Abstract
Background
The incidence of post-partum anaemia (PPA) is 14–24%. Treatment of PPA with injectable iron replenishes the iron store. Ferric carboxymaltose complex (FCM) is a non-dextran containing intravenous iron agent, having a very low immunogenic potential, designed to be administered in large doses in a short period of time.
Objective
To compare the efficacy and safety of intravenous FCM and iron sucrose (IS) in post-partum iron-deficiency anaemia.
Material and Method
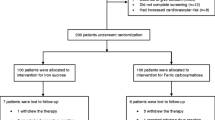
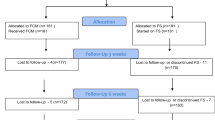
In this prospective, comparative study, 120 post-partum women with iron-deficiency anaemia (Hb < 10 g%) were divided into two groups. A fixed dose of 1000 mg of FCM or IS was given within 10 days of delivery. Hb and serum ferritin were repeated 14 days post-transfusion.
Result
There is a mean increase in Hb (P value 0.000, 0.000) and ferritin (P value 0.000, 0.000) in both the groups. For intergroup comparison, independent Student’s t test was performed which showed FCM was superior to IS (P value 0.000 and 0.000).
Conclusion
In our study, FCM was very effective in improving Hb concentration as well as in early replenishment of iron stores in patients with PPA. Large doses given in a short period of time not only save hospital resources but also improve patient satisfaction. It has significant benefit for use in the outpatient department. From this study, we can recommend its use in post-partum women with iron-deficiency anaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pavord S, Myers B, Robinson S, Allard S, Strong J, Oppenheimer C, et al. UK guidelines on the management of iron deficiency in pregnancy. Br J Haematol. 2012;156:588–600.
Kouser S, Kouser S, Malik M, Malik A. safety and efficacy of intravenous iron therapy in postnatal patients with iron def anaemia. J South Asian Fed Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;3:25–7.
Milman N. Postpartum anemia I: definition, prevalence, causes and consequences. Ann Haematol. 2011;90:1247–53.
Covic A, Mircescu G. The safety and efficacy of IV FCM in anaemic patients undergoing haemodialysis: a multicentre, open-label, clinical study. Nephrol Dial Trasplant. 2010;25(8):2722–30.
Klaire E, Nancy T, Andrea A, Atif K, Shahed A. Efficacy and safety profile of single dose IV FCM in the management of renal anaemia-a single centre experience. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(1):363–4.
Hussain I, Bhoyroo J, Butcher A. Direct comparison of the safety and efficacy of Ferric carboxymaltose versus iron dextran in patients with iron deficiency anemia. Anemia. 2013;2013:169107.
Friedrisch JR, Cancado RD. Intravenous ferric carboxymaltose for the treatment of iron deficiency. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2015;37(6):400–5.
Rathod S, Samal SK, Mahapatra PC. Ferric carboxymaltose: a revolution in the treatment of postpartum anemia in Indian women. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2015;5(1):25–30.
Bisbe E, Garcia-Erce JA, Diez-Lodo AI, Munoz MA. multicentre comparative study on the efficacy of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose and iron sucrose for correcting preoperative anaemia in patients undergoing major elective surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2011;107(3):477–8.
Froessler B, Collingwood J, Hodyl NA, et al. Intravenous ferric carboxymaltose for anaemia in pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Child Birth. 2014;14:115.
Dillon R, Momoh I, Cameron L, et al. Comparative efficacy of three forms of parenteral iron. J Blood Transfus. 2012;2012:473514.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Nalini Sharma, Tanie Natung, J Lalnunnen Thiek, Santa Singh Ahanthem declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Institutional ethical committee clearance was obtained for study.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in study.
Additional information
Nalini Sharma is an Assistant Professor at Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, North-eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences, Shillong, Meghalaya, India; Lalnunnem Thiek is a Senior resident at Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, North-eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences, Shillong, Meghalaya, India; Tanie Natung is an Assistant Professor at Department of Ophthalmology, North-eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences, Shillong, Meghalaya, India; Santa Singh Ahanthem is a DNB Professor and head at Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, North-eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences, Shillong, Meghalaya, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N., Thiek, J.L., Natung, T. et al. Comparative Study of Efficacy and Safety of Ferric Carboxymaltose Versus Iron Sucrose in Post-partum Anaemia. J Obstet Gynecol India 67, 253–257 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-017-0971-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-017-0971-x