Abstract
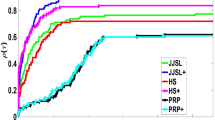
The restarted GMRES (REGMRES) is one of the well used Krylov subspace methods for solving linear systems. However, the price to pay for the restart usually is slower speed of convergence. In this paper, we draw inspirations from the locally optimal CG and the heavy ball methods in optimization to propose two variants of the restarted GMRES that can overcome the slow convergence. Compared to various existing hybrid GMRES which are also designed to speed up REGMRES and which usually require eigen-region estimations, our variants preserve the appealing feature of GMRES and REGMRES—their simplicity. Numerical tests on real data are presented to demonstrate the superiority of the new methods over REGMRES and its variants.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A (square or rectangular) matrix X is upper-Hessenberg if \(X_{(i,j)}=0\) for all \(i>j+1\).
For the non-generic case, GMRES—Algorithm 1 will yield the exact solution.
References
Bai, Z., Li, R.-C.: Minimization principle for linear response eigenvalue problem, I: theory. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 33(4), 1075–1100 (2012)
Bai, Z., Li, R.-C.: Minimization principles for the linear response eigenvalue problem II: computation. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 34(2), 392–416 (2013)
Bai, Z., Li, R.-C.: Minimization principles and computation for the generalized linear response eigenvalue problem. BIT Numer. Math. 54(1), 31–54 (2014)
Davis, T., Hu, Y.: The University of Florida sparse matrix collection. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 38(1), 1:1–1:25 (2011)
Driscoll, Tobin A., Toh, Kim-Chuan, Trefethen, Lloyd N.: From potential theory to matrix iterations in six steps. SIAM Rev. 40(3), 547–578 (1998)
Elman, H.C.: Iterative methods for large, sparse nonsymmetric systems of linear equations. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Computer Science, Yale University (1982)
Elman, H.C., Saad, Y., Saylor, P.E.: A hybrid Chebyshev Krylov subspace algorithm for solving nonsymmetric systems of linear equations. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 7(3), 840–855 (1986)
Elman, H.C., Streit, R.L.: Polynomial iteration for nonsymmetric indefinite linear systems. In: Hennart, J.-P. (ed.) Numerical Analysis. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 1230, pp. 103–117. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (1986)
Ernst, Oliver G.: Residual-minimizing Krylov subspace methods for stabilized discretizations of convection–diffusion equations. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 21(4), 1079–1101 (2000)
Golub, G., Ye, Q.: An inverse free preconditioned Krylov subspace methods for symmetric eigenvalue problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 24, 312–334 (2002)
Greenbaum, A.: Iterative Methods for Solving Linear Systems. SIAM, Philadelphia (1997)
Imakura, A., Li, R.-C., Zhang, S.-L.: Locally optimal and heavy ball GMRES methods. Technical Report 2015-02, Department of Mathematics, University of Texas at Arlington. http://www.uta.edu/math/preprint/. Accessed Jan 2015
Knyazev, A.V.: Toward the optimal preconditioned eigensolver: locally optimal block preconditioned conjugate gradient method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 23(2), 517–541 (2001)
Li, R.-C.: Rayleigh quotient based optimization methods for eigenvalue problems. In: Bai, Z., Gao, W., Su, Y (eds.) Matrix Functions and Matrix Equations, Series in Contemporary Applied Mathematics, vol. 19. Lecture summary for 2013 Gene Golub SIAM Summer School, 22 July to 2 August 2013, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. World Scientific, Singapore (2015)
Li, R.-C., Zhang, W.: The rate of convergence of GMRES on a tridiagonal Toeplitz linear system. Numer. Math. 112, 267–293 (2009). (published online 19 December 2008)
Liang, X., Li, R.-C.: The hyperbolic quadratic eigenvalue problem. Technical Report 2014-01, Department of Mathematics, University of Texas at Arlington. http://www.uta.edu/math/preprint/. Accessed Jan 2014
Liesen, J., Strakoš, Z.: Convergence of GMRES for tridiagonal Toeplitz matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 26(1), 233–251 (2004)
Liesen, J., Strakoš, Z.: Krylov Subspace Methods: Principles and Analysis. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2013)
Manteuffel, T.A.: Adaptive procedure for estimating parameters for the nonsymmetric Tchebychev iteration. Numer. Math. 31(2), 183–208 (1978)
Money, J., Ye, Q.: EIGIFP: a MATLAB program for solving large symmetric generalized eigenvalue problems. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 31, 270–279 (2005)
Morgan, R.: A restarted GMRES method augmented with eigenvectors. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 16(4), 1154–1171 (1995)
Morgan, R.: GMRES with deflated restarting. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 24(1), 20–37 (2002)
Nachtigal, N.M., Reichel, L., Trefethen, L.N.: A hybrid GMRES algorithm for nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 13(3), 796–825 (1992)
Polyak, B.T.: Introduction to Optimization. Optimization Software, New York (1987)
Quillen, P., Ye, Qiang: A block inverse-free preconditioned Krylov subspace method for symmetric generalized eigenvalue problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 233(5), 1298–1313 (2010)
Saad, Y.: Least squares polynomials in the complex plane and their use for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 24(1), 155–169 (1987)
Saad, Y.: Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. PWS Publishing Company, Boston (1996)
Saad, Y.: Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems, 2nd edn. SIAM, Philadelphia (2003)
Saad, Y., Schultz, M.: GMRES: a generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 7, 856–869 (1986)
Smolarski, D.C., Saylor, P.E.: An optimum iterative method for solving any linear system with a square matrix. BIT 28(1), 163–178 (1988)
Takahashi, I.: A note on the conjugate gradient method. Inform. Process. Jpn. 5, 45–49 (1965)
Yang, C., Meza, J.C., Lee, B., Wang, L.-W.: KSSOLV—a MATLAB toolbox for solving the Kohn–Sham equations. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 36(2), 1–35 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to an anonymous referee for useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by Strategic Programs for Innovative Research (SPIRE) Field 5 “The origin of matter and the universe”, JSPS Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Nos. 25870099, 25286097), MEXT Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 22104004), NSF grants DMS-1115834 and DMS-1317330, NSF CCF-1527104 a Research Gift Grant from Intel Corporation, and NSFC Grant 11428104.
About this article
Cite this article
Imakura, A., Li, RC. & Zhang, SL. Locally optimal and heavy ball GMRES methods. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 33, 471–499 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-016-0220-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-016-0220-1