Abstract
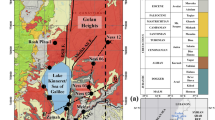
Drilling wells reveal that the organic matter abundance of Miocene marine source rocks in shallow water area of the Qiongdongnan Basin is relatively low with poor hydrocarbon generation potential. However, in some drilling wells of deep water area close to the central depression belt, Miocene marine source rocks with better organic matter abundance and hydrocarbon generation have been found, which have achieved better source rock standard based on the analysis of geochemical characteristics. Although there are no exploratory wells in deep water area of the research region, through the comparative analysis of geochemical data of several typical exploratory wells respectively from shallow water area in the basin, central depression belt margin in deep-water area of the basin and Site 1148 of deep sea drilling in the South China Sea Basin, it reveals that the tendency of the quality of source rocks becomes positive gradually from delta to bathyal environment, which then becomes negative as in deep oceanic environment. Owing to the lack of terrestrial organic matter input, the important controlling factors of Miocene marine source rocks in the Qiongdongnan Basin are ocean productivity and preservation conditions of organic matter. The element geochemistry data indicate that the tendency of the paleoproductivity and the preservation conditions of organic matter become positive as water depth increase from shallow area to bathyal area close to central depression belt. So it is speculated that there must exist high quality source rocks in the central depression area where the preservation conditions of organic matter are much better. Besides, in theory, in oxygen-poor zone of oceanic environment at the water depth 400–1 000 m, the preservation conditions of organic matter are well thus forming high-quality marine source rocks. The resulting speculation, it is reasonable to consider that there are high hydrocarbon generation potential source rocks in bathyal environment of the Qiongdongnan Basin, especially at the water depth 400–1 000 m.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelson J M, Helz G R, Miller C V. 2001. Reconstructing the rise of recent coastal anoxia: molybdenum in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(2): 237–252
Arnaboldi M, Meyers P A. 2007. Trace element indicators of increased primary production and decreased water-column ventilation during deposition of latest Pliocene sapropels at five locations across the Mediterranean Sea. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 249: 425–443
Bally A W, Watts A B, Grow J A, et al. 1981. Geology of Passive Continential Margins: History. Structure and Sedimentologic Record. Tulsa: Association of Petroleum Geologists. Education Course Note Series, 19: 1–48
Chaillou G, Anschutz P, Lavaux G, et al. 2002. The distribution of Mo, U, and Cd in relation to major redox species in muddy sediments of the Bay of Biscay. Marine Chemistry, 80: 41–59
Chen Weihuang, He Jiaxiong, Xia Bin. 2005. Review and proposal upon offshore gas exploration in Yingqiong basin. Natural Gas Geoscience (in Chinese), 16(4): 412–415
Demaison G J, Moore G T. 1980. Anoxic environments and oil source bed genesis: Bull. AAPG, 64(8): 1179–1209
Dong Weiliang, Huang Baojia. 2000. Identification marks and source discrimination of the coal type gas in Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basin of South China Sea. Natural Gas Industry (in Chinese), 20(1): 23–27
Fu Ning, Mi Lijun, Zhang Gongcheng. 2007. Source rocks and origin of oil and gas in the northern Baiyun Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica (in Chinese), 28(3): 32–38
Fu Ning, Yu Xiaoguo. 2000. Mixing characteristics of oil and gas in YA13-1 gas field. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 27(1): 19–22
Hao Fang, Jin Zhijun, Zou Huayao, et al. 2005. Kinetics of hydrocarbon generation and mechanisms of petroleum accumulation in overpressured basins (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press
He Jiaxiong, Xia Bin, Wang Zhixin, et al. 2006. Hydrocarbon accumulation and exploratory orientation in the western marginal basin of the northern South China Sea. Acta Petrolei Sinica (in Chinese), 27: 8–14
Hu Zhongliang. 2005. Study on Petroleum Generation Kinetics of Source Rocks and Gas Pool Formation in the Yanan Depression of the Qiongdongnan Basin [dissertation] (in Chinese). Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Science
Huang Baojia. 1999. Gas potential and its favorable exploration areas in Qiongdongnan basin. Natural Gas Industry (in Chinese), 19: 34–39
Huang Baojia, Huang Heting, Li Li, et al. 2010. Characteristics of marine source rocks and effect of high temperature and overpressure to organic matter maturation in Yingehai-Qiongdongnan basin. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology (in Chinese), 15: 11–18
Huang Baojia, Xiao Xianming, Dong Weiliang. 2002. Source rocks and generation & evolution model of natural gas in Yinggehai basin. Natural Gas Industry (in Chinese), 26–32
Jones B J, Manning A C. 1994. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclim atol Palaeoecol, 111: 111–129
Li Youchuan, Zhang Gongcheng, Fu Ning. 2010. A study on hydrocarbon generation characteristics in the deepwater region, the northern South China Sea. China Offshore Oil and Gas (in Chinese), 22: 375–381
Li Youchuan, Mi Lijun, Zhang Gongcheng, et al. 2011. The formation and distribution of Source for deep water area in the northern of South China Sea. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica (in Chinese), 29(5): 970–979
Lin Renzi, Jiang Jiping. 1983. Analysis of the development of steranes and terpenes. Journal of oil and Gas Technology (in Chinese), 20–35
Murray R W, Leinen M. 1996. Scavenged excess Al and its relationship to bulk Ti in biogenic sediment from the central equatorial Pacific Ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60: 3869–3878
Naimo D, Paola A, Imperato M, et al. 2005. Mineralogy and geochemistry of a marine sequence, Gulf of Salerno, Italy. Quaternary International, 140–141: 53–63
Pan Xianzhuang, Zhang Guohua, Huang Yiwen, et al. 2001. The mixed gas sources in Yacheng 13-1 Gas-field. China Offshore Oil and Gas (in Chinese), 15(2): 99–104
Palacas J G. 1984. Petroleum geochemistry and source rock potential of carbonate rocks. Tulsa, Oklahoma USA: AAPG, 191–221
Pedersen T F, Calvert S E. 1990. Anoxia vs. productivity: what controls the formation of organic-carbonrich sediments and sedimentary rocks. AAPG Bulletin, 74(4): 454–466
Piper D Z, Perkins R B. 2004. A modern vs. Permian black shale-the hydrography, primary productivity, and water-column chemistry of deposition. Chemical geology, 206: 177–197
Qin Jianzhong, Tenger, Fu Xiaodong. 2009. Study of forming condition on marine excellent source rocks and its evaluation. Petroleum Geology & Experiment (in Chinese), 31: 366–372, 378
Tenger, Liu Wenhui, Xu Yongchang, et al. 2005. Correlative study on parameters of inorganic geochemistry and hydrocarbon source rocks formative environment. Advance in Earth Science (in Chinese), 20: 193–200
Xiao Xianming, Xiong Min, Tian Hui, et al. 2006. Determination of the source area of the Ya13-1 gas pool in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Organic Geochemistry, 37: 990–1002
Zhu Junzhang, Shi Hesheng, Pang Xiong, et al. 2005. Natural gas origin and gas source studies of Panyu low uplift in the Pearl River Mouth Baisn. Natural Gas Geoscience (in Chinese), 16(4): 456–459
Zhu Junzhang, Shi Hesheng, He Min, et al. 2008. Origins and geochemical characteristics of gases in Well LW3-1-1 in the deep sea area of Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience (in Chinese), 19(2): 229–233
Zhu Weilin, Huang Baojia, Mi Lijun, et al. 2009. Geochemistry, origin, and deep-water exploration potential of natural gases in the Pearl River Mouth and Qiongdongnan basins, South China Sea. AAPG Bulletin, 93(6): 741–761
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Major State Basic Research Development Program (973 Program) under contract No. 2009CB219402.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Zhang, Z., Li, Y. et al. New perspective of Miocene marine hydrocarbon source rocks in deep-water area in Qiongdongnan Basin of northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 31, 107–114 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-012-0241-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-012-0241-9