Abstract
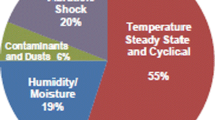
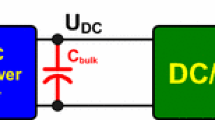
This paper presents a very simple and cheap off-line technique that is able to evaluate the aluminum electrolytic capacitors condition. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors equivalent circuit is composed by an internal resistance and a capacitance. The capacitors internal resistance increases with aging while the capacitance decreases. Manufacturers define the end of life limit of the capacitor when its internal resistance doubles its initial value or the capacitance changes more than 20% when it is compared with the initial one. The proposed technique evaluates the capacitor condition through the identification of both capacitor internal resistance and capacitance. To compute both capacitor internal resistance and capacitance a very simple, cheap, and practical experimental setup is proposed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Application notes–TD003, BHC Components, Evox Rifa Group
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Technical guide, TGAr-7, Panasonic, Matsushita Electronic Components
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors: general technical information. Epcos, January, 2008
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors: precautions and guidelines, CAT. No. E1001H, Nippon Chemi-con, pp. 3–10
Amaral A, Cardoso A (2008a) An economic offline technique for estimating the equivalent circuit of aluminum electrolytic capacitors. IEEE Trans Inst Meas 57(12):2697–2710
Amaral A and Cardoso A (2008) An automatic technique to obtain the equivalent circuit of aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Proceedings of the 34th annual conference of IEEE Industrial electronics, Orlando, Florida, USA, 10–13 November, 2008, pp. 539–544
Amaral A, Cardoso A (2009a) A simple off-line technique for evaluating the condition of aluminum-electrolytic-capacitors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56(8):3230–3237
Amaral A, Cardoso A (2009) Using a simple charge-discharge circuit to estimate capacitors equivalent circuit at their operating conditions. Proceedings of the IEEE International instrumentation and measurement technology conference, Singapore, 5–7 May 2009, pp. 737–742
Application guide, Aluminum electrolytic capacitors, Cornell Dubilier, pp. 2.183–2.202
Dai L, Lin F, Zhu Z, Li J (2005) Electrical characteristics of high energy density multilayer ceramic capacitor for pulse power application. IEEE Trans Magn 41(1):281–284
Efford T, Shibata Y, Ando S and Kanezaki A (1997) Development of aluminum electrolytic capacitors for EV inverter applications. Proceedings of the 32th IEEE industry applications society, annual meeting, New Orleans, Louisiana, 5–7 October 1997, pp. 1035–1041
Fodor D, Klug O, Balint I, Horvath A and Riz A (2006) Electrolyte measurements automation for capacitor research and development. Proceedings of the 12th power electronics and motion control conference (EPE-PEMC 2006), Portoroz, Slovenia, 30 August–1 September, 2006, pp. 1277–1282
Gasperi M (2005) Life prediction model of bus capacitors in AC variable-frequency drives. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 41(6):1430–1435
Harada K, Katsuki A, Fujiwara M (1993) Use of ESR for deterioration diagnosis of electrolytic capacitor. IEEE Trans Power Electron 8(4):355–361
Lahyani A, Venet P, Grellet G, Viverge P (1998) Failure prediction of electrolytic capacitors during operation of switchmode power supply. IEEE Trans Power Electron 13(6):1199–1207
Parler S (2003) Improved spice models of aluminum electrolytic capacitors for inverter applications. IEEE Transactions on industry applications, vol. 39, 4 July/August 2003, pp. 929–935
Poole R (1981) Aluminum electrolytic capacitors: an alternative to tantalum electrolytic capacitors? IEEE Trans Consum Electron CE-27(3):424–432
Sarjeant W, Zirnheld J, MacDougall F (1998) Capacitors. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 26(5):1368–1392
Tsai M, Lu Y, Do J (2002) High-performance electrolyte in the presence of dextrose and its derivatives for aluminum electrolytic capacitors. J Power Sources 112:643–648
Venet P, Perisse F, Husseini M, Rojat G (2002) Realization of a smart electrolytic capacitor circuit. IEEE Ind Appl Mag 8:16–20
Will N and Fischer E (2000) New electrolytic capacitors with low inductance simplify inverter. Proceedings of the IEEE industry applications conference, Rome, Italy, 2000, vol. 5, pp. 3059–3062
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Professor Beatriz Borges and Eng. Hugo Ribeiro for providing the Impedance Gain-Phase analyzer for the experimental tests. This work was supported in part by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) under Project No: SFRH/BD/37093/2007 and Project No: SFRH/BSAB/950/2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amaral, A.M.R., Marques Cardoso, A.J. Condition monitoring of electrolytic capacitors. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 2, 325–332 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-012-0085-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-012-0085-x