Abstract
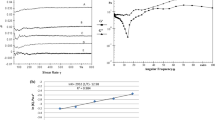
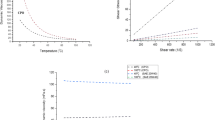
The aim of this research was to determine the changes in the physicochemical properties of palm oil and its blends by FTIR and rheological measurements. Application of heat produces some chemical compounds as impurities and even toxic compounds in oils and fats that give absorbance at different region. FTIR spectra of pure palm olein shows an absorbance at 3002 cm−1 whereas other pure oils show maximum absorption at around 3007 cm−1 due to C-H stretching vibration of cis-double bond (=C-H). By blending of high unsaturated oils with palm olein, a clear shift of 3007 cm−1 band to 3005 cm−1 occurs. Viscosity of palm olein was found higher among all oils while it subsequently and substantially reduced by blending with other oils. Since it is a function of temperature, viscosity of pure oils and their blends decreases with the increase of temperature. The loss modulus (G′′), for all oil blends before and after frying, in rheological experiment was found higher for all oils than the storage modulus (G′), therefore, the viscous property was found higher than elastic property of oils and blends. However, the critical stress for all oil blends was found higher than that of pure oils.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belitz H-D, Grosch W, Schieberle P (2009) Edible fats and oils. Food Chem Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 640–669
Bendini A, Cerretani L, Di Virgilio F, Belloni P, Bonoli-Carbognin M, Lercker G (2007) Preliminary evaluation of the application of the ftir spectroscopy to control the geographic origin and quality of virgin olive oils. J Food Quality 30:424–437
Chugh B, Dhawan K (2011) Storage studies on mustard oil blends. J Food Sci Tech. doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0540-8
Diáz Gamboa OW, Gioielli LA (2003) Consistencia de lipídios estruturados a partir de aceite de pescado y grasa de palmiste. Grasas y Aceites 54:122–129
Enríquez- Fernández BE, Álvarez De La Cadena Y, Yañez L, Sosa-morales ME (2011) Comparison of the stability of palm olein and a palm olein/canola oil blend during deep-fat frying of chicken nuggets and French fries. Int J Food Sci Tech 46:1231–1237
Ferry JD (1970) Viscoelastic properties of polymers. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York, 217
Frankel EN (1998) Lipid oxidation. The Oily Press, Dundee
Geller D, Goodrum J (2000) Rheology of vegetable oil analogs and triglycerides. J Am Oil Chem' Soc 77:111–114
Gloria H, Aguilera JM (1998) Assessment of the quality of heated oils by differential scanning calorimetry. J Agri Food Chem 46:1363–1368
Go'mez-Alonso S, Fregapane G, Salvador MD, Gordon MH (2003) Changes in phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of virgin olive oil during frying. J Agri Food Chem 51:667–672
Graef VD, Goderis B, Puyvelde PV, Foubert I, Dewettinck K (2008) Development of a rheological method to characterize palm oil crystallizing under shear. Eur J Lipid Sci and Tech 110:521–529
Guillén MD, Cabo N (2002) Fourier transform infrared spectra data versus peroxide and anisidine values to determine oxidative stability of edible oils. Food Chem 77:503–510
Guillén MD, Cabo N (2000) Some of the most significant changes in the Fourier transform infrared spectra of edible oils under oxidative conditions. J Sci Food Agri 80:2028–2036
Guillén MD, Cabo N (1997) Characterization of edible oils and lard by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Relationships between composition and frequency of concrete bands in the fingerprint region. J Am Oil Chem Soc 74:1281–1286
Guillén MD, Cabo N (1999) Usefullness of the frequency data of the Fourier transform infrared spectra to evaluate the degree of oxidation of edible oils. J Agri Food Chem 47:709–719
Kim J, Kim DN, Lee SH, Yoo SH, Lee S (2010) Correlation of fatty acid composition of vegetable oils with rheological behaviour and oil uptake. Food Chem 118:398–402
Kritchevsky D (2008) Fats and Oils in Human Health. In: Casimir CC, Min DB (eds) Food lipids Chemistry, nutrition, and biotechnology, 3rd edn. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, Boca Raton
Lioumbas JS, Ampatzidis C, Karapantsios TD (2012) Effect of potato deep-fat frying conditions on temperature dependence of olive oil and palm oil viscosity. J Food Eng 113(2):217–225
Marco ED, Savaresea M et al (2007) Frying performance of a sunflower/palm oil blend in comparison with pure palm oil. Eur J Lipid Sci Tech 109:237–246
Márquez-Ruiz G, Dobarganes C (1996) Short-chain fatty acids formation during thermoxidation and frying. J Sci Food Agri 70:120–126
Mishra R, Sharma HK (2011) Effect of frying conditions on the physico-chemical properties of rice bran Oil and its belnded oils. J Food Sci Tech. doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0602-y
Rao MA (2007) Rheology of fluid and semisolid foods principles and applications, . Springer Science + Business Media, LLC, New York
Rohman A, Man YBC (2010) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy for analysis of extra virgin olive oil adulterated with palm oil. Food Res Int 43:886–892
Safar M, Bertrand D, Robert P, Devaux M, Genot C (1994) Characterization of edible oils, butters and margarines by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy with attenuated total reflectance. J Am Oil Chem’ Soc 71:371–377
Sanahuja AB, Moya MSP, Perez SEM, Teruel NG, Carratala ML (2009) Classification of four almond cultivars asing oil degradation parameters based on FTIR and GC data. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86:51–58
Santos JCO, Santos IMG, Souza AG (2005) Effect of heating and cooling on rheological parameters of edible vegetable oils. J Food Eng 67:401–405
Siddique BM, Ahmad A, Alkarkhi AFM, Ibrahim MH, Omar AKM (2011) Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of candlenut Oil extracted by supercritical CO2. J Food Sci 76(4):C535–C542
Siddique BM, Ahmad A, Ibrahim MH, Hena S, Rafatullah M, Mohd Omar AK (2010) Physico-chemical properties of blends of palm olein with other vegetable oils. Grasas y Aceites 61:423–429
Stevenson SG, Vaisey-Genser M, Eskin NAM (1984) Quality control in the use of deep frying oils. J Am Oil Che Soc 61:1102–1108
Tena N, Aparicio R, Garci'a-Gonza'lez DL (2009) Thermal deterioration of virgin olive oil monitored by ATR-FTIR analysis of trans content. J Agri Food Chem 57:9997–10003
Vaclavik VA, Christian EW (2003) Fat and Oil Products. In: Heldman DR (ed) Essentials of Food Science. Springer Science + Business Media, LLC, New York
Vlachos N, Skopelitis Y, Psaroudaki M, Konstantinidou V, Chatzilazarou A, Tegou E (2006) Application of Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy to edible oils. Anal Chim Acta 573–574:459–465
Wan Nik WB, Ani FN, Masjuki HH, Eng Giap SG (2005) Rheology of bioedible oils according to several rheological models and its potential as hydraulic fluid. Ind Crops Prod 22:249–255
Wang T, Briggs J (2002) Rheological and thermal properties of soybean oils with modified FA compositions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 79(8):831–836
Yalchin H, Toker OS, Dogan M (2012) Effect of Oil type and fatty acid composition on dynamic and steady shear rheology of vegetable oils. J Oleo Sci 61(4):181–187
Yang H, Irudayaraj J, Paradkar MM (2005) Discriminant analysis of edible oils and fats by FTIR, FT-NIR and FT-Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem 93:25–32
Acknowledgement
We gratefully acknowledge the research facilities provided by the School of Industrial Technology as well as the financial assistance provided by the Universiti Sains Malaysia. The first author thanks to Mr. Jubaer Ahmed (faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia) for his invaluable help and discussion on statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddique, B.M., Muhamad, I.I., Ahmad, A. et al. Effect of frying on the rheological and chemical properties of palm oil and its blends. J Food Sci Technol 52, 1444–1452 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1124-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1124-6