Abstract
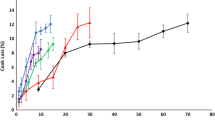
Changes in protein stability in relation to ice crystals development in salmon fillets during superchilled storage were studied. Due to the significant differences in ice crystal sizes observed in our previous studies, the protein solubility was analysed separately, at the surfaces and centres of the superchilled samples. The water-soluble proteins were stable for the entire storage time. The salt-soluble proteins in the superchilled samples were stable for 1 week of storage. The salt-soluble proteins were significantly decreased at day 7 and 14 of the centre and surface of the superchilled samples, respectively. In contrast, the salt-soluble proteins were significantly increased at day 21 both at the centre and surface of the superchilled samples. These findings are significant for the industry because it provides valuable information on the quality of food in relation to ice crystallization/recrystallization during superchilled storage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh E, Chapleau N, de Lamballerie M, Le Bail A (2007) Effect of different freezing processes on the microstructure of Atlantic salmon (Salmon salar) fillets. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 8:493–499. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2006.12.003
Ando M, Nakamura H, Harada R, Yamane A (2004) Effect of super chilling storage on maintenance of freshness of Kuruma Prawn. J Food Sci Technol Res 10:25–31. doi:10.3136/fstr.10.25
Bahuaud D, Mørkøre T, Langsrud Ø, Sinnes K, Veiseth E, Ofstad R, Thomasse MS (2008) Effects of −1.5 oC superchilling on quality of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) pre-rigor fillets: Cathepsin activity, muscle histology, texture and liquid leakage. Food Chem 111:329–339. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.03.075
Bao HND, Arason S, Thórarinsdóttir KA (2007) Effects of dry ice and superchilling on quality and shelf life of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) fillets. Int J Food Eng 3:1–27. doi:10.2202/1556-3758.1093
Beaufort A, Cardinal M, Le-Bail A, Midelet-Bourdin G (2009) The effects of superchilled storage at −2 oC on the microbiological and organoleptic properties of cold-smoked salmon before retail display. Int J Refrig 32(7):1850–1857. doi:10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2009.07.001
Benjakul S, Visessanguan W (2010) Impacts of freezing and frozen storage on quality changes of seafoods. In: Devahastin S (ed) Physicochemical aspects of food engineering and processing. CRC press, New York, pp 283–306
Blond G, Meste ML (2004) Principes of frozen storage. In: Murell KD, Hui YH, Nip W-K, Lim MH, Lugarreta IG, Cornillon P (eds) Handbook of frozen foods. CRCMarcel Dekker, Inc, United State of America. doi:10.1201/9780203022009.ch3
Chevalier D, Sequeira-Munoz A, Bail AL, Simpson BK, Ghoul M (2001) Effect of freezing conditions and storage on ice crystal and drip volume in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Evaluation of pressure shift freezing vs. air-blast freezing. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 1:193–201. doi:10.1016/S1466-8564(00)00024-2
Duun AS (2008) Superchilling of muscle food storage stability and quality aspects of salmon (Salmo salar), cod (Gadus morhua) and pork. Doctoral theses. Trondheim: Dep. Biotechnology, NTNU. http://ntnu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:124388/FULLTEXT01.pdf. Retrieved on 01.11.14
Duun AS, Rustad T (2007) Quality changes during superchilled storage of cod (Gadus morhua) fillets. Food Chem 105(3):1067–1107. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.05.020
Duun AS, Rustad T (2008) Quality of superchilled vacuum packed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets stored at −1.4 and −3.6 °C. Food Chem 106(1):122–131. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.05.051
Einarsson H (1988) Deep chilling (superchilling, partial freezing) – a literature survey. SIKs Service series (30) Goteborg, Sweden, SIK – The Swedish food Institute, Chalmers University of Technology
Erikson U, Misimi EL, Gallart-Jornet E (2011) Superchilling of rested Atlantic salmon: different chilling strategies and effects on fish and fillet quality. Food Chem 127:1427–1437. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.036
Gallart-Jornet L, Rustad T, Barat JM, Fito P, Escriche I (2007) Effect of superchilled storage on the freshness and salting behavior of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets. Food Chem 103:1268–1281. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.040
Hagiwara T, Wang H, Suzuki T, Takai R (2002) Fractal analysis of ice crystals in frozen food. J Agric Food Chem 50:3085–3089. doi:10.1021/jf011240g
Hultmann L, Rustad T (2002) Textural changes during iced storage of salmon (Salmo salar) and cod (Gadus morhua). J Aquat Food Prod Technol 11(3/4):105–123. doi:10.1300/J030v11n03_09
Jaczynski J, Tahergorabi R, Hunt AL, Park JW (2012) Safety and quality of frozen aquatic food products. In: Sun D-W (ed) Handbook of frozen food processing, 2nd edn. CRC press, Taylor & Francis group
Jiang ST, Lee TC (1985) Changes in free amino acids and protein denaturation of fish muscle during frozen storage. J Agric Food Chem 33:839–844. doi:10.1021/jf00065a018
Kaale LD (2014) Modelling and ice crystallization/recrystallization of foods in superchilling technology. Superchilling of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). PhD thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Norway
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM (2014) The development of ice crystals in food products during the superchilling process and following storage, a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 39(2):91–103. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2014.07.004
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM, Rustad T, Kolsaker K (2011) Superchilling of food, a review. J Food Eng 107(2):141–146. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.06.004
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM, Bardal T, Kjorsvik E (2013a) A study of the ice crystals in vacuum-packed salmon fillets (Salmon salar) during superchilling process and following storage. J Food Eng 115:20–25. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.09.014
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM, Bardal T, Kjorsvik E, Nordtvedt TS (2013b) The effect of cooling rates on the ice crystal growth in air-packed salmon fillets during superchilling and superchilled storage. Int J Refrig 36:110–119. doi:10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2012.09.006
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM, Kolsaker K, Stevik AM (2013c) Modelling and simulation of food products in superchilling technology. J Aquat Food Prod Technol 23:409–420. doi:10.1080/10498850.2012.721160
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM, Rustad T, Nordtvedt TS, Bardal T, Kjørsvik E (2013d) Ice crystal development in pre-rigor Atlantic salmon fillets during superchilling process and following storage. Food Control 31(2):491–498. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.11.047
Kaale LD, Eikevik TM, Rustad T, Nordtvedt TS (2014) Changes in water holding capacity and drip loss of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) muscle during superchilled storage. LWT - Food Sci Technol 55(2):528–535. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.021
Kiani H, Sun D-W (2011) Water crystallization and its importance to freezing of foods: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 22:407–426. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2011.04.011
Martino MN, Zaritzky NE (1988) Ice crystal size modifications during frozen beef storage. J Food Sci 53(6):1631–1637. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1988.tb07802.x
Martino MN, Otero L, Sanz PD, Zaritzky NE (1998) Size and location of ice crystals in pork frozen by high-pressure-assisted freezing as compared to classical methods. Meat Sci 50:303–313. doi:10.1016/S0309-1740(98)00038-2
Mittal GS, Griffiths MW (2005) Pulsed electric field processing of liquid foods and beverage. In: Sun D-W (ed), Emerging technologies for food processing. Food science and technology, international series, Elsevier Ltd
Ocano-Higuera VM, Marquez-Rios E, Canizales-Davila M, Castillo-Yanez FJ, Pacheco-Aguilar R, Lugo-Sanchez ME, Garcia-Orozco KD, Graciano-Verdugo AZ (2009) Postmortem changes in cazon fish muscle stored on ice. Food Chem 116:933–938. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.03.049
Petzold G, Aguilera JM (2009) Ice morphology: fundamentals and technological applications in foods. Food Biophys 4:378–396. doi:10.1007/s11483-009-9136-5
Shenouda YKS (1980) Theories of protein denaturation during frozen storage of fish flesh. Adv Food Res 26:275–311
Smith PG (2011) Introduction to food process engineering, 2nd edn. Food Science Text Series (chapter 11), United Kingdom. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7662-8
Sotelo CG, Aubourg SP, Perez-Martin RI, Gallardo JM (1994) Protein denaturation in frozen stored hake (Merluccius merluccius L.) muscle: the role of formaldehyde. Food Chem 50:267–275. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(94)90131-7
Tejada M (2001) Aggregation of myofibrillar proteins during frozen storage of fish. In: Bozoglu F, Deak T and Ray B (eds) Novel processes and control technologies in the food industry. NATO science series
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Research Council of Norway (RCN project number 178280) for its financial support. We also acknowledged the NTNU SeaLab for giving access in their laboratory for the tissue processing and microscopic analysis experiments and Department of Biotechnology at Norwegian University of Science and Technology for analyzing water and salt-soluble proteins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• Water and salt protein solubility during superchilled storage were analysed
• The development of ice crystals and protein solubility were studied
• The water-soluble proteins were stable for the whole storage time
• Salt-soluble proteins were stable for 1 week of storage
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaale, L.D., Eikevik, T.M. Changes of proteins during superchilled storage of Atlantic salmon muscle (Salmo salar). J Food Sci Technol 53, 441–450 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1979-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1979-9