Abstract
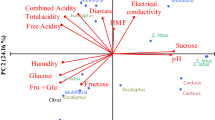
The aim of this work was to evaluate the quality of 16 honey samples from Castelo Branco region (Portugal). Twelve are monofloral from Calluna vulgaris, Erica, Lavandula, Echium and Campanula. The mean values obtained for physicochemical parameters were: 3.82 pH; 16.80% moisture; 81.6°Brix; 0.21% ash; 357.6 μS cm−1 electrical conductivity; 33.7 meq/kg free acidity; 5.7 meq/kg lactonic acidity; 39.3 meq/kg total acidity; 9.11 mg/kg HMF; 21.3 IN invertase and 9.0° Gothe for diastase activities. The results indicate a good quality, adequate processing, good maturity and freshness of honey. Additionally, the determination of mineral contents revealed that the K was the major element. Mean values obtained were (mg/kg): Ca, 28.36; K, 701.87; Mg, 74.00; Na, 31.04; Fe, 097; Cu, 0.65; Zn, 1.23; Mn, 2.78 and P, 48.80. Among the overall determined parameters, CB2 stands out by its high values in minerals, pH, moisture, ash, electrical conductivity and enzyme activity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mamary M, Al-Meeri A, Al-Habori M (2002) Antioxidant activities and total phenolics of different types of honey. Nutr Res 22(9):1041–1047
Alves A, Ramos A, Gonçalves MM, Bernardo M, Mendes B (2013) Antioxidant activity, quality parameters and mineral content of Portuguese monofloral honeys. J Food Compost Anal 30(2):130–138
Andrade PB, Amaral MT, Isabel P, Carvalho JCMF, Seabra RM, Proença da Cunha A (1999) Physicochemical attributes and pollen spectrum of Portuguese heather honeys. Food Chem 66(4):503–510
Anklam E (1998) A review of the analytical methods to determine the geographical and botanical origin of honey. Food Chem 63(4):549–562
Babarinde GA, Babarinde SA, Adegbola DO, Ajayeoba SI (2011) Effects of harvesting methods on physicochemical and microbial qualities of honey. J Food Sci Technol 48(5):628–634
Bath PK, Singh N (1999) A comparison between Helianthus annuus and Eucalytus lanceolatus honey. Food Chem 67:389–397
Bettar I, González-Miret ML, Hernanz D, Marconi A, Heredia FJ, Terrab A (2015) Characterisation of Moroccan Spurge (Euphorbia) honeys by their physicochemical characteristics, mineral contents and colour. Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.01.003
Bogdanov S (2007) Authenticity of honey and other bee products: state of the art. Bull USAMV-CN 63–64
Bogdanov S, Martin P, Lüllman C (1997) Harmonised method of the European Honey Commission. In: Apidologie, Elsevier, Paris, pp 1–59. http://www.apis.admin.ch/host/doc/pdfhoney/IHCmethods_e.pdf
Bogdanov S, Ruoff K, Oddo LP (2004) Physico-chemical methods for the characterisation of unifloral honeys: a review. Apidologie 35(Suppl. 1):S4–S17
Castro-Vázquez L, Leon-Ruiz V, Alañon ME, Pérez-Coello MS, González-Porto AV (2014) Floral origin markers for authenticating Lavandin honey (Lavandula angustifolia × latifolia). Discrimination from Lavender honey (Lavandula latifolia). Food Control 37:362–370
Conti ME (2000) Lazio region (central Italy) honeys: a survey of mineral content and typical quality parameters. Food Control 11(6):459–463
Costa LSM, Albuquerque MLS, Trugo LC, Quinteiro LMC, Barth OM, Ribeiro M, De Maria CAB (1999) Determination of non-volatile compounds of different botanical origin Brazilian honeys. Food Chem 65(3):347–352
Decreto-lei N° 214 (2003) Portuguese Legislation. 18 September 2003
Downey G, Hussey K, Daniel Kelly J, Walshe TF, Martin PG (2005) Preliminary contribution to the characterisation of artisanal honey produced on the island of Ireland by palynological and physico-chemical data. Food Chem 91(2):347–354
Echigo T, Takenaka T (1974) Production of organic acids in honey by honeybees. Nippon Nōgeikagaku Kaishi 48(4):225–230
Escuredo O, Silva LR, Valentão P, Seijo MC, Andrade PB (2012) Assessing Rubus honey value: pollen and phenolic compounds content and antibacterial capacity. Food Chem 130(3):671–678
Estevinho LM, Feás X, Seijas JA, Pilar Vázquez-Tato M (2012) Organic honey from Trás-Os-Montes region (Portugal): chemical, palynological, microbiological and bioactive compounds characterization. Food Chem Toxicol 50(2):258–264
European Community (2002) EEC Council directive of 20 December 2001 relating to honey. Off J Eur Commun 12:47–52
Flores MSR, Escuredo O, Carmen Seijo M (2015) Assessment of physicochemical and antioxidant characteristics of Quercus pyrenaica honeydew honeys. Food Chem 166:101–106
Hernández OM, Fraga JMG, Jiménez AI, Jiménez F, Arias JJ (2005) Characterization of honey from the Canary Islands: determination of the mineral content by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Food Chem 93(3):449–458
Louveaux J, Maurizio A, Vorwohl G (1978) Methods of melissopalynology. Bee World 59(4):139–157
Mendes E, Brojo Proença E, Ferreira IMPLVO, Ferreira MA (1998) Quality evaluation of Portuguese honey. Carbohydr Polym 37(3):219–223
Mnatzaganian G, Galai N, Sprung CL, Zitser-Gurevich Y, Mandel M, Ben-Hur D, Gurman G, Klein M, Lev A, LeviL Bar-Lavi Y, Zveibil F, Simchen E (2005) Increased risk of bloodstream and urinary infections in intensive care unit (ICU) patients compared with patients fitting ICU admission criteria treated in regular wards. J Hosp Infect 59(4):331–342
Moita E, Gil-Izquierdo A, Sousa C, Ferreres F, Silva LR, Valentão P, Domínguez-Perles R, Baenas N, Andrade PB (2013) Integrated analysis of COX-2 and iNOS derived inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW macrophages pre-exposed to Echium plantagineum L. bee pollen extract. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59131
Nanda V, Sarkar BC, Sharma HK, Bawa AS (2003) Physico-chemical properties and estimation of mineral content in honey produced from different plants in Northern India. J Food Compost Anal 16(5):613–619
Ojeda de Rodríguez G, Sulbarán de Ferrer B, Ferrer A, Rodríguez B (2004) Characterization of honey produced in Venezuela. Food Chem 84(4):499–502
Pohl P (2009) Determination of metal content in honey by atomic absorption and emission spectrometries. Trends Analyt Chem 28(1):117–128
Siegenthaler U (1977) Eine einfache und rasche Methode zurBestimmung der alpha-Glucosidase (Saccharase) im Homig, Mitt. Gebiete Lebensm Hyg 68:251–258
Silva LR, Videira R, Monteiro AP, Valentão P, Andrade PB (2009) Honey from Luso region (Portugal): physicochemical characteristics and mineral contents. Microchem J 93(1):73–77
Silva JC, Rodrigues S, Feás X, Estevinho LM (2012) Antimicrobial activity, phenolic profile and role in the inflammation of propolis. Food Chem Toxicol 50(5):1790–1795
Singh N, Bath PK (1997) Quality evaluation of different types of Indian honey. Food Chem 58(1–2):129–133
Terrab A, Díez MJ, Heredia FJ (2002) Characterisation of Moroccan unifloral honeys by their physicochemical characteristics. Food Chem 79(3):373–379
Terrab A, Díez MJ, Heredia FJ (2003) Palynological, physico-chemical and colour characterization of Moroccan honeys. II. Orange (Citrus sp.) honey. Int J Food Sci Technol 38(4):387–394
Terrab A, Recamales AF, Hernanz D, Heredia FJ (2004) Characterisation of Spanish thyme honeys by their physicochemical characteristics and mineral contents. Food Chem 88(4):537–542
Tuzen M, Silici S, Mendil D, Soylak M (2007) Trace element levels in honeys from different regions of Turkey. Food Chem 103(2):325–330
White JW Jr (1978) Honey. Adv Food Res 24:287–374
White JW Jr. (1979) Honey: a comprehensive survey. In: Crane E (ed) Composition of honey. Heinemann, London, pp 157–158
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by FEDER funds through the POCI—COMPETE 2020—Operational Programme Competitiveness and Internationalisation in Axis I—Strengthening research, technological development and innovation (Project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007491) and National Funds by FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology (Project UID/Multi/00709/2013). Luís R. Silva (SFRH/BPD/105263/2014) was supported by post doc grants from FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, L.R., Sousa, A. & Taveira, M. Characterization of Portuguese honey from Castelo Branco region according to their pollen spectrum, physicochemical characteristics and mineral contents. J Food Sci Technol 54, 2551–2561 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2700-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2700-y