Abstract
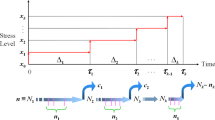
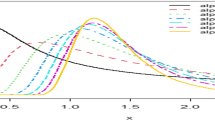
A life testing of manufactured units is performed in order to speed up testing through either reducing the time required for testing or establishing a predefined number of failures to stop the test. In this paper, we develop a testing cost model for Weibull distribution life time units embedded with its unknown parameter estimators with respect to Type-II censoring life test. In other words, the life test starts with n units and is terminated at a pre-assigned number of failures r. We then determine the optimum sample size on test which minimizes the expected total cost of performing the life testing subject to the unknown parameters of the Weibull distribution lifetime for a fixed number of failures equal to 2. Several numerical examples based on real failure data applications are presented to illustrate the proposed optimal cost design model.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodson B (2006) The Weibull analysis handbook, 2nd edn. ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee
Ehrlich W, Prasanna B, Stampfel J, Wu J (1993) Determining the cost of a stop-test decision. IEEE Softw 10(2):33–42
Klein JP, Moeschberger ML (2003) Survival analysis: techniques for censored and truncated data, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Nga HKT, Luoa L, Hua Y, Duan F (2012) Parameter estimation of three-parameter Weibull distribution based on progressively Type-II censored samples. J Stat Comput Simul 82(11):1661–1678
Pham H (1992) Optimal design of life testing for ULSI circuit manufacturing. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 5(1):68–70
Pham H (2006) Springer handbook of engineering statistics. Springer, London
Pham H (2014) Reliability: models, statistical methods, and applications. Rutgers University, Brunswick
Pham H, Zhang X (1999) A software cost model with warranty and risk costs. IEEE Trans Comput 48(1):71–75
Pham H, Wang H (2001) A quasi-renewal process for software reliability and testing costs. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 31(6):623–631
Teng X, Pham H (2004) A software cost model for quantifying the gain with considerations of random field environments. IEEE Trans Comput 53(3):380–384
You D, Pham H (2015) Reliability analysis of the CNC system based on field failure data in operating environments. Qual Reliab Eng Int. doi:10.1002/qre.1926
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordeiro, J.B., Pham, H. Optimal design of life testing cost model for Type-II censoring Weibull distribution lifetime units with respect to unknown parameters. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8, 28–32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0511-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0511-6