Abstract
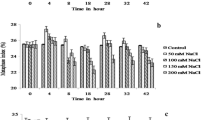
Mesorhizobium ciceri Rch125 is a salt-sensitive strain isolated from root nodules of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). The aim of this work was to investigate the genes responsible for the sensitivity to salinity. Twelve Rch125 salt-tolerant mutants were isolated after random Tn5 mutagenesis and selected using a medium containing 300 mM NaCl, where growth of the wild-type is totally inhibited. In addition to this NaCl tolerance, the mutants also displayed higher tolerance to LiCl, CaCl2 and sucrose. Genes that were disrupted in the salt-tolerant mutants were in one of three functional categories: membrane transporters, outer membrane proteins, and genes of unknown function. Genetic complementation experiments demonstrated that the genes identified were involved in the salt sensitivity of the Rch125 strain. In most cases, disruption of the salt-sensitivity genes did not negatively affect the free-living or the symbiotic capabilities of Rch125 under non-saline conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmoumen H, Filali Maltouf A, Neyra M, Belabed A, El Idrissi MM (1999) Effects of high salt concentrations on the growth of rhizobia and responses to added osmotica. J Appl Microbiol 86:889–898
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSLBLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Biswas S, Das RH, Sharma GL, Das HR (2008) Isolation and characterization of a novel cross-infective rhizobia from sesbania aculeata (dhaincha). Curr Microbiol 56:48–54
Blatny JM, Brautaset T, Winther-Larsen HC, Haugan K, Valla S (1997) Construction and use of a versatile set of broad-host-range cloning and expression vectors based on the RK2 replicon. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:370–374
Boscari A, Mandon K, Dupont L, Poggi MC, Le Rudulier D (2002) BetS is a major glycine betaine/proline for early osmotic adjustment in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 184:2654–2663
Boscari A, Mandon K, Poggi MC, Le Rudulier D (2004) Functional expression of Sinorhizobium meliloti BetS, a high-affinity betaine transporter, in Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5916–5922
Brígido C, Alexandre A, Oliveira S (2012) Transcriptional analysis of major chaperone genes in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive mesorhizobia. Microbiol Res 167:623–629
Chang C, Damiani I, Puppo A, Frendo P (2009) Redox changes during the legume–rhizobium symbiosis. Mol Plant 2:370–377
Domínguez-Ferreras A, Muñoz S, Olivares J, Soto MJ, Sanjuán J (2009a) Role of potassium uptake systems in Sinorhizobium meliloti osmoadaptation and symbiotic performance. J Bacteriol 191:2133–2143
Domínguez-Ferreras A, Soto MJ, Pérez-Arnedo R, Olivares J, Sanjuán J (2009b) Importance of trehalose biosynthesis for Sinorhizobium meliloti osmotolerance and nodulation of alfalfa roots. J Bacteriol 191:7490–7499
Dogra T, Priyadarshini A, Kumar KA, Singh NK (2013) Identification of genes involved in salt tolerance and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in chickpea rhizobium mesorhizobium ciceri Ca181. Symbiosis 61:135–143
Ferguson GP, Datta A, Carlson RW, Walker GC (2005) Importance of unusually modified lipid a in sinorhizobium stress resistance and legume symbiosis. Mol Microbiol 56:68–80
Fischer SE, Miguel MJ, Mori GB (2003) Effect of root exudates on the exopolysaccharide composition and the lipopolysaccharide profile of Azospirillum brasilense Cd under saline stress. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219:53–62
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Henderson IR, Navarro-Garcia F, Nataro JP (1998) The great scape: structure and function of autotrasporter proteins. Trends Microbiol 6:370–378
Jiang JQ, Wei W, Du BH, Li XH, Wang L, Yang SS (2004) Salt-tolerance genes involved in cation efflux and osmoregulation of sinorhizobium fredii RT19 detected by isolation and characterization of Tn5 mutants. FEMS Microbiol Lett 239:139–146
Kaneko T, Nakamura Y, Sato S, Asamizu E, et al. (2000) Complete genome structure of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium mesorhizobium loti. DNA Res 7(6):331–338
Koonin EV, Wolf YI, Aravind L (2000) Protein fold recognition using sequence profiles and its application in structural genomics. Adv Protein Chem 54:245–275
Kulkarni S, Surange S, Nautiyal CS (2000) Crossing the limits of rhizobium existence in extreme conditions. Curr Microbiol 41:402–409
Laranjo, Oliveira (2011) Tolerance of mesorhizobium type strains to different environmental stresses. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 99:651–662
Laranjo M, Young JPW, Oliveira S (2012) Multilocus sequence analysis reveals multiple symbiovars within mesorhizobium species. Syst Appl Microbiol 35:359–367
Leonard LT (1943) A simple assembly for use in the testing of cultures of rhizobia. J Bacteriol 45:523–527
Maatallah J, Berraho EB, Munoz S, Sanjuan J, Lluch C (2002) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of chickpea rhizobia isolated from different areas of morocco. J Appl Microbiol 93:531–540
McIntyre J, Baranowska H, Skoneczna A, Halas A, Sledziewska-Gojska E (2007) The spectrum of spontaneous mutations caused by deficiency in proteasome maturase Ump1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 52:221–228
Meade HM, Long SR, Ruvkun GB, Brown SE, Ausubel FM (1982) Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol 149:114–122
Mhadhbi H, Jebara M, Zitoun A, Limam F, Aouani ME (2007) Symbiotic effectiveness and response to mannitol-mediated osmotic stress of various chickpea–rhizobia associations. Word J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1027–1035
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 466 pp
Miller-Williams M, Loewen PC, Oresnik IJ (2006) Isolation of salt-sensitive mutants of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm1021. Microbiology 152:2049–2059
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Ann Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nies DH, Koch S, Wachi S, Peitzsch N, Saier Jr MH (1998) CHR, a novel family of prokaryotic proton motive force driven transporters probably containing chromate/sulfate antiporters. J Bacteriol 180:5799–5802
Nogales J, Campos R, BenAbdelkhalek H, Olivares J, Lluch C, Sanjuan J (2002) Rhizobium tropici genes involved in free-living salt tolerance are required for the establishment of efficient nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 15:225–232
Ogura M, Tanaka T (1997) Bacillus subtilis ComK negatively regulates degR gene expression. Mol Gen Genet 254:157–165
Ohwada T, Sasaki Y, Koike H, Igawa K, Sato T (1998) Correlation between NaCl sensitivity of rhizobium bacteria and ineffective nodulation of leguminous plants. Biosci Biotec Biochem 62:2086–2090
Payakapong W, Tittabutr P, Teaumroong N, Borthakur D, Boonkerd N (2006) Isolation of genes for salt tolerance from sinorhizobium LT11. Cur Plant Sci Biotechnol Agric 41:301–302
Romisch-Margl W, Eisenreich W, Haase I, Bacher A, Fischer M (2008) 2,5-diamino-6-ribitylamino-4(3 H)-pyrimid inone5′-phosphate synthases of fungi and archaea. Febs j 275:4403–4414
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor NewYork
Simon R, Priefer U, Pülher A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram negative bacteria. Biotech 1:784–791
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Soussi M, Ocaña A, Lluch C (1998) Effects of salt stress on growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation in chickpea (cicer arietinum). J Exp Bot 49:1329–1337
Soussi M, Santamaría M, Ocaña A, Lluch C (2001) Effects of salinity on protein and lipopolysaccharide pattern in a salt-tolerant strain of mesorhizobium ciceri. J Appl Microbiol 90:476–481
Udvardi M, Poole P (2013) Transport and metabolism in legume-rhizobia symbioses. Ann Rev Plant Pathol 64:781–805
Unni S, Rao KK (2001) Protein and lipopolysaccharide profiles of a salt-sensitive rhizobium sp. and its exopolysaccharide-deficient mutant. Soil Biol Biochem 33:111–115
Vauclare P, Bligny R, Gout E, Widmer F (2013) An overview of the metabolic differences between Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110 bacteria and differentiated bacteroids from soybean (Glycine max) root nodules: an in vitro 13C- and 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. FEMS Microbiol Lett 343:49–56
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root-nodule bacteria, IBP handbook N°15 oxford, vol 164. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Wei W, Jiang J, Li X, Wang L, Yang SS (2004) Isolation of salt-sensitive mutants from Sinorhizobium meliloti and characterization of genes involved in salt tolerance. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:278–283
Zahran HH (1999) Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and nitrogen fixation under severe conditions and in an arid climate. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:968–989
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants AECI 173/03/P and AECI A/6935/06 from Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional to JS and BB and grants BIO2005-08089-C02-01 (Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia, Spain) and BIO2008-02447 (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación) to JS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moussaid, S., Nogales, J., Muñoz, S. et al. Isolation of salt-tolerant mutants of Mesorhizobium ciceri strain Rch125 and identification of genes involved in salt sensitivity. Symbiosis 67, 69–77 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-015-0357-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-015-0357-8