Abstract
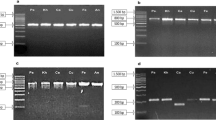
Amplification success and species discrimination efficiency of universal DNA barcode primers (trnH–psbA, trnL, ycf1b, atpF–atpH, matK and rbcL) was evaluated in 46 representative medicinal plant species of 28 families on agarose gel. The results showed that amplicons length polymorphism revealed by the primers atpF–atpH, trnH–psbA and trnL can simultaneously discriminate all the 46 species under study precisely. Some of the plant species included in this study are used as potential adulterants to other plant species. We were able to successfully discriminate the plant species from their potential substitute. Vitex negundo is an adulterant of Ocimum sanctum which has been successfully discriminated by all these three markers. Another example of adulteration between Bacopa monnieri and Centella asiatica was successfully discriminated by atpF–atpH, trnL and trnH–psbA on the basis of variability in amplicon length of these two medicinal herbs. Further, Cassia tora and Cassia fistula are also adulterants for each other and variability in amplicon length between these two species was revealed by atpF–atpH and trnH–psbA markers. A colour code distance matrix based on amplicon length polymorphism was designed to select primers which can effectively discriminate plants species on the basis of their amplicon length. Discrimination of plant species with the universal markers on agarose gel is a noble and inexpensive approach as it does not require sequencing of amplicons. This procedure will provide a way for the development of diagnostic markers to identify adulteration not only in herbal drug formulations but also in food material.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2018) Annual report, 2017–18. Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy, India
Borsch T, Hilu K, Quandt D, Wilde V, Neinhuis C, Barthlott W (2003) Noncoding plastid trnT-trnF sequences reveal a well resolved phylogeny of basal angiosperms. J Evol Biol 16:558–576. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1420-9101.2003.00577.x
CBOL Plant Working Group (2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12794–12797. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905845106
Chang CC, Lin HC, Lin IP, Chow TY, Chen HH, Chen WH (2006) The chloroplast genome of Phalaenopsis aphrodite (Orchidaceae): comparative analysis of evolutionary rate with that of grasses and its phylogenetic implications. Mol Biol Evol 23:279–291. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006319803002
Chase MW, Cowan RS, Hollingsworth PM, van den Berg C, Madriñán S, Petersen G (2007) A proposal for a standardized protocol to barcode all land plants. Taxon 56:295–299
Chen S, Yao H, Han J, Liu C, Song J et al (2010) Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species. PLoS One 5:e8613. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008613
D’yachenko EA, Filyushin MA, Pronin EP, Kochieva EZ (2015) Variability of the trnL Plastid Gene’s Intron in the Faboideae Species (Fabaceae). Russ J Genet 5:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059715030053
Dong W, Liu J, Yu J, Wang L, Zhou S (2012) Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS One 7:e35071. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035071
Dong W, Chao XC, Li C, Sun J, Zuo Y, Shi S, Cheng T, Guo J, Zhou S (2015) ycf1, the most promising plastid DNA barcode of land plants. Sci Rep 5:8348. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08348
Drager RG, Hallick RB (1993) A novel Euglena gracilis chloroplast operon encoding 4 ATP synthase subunits and 2 ribosomal-proteins contains 17 Introns. Curr Genet 23:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351506
Efferth T, Greten HJ (2012) Medicinal and aromatic plant research in the 21st century. Med Aromat Plants 1:e110. https://doi.org/10.4172/2167-0412.1000e110
El-Atroush H, Magdy M, Werner O (2015) DNA Barcoding of two endangered medicinal plants from Abou Galoom protectorate. Life Sci J 12:101–109. https://doi.org/10.7537/marslsj120915.14
Giang PM, Otsukab H (2018) New compounds and potential candidates for drug discovery from medicinal plants of Vietnam. Chem Pharm Bull 66:493–505. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c17-00628
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, DeWaard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B: Biol Sci 270:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2002.2218
James D, Schmidt A (2004) Use of an intron region of a chloroplast tRNA gene (trnL) as a target for PCR identification of specific food crops including sources of potential allergens. Food Res Int 37:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2004.02.004
Kress WJ, Wurdack KJ, Zimmer EA, Weigt LA, Janzen DH (2005) Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8369–8374. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503123102
Kumar SP (2014) Adulteration and substitution in endangered ASU medicinal plants of India: a review. Int J Med Arom Plants 4:56–73
Lahaye R, Savolainen V, Duthoit S, Maurin O, van der Bank M (2008) A test of psbK–psbI and atpF–atpH as potential plant DNA barcodes using the flora of the Kruger National Park as a model system (South Africa). Nature Proc
Monkheang P, Sudmoon R, Tanee T, Noikotr K, Bletter N, Chaveerach A (2011) Species diversity, usages, molecular markers and barcode of medicinal Senna species (Fabaceae, Caesalpinioideae), Thailand. J Med Plant Res 5:6173–6181
Mower JP, Touzet P, Gummow JS, Delph LF, Palmer JD (2007) Extensive variation in synonymous substitution rates in mitochondrial genes of seed plants. BMC Evol Biol 7:135. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-7-135
Newmaster SG, Grguric M, Shanmughanandhan D, Ramalingam S, Ragupathy S (2013) DNA barcoding detects contamination and substitution in North American herbal products. BMC Med 11:222–235. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-222
Osathanunkul M, Suwannapoomb C, Osathanunkul K, Madesise P, Boerf HD (2016) Evaluation of DNA barcoding coupled high resolution melting for discrimination of closely related species in phytopharmaceuticals. Phytomedicine 23:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2015.11.018
Quandt D, Muller K, Stech M, Frahm JP, Frey W, Hilu KW, Borsch T (2004) Molecular evolution of the chloroplast trnL-F region in land plants. Monogr Syst Bot Missouri Bot Gard 98:13–37
Ridgway K, Duck J, Young J (2003) Identification of roots from grass swards using PCR-RFLP and FFLP of the plastid trnL (UAA) intron. BMC Ecol 3:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6785-3-8
Rohlf FJ (1997) NTSYS-pc Version. 2.02i Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Applied Biostatistics Inc., Exeter Software, Setauket
Seth BP, Thaker VS (2015) Identification of a herbal powder by deoxyribonucleic acid barcoding and structural analyses. Pharmacogn Mag 11:S570–S574. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.172963
Shaw J, Lickey EB, Schilling EE, Small RL (2007) Comparison of whole Chloroplast genome sequence to choose non-coding region for phylogenetic studies in angiosperm: the tortoise and the hare III. Am J Bot 94:275–288. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.94.3.275
Sikdar S, Tiwari S, Sapre S, Thakur VV (2018) Simple approach for species discrimination of fabaceae family on the basis of length variation in pcr amplified products using barcode primers. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 7:921–928. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.712.115
Soni HB, Dabhi M, Thomas S (2013) Perspective on phytochemical and biochemical compounds of selected Indian medicinal plants. Int Res J Chem 1:37–45
Spaniolas S, Bazakos C, Spano T, Zoghby C, Kalaitzis P (2010) The potential of plastid trnL (UAA) intron polymorphisms for the identification of the botanical origin of plant oils. Food Chem 122:850–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.039
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17:1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037152
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Gielly L, Miquel C, Valentini A, Vermat T, Corthier G, Brochmann C, Willerslev E (2007) Power and limitations of the chloroplast trnL (UAA) intron for plant DNA barcoding. Nucleic Acids Res 35:e14. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl938
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (2009) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17:1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037152
Techen N, Parveen I, Pan Z, Khan IA (2014) DNA barcoding of medicinal plant material for identification. Curr Opin Biotechnol 103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.010
Tsai L, Yu Y, Hsieh H, Wang J, Linacre A, Lee JC (2006) Species identification using sequences of the trnL intron and the trnL-trnF IGS of chloroplast genome among popular plants in Taiwan. Forensic Sci Int 164:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.01.007
Vijayan K, Tsou CH (2010) DNA barcoding in plants: taxonomy in a new perspective. Curr Sci 99:1530–1541
Wang W, Wu Y, Yan Y, Ermakova M, Kerstetter R, Messing J (2010) DNA barcoding of the Lemnaceae, a family of aquatic monocots. BMC Plant Biol 10:205. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-205
Yadav A, Ahmad J, Chaudhary AA, Ahmad A (2012) Development of sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) marker for the authentication of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. Eur J Med Plants 2:186–98. https://doi.org/10.9734/EJMP/2012/1192
Acknowledgements
ST acknowledges grant from Madhya Pradesh State Agriculture Marketing Board, Bhopal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VVT and ST planned the work; GT and VVT collected the experimental materials; and VVT and NT conducted the experiments. ST, VVT and NT have contributed equally in analysis and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, V.V., Tiwari, S., Tripathi, N. et al. Molecular identification of medicinal plants with amplicon length polymorphism using universal DNA barcodes of the atpF–atpH, trnL and trnH–psbA regions. 3 Biotech 9, 188 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1724-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1724-6