence of surfactants on lipase fat digestion in a model gastro-intestinal system. Food Biophys 3:370–381
Reis P, Holmberg K, Watzke H, Leser ME, Miller R (2009) Lipases at interfaces: a review. Adv Colloid InterfSci 147–148:237–250
Sarkar A, Horne DS, Singh H (2010) Pancreatin-induced coalescence of oil-in-water emulsions in an in vitro duodenal model. Int Dairy J 20:589–597
Sek L, Porter CJ, Kaukonen AM, Charman WN (2002) Evaluation of the in‐vitro digestion profiles of long and medium chain glycerides and the phase behaviour of their lipolytic products. J Pharm Pharmacol 54:29–41
Shimizu S, Tani Y, Yamada H, Tabata M, Murachi T (1980) Enzymatic determination of serum-free fatty acids: a colorimetric method. Anal Biochem 107:193–198
Simoneau C, McCarthy MJ, Reid DS, German JB (1993) Influence of triglyceride composition on crystallization kinetics of model emulsions. J Food Engineer 4:365–387
Torcello-Gómez A, Maldonado-Valderrama J, Martín-Rodríguez A, McClements DJ (2011) Physicochemical properties and digestibility of emulsified lipids in simulated intestinal fluids: influence of interfacial characteristics. Soft Matter 7:6167–6177
Versantvoort CH, Oomen AG, Van de Kamp E, Rompelberg CJ, Sips AJ (2005) Applicability of an in vitro digestion model in assessing the bioaccessibility of mycotoxins from food. Food Chem Toxicol 43:31–40
Williams HD, Sassene P, Kleberg K, Bakala‐N’Goma J, Calderone M, Jannin V, Igonin A, Partheil A, Marchaud D, Jule E (2012) Toward the establishment of standardized in vitro tests for lipid‐based formulations, part 1: method parameterization and comparison of in vitro digestion profiles across a range of representative formulations. J Pharm Sci 101:3360–3380
Wright AJ, Pietrangelo C, MacNaughton A (2008) Influence of simulated upper intestinal parameters on the efficiency of beta carotene micellarisation using an in vitro model of digestion. Food Chem 107:1253–1260
Ye A, Cui J, Zhu X, Singh H (2013) Effect of calcium on the kinetics of free fatty acid release during in vitro lipid digestion in model emulsions. Food Chem 139:681–688
Zangenberg NH, Müllertz A, Kristensen HG, Hovgaard L (2001) A dynamic in vitro lipolysis model: I. Controlling the rate of lipolysis by continuous addition of calcium. Eur J Pharm Sci 14:115–122
Acknowledgments
This work was partly funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). The authors are involved in the Food and Agriculture European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST) Action FA1005 "Improving health properties of food by sharing our knowledge on the digestive process (INFOGEST)".
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest and no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eldemnawy, H.Y., Wright, A. & Corredig, M. A Better Understanding of the Factors Affecting In vitro Lipolysis Using Static Mono-compartmental Models. Food Dig. Res Curr Opin 6, 10–18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13228-015-0038-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13228-015-0038-3