Abstract
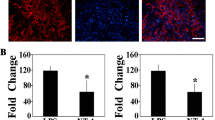
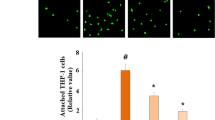
Neuroinflammation contributes to the pathophysiology of diverse diseases including stroke, traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, resulting in neurodegeneration and loss of neurological function. The response of the microvascular endothelium often contributes to neuroinflammation. One such response is the upregulation of endothelial adhesion molecules which facilitate neutrophil adhesion to the endothelium and their migration from blood to tissue. Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) is an endogenous growth factor which has been reported to have anti-inflammatory effects in experimental stroke models. We hypothesized that NRG1 would decrease the endothelial response to inflammation and result in a decrease in neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells. We tested this hypothesis in an in vitro model of cytokine-induced endothelial injury, in which human brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) were treated with IL-1β, along with co-incubation with vehicle or NRG1-β. Outcome measures included protein levels of endothelial ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin, as well as the number of neutrophils that adhere to the endothelial monolayer. Our data show that NRG1-β decreased the levels of VCAM-1, E-selectin, and neutrophil adhesion to brain microvascular endothelial cells activated by IL1-β. These findings open new possibilities for investigating NRG1 in neuroprotective strategies in brain injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular cell adhesion molecule
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1 beta
- NRG1-β:
-
Neuregulin 1-beta
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 or vascular cell adhesion protein-1
References
Brothers HM, Bardou I, Hopp SC, Marchalant Y, Kaercher RM, Turner SM, et al. Time-dependent compensatory responses to chronic neuroinflammation in hippocampus and brainstem: the potential role of glutamate neurotransmission. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism. 2013;3:110. doi:10.4172/2161-0460.1000110.
Winter CD, Iannotti F, Pringle AK, Trikkas C, Clough GF, Church MK. A microdialysis method for the recovery of IL-1beta, IL-6 and nerve growth factor from human brain in vivo. J Neurosci Methods. 2002;119(1):45–50.
Woodroofe MN, Sarna GS, Wadhwa M, Hayes GM, Loughlin AJ, Tinker A, et al. Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in adult rat brain, following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol. 1991;33(3):227–36.
Boato F, Rosenberger K, Nelissen S, Geboes L, Peters EM, Nitsch R, et al. Absence of IL-1beta positively affects neurological outcome, lesion development and axonal plasticity after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2013;10:6. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-10-6.
Ghosh S, Wu MD, Shaftel SS, Kyrkanides S, LaFerla FM, Olschowka JA, et al. Sustained interleukin-1beta overexpression exacerbates tau pathology despite reduced amyloid burden in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Neurosci. 2013;33(11):5053–64. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4361-12.2013.
Lyman M, Lloyd DG, Ji X, Vizcaychipi MP, Ma D. Neuroinflammation: the role and consequences. Neurosci Res. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2013.10.004.
Brooks TA, Hawkins BT, Huber JD, Egleton RD, Davis TP. Chronic inflammatory pain leads to increased blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein alterations. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289(2):H738–43. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01288.2004.
Bevilacqua MP, Gimbrone Jr MA. Inducible endothelial functions in inflammation and coagulation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987;13(4):425–33. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1003519.
Finnie JW. Neuroinflammation: beneficial and detrimental effects after traumatic brain injury. Inflammopharmacology. 2013;21(4):309–20. doi:10.1007/s10787-012-0164-2.
Lok J, Zhao S, Leung W, Seo JH, Navaratna D, Wang X, et al. Neuregulin-1 effects on endothelial and blood-brain-barrier permeability after experimental injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2012;3 Suppl 1:S119–24. doi:10.1007/s12975-012-0157-x.
Mellergard P, Aneman O, Sjogren F, Saberg C, Hillman J. Differences in cerebral extracellular response of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10 after subarachnoid hemorrhage or severe head trauma in humans. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(1):12–9. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181ef2a40. discussion 9.
Hutchinson PJ, O’Connell MT, Rothwell NJ, Hopkins SJ, Nortje J, Carpenter KL, et al. Inflammation in human brain injury: intracerebral concentrations of IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, and their endogenous inhibitor IL-1ra. J Neurotrauma. 2007;24(10):1545–57. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0295.
Rigor RR, Beard Jr RS, Litovka OP, Yuan SY. Interleukin-1beta-induced barrier dysfunction is signaled through PKC-theta in human brain microvascular endothelium. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;302(10):C1513–22. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00371.2011.
Ridder DA, Lang MF, Salinin S, Roderer JP, Struss M, Maser-Gluth C, et al. TAK1 in brain endothelial cells mediates fever and lethargy. J Exp Med. 2011;208(13):2615–23. doi:10.1084/jem.20110398.
Mako V, Czucz J, Weiszhar Z, Herczenik E, Matko J, Prohaszka Z, et al. Proinflammatory activation pattern of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and LPS. Cytom A. 2010;77(10):962–70. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20952.
Schaff U, Mattila PE, Simon SI, Walcheck B. Neutrophil adhesion to E-selectin under shear promotes the redistribution and co-clustering of ADAM17 and its proteolytic substrate L-selectin. J Leukoc Biol. 2008;83(1):99–105. doi:10.1189/jlb.0507304.
Falls DL. Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284(1):14–30.
Rieff HI, Raetzman LT, Sapp DW, Yeh HH, Siegel RE, Corfas G. Neuregulin induces GABA(A) receptor subunit expression and neurite outgrowth in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1999;19(24):10757–66.
Rio C, Rieff HI, Qi P, Khurana TS, Corfas G. Neuregulin and erbB receptors play a critical role in neuronal migration. Neuron. 1997;19(1):39–50.
Kwon OB, Longart M, Vullhorst D, Hoffman DA, Buonanno A. Neuregulin-1 reverses long-term potentiation at CA1 hippocampal synapses. J Neurosci. 2005;25(41):9378–83. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2100-05.2005.
Fisahn A, Neddens J, Yan L, Buonanno A. Neuregulin-1 modulates hippocampal gamma oscillations: implications for schizophrenia. Cereb Cortex. 2009;19(3):612–8. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn107.
Ozaki M, Sasner M, Yano R, Lu HS, Buonanno A. Neuregulin-beta induces expression of an NMDA-receptor subunit. Nature. 1997;390(6661):691–4. doi:10.1038/37795.
Tan GH, Liu YY, Hu XL, Yin DM, Mei L, Xiong ZQ. Neuregulin 1 represses limbic epileptogenesis through ErbB4 in parvalbumin-expressing interneurons. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(2):258–66. doi:10.1038/nn.3005.
Ting AK, Chen Y, Wen L, Yin DM, Shen C, Tao Y, et al. Neuregulin 1 promotes excitatory synapse development and function in GABAergic interneurons. J Neurosci. 2011;31(1):15–25. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2538-10.2011.
Wen Y, Planel E, Herman M, Figueroa HY, Wang L, Liu L, et al. Interplay between cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta mediated by neuregulin signaling leads to differential effects on tau phosphorylation and amyloid precursor protein processing. J Neurosci. 2008;28(10):2624–32. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5245-07.2008.
Norton N, Moskvina V, Morris DW, Bray NJ, Zammit S, Williams NM, et al. Evidence that interaction between neuregulin 1 and its receptor erbB4 increases susceptibility to schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006;141B(1):96–101. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30236.
Makinodan M, Rosen KM, Ito S, Corfas G. A critical period for social experience-dependent oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Science. 2012;337(6100):1357–60. doi:10.1126/science.1220845.
Iivanainen E, Paatero I, Heikkinen SM, Junttila TT, Cao R, Klint P, et al. Intra- and extracellular signaling by endothelial neuregulin-1. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(13):2896–909. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.042.
Kalinowski A, Plowes NJ, Huang Q, Berdejo-Izquierdo C, Russell RR, Russell KS. Metalloproteinase-dependent cleavage of neuregulin and autocrine stimulation of vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2010;24(7):2567–75. doi:10.1096/fj.08-129072.
Russell KS, Stern DF, Polverini PJ, Bender JR. Neuregulin activation of ErbB receptors in vascular endothelium leads to angiogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1999;277(6 Pt 2):H2205–11.
Lok J, Wang H, Murata Y, Zhu HH, Qin T, Whalen MJ, et al. Effect of neuregulin-1 on histopathological and functional outcome after controlled cortical impact in mice. J Neurotrauma. 2007;24(12):1817–22. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0372.
Dimayuga FO, Ding Q, Keller JN, Marchionni MA, Seroogy KB, Bruce-Keller AJ. The neuregulin GGF2 attenuates free radical release from activated microglial cells. J Neuroimmunol. 2003;136(1–2):67–74.
Mencel M, Nash M, Jacobson C. Neuregulin upregulates microglial alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in immortalized cell lines: implications for regulating neuroinflammation. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e70338. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070338.
Asp L, Beraki S, Kristensson K, Ogren SO, Karlsson H. Neonatal infection with neurotropic influenza A virus affects working memory and expression of type III Nrg1 in adult mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2009;23(6):733–41. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2009.04.004.
Xu Z, Jiang J, Ford G, Ford BD. Neuregulin-1 is neuroprotective and attenuates inflammatory responses induced by ischemic stroke. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322(2):440–6. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.149.
Kanakry CG, Li Z, Nakai Y, Sei Y, Weinberger DR. Neuregulin-1 regulates cell adhesion via an ErbB2/phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt-dependent pathway: potential implications for schizophrenia and cancer. PLoS One. 2007;2(12):e1369. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001369.
Marballi K, Quinones MP, Jimenez F, Escamilla MA, Raventos H, Soto-Bernardini MC, et al. In vivo and in vitro genetic evidence of involvement of neuregulin 1 in immune system dysregulation. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010;88(11):1133–41. doi:10.1007/s00109-010-0653-y.
Calvo M, Zhu N, Tsantoulas C, Ma Z, Grist J, Loeb JA, et al. Neuregulin-ErbB signaling promotes microglial proliferation and chemotaxis contributing to microgliosis and pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci. 2010;30(15):5437–50. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5169-09.2010.
Finigan JH, Mishra R, Vasu VT, Silveira LJ, Nethery DE, Standiford TJ, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage neuregulin-1 is elevated in acute lung injury and correlates with inflammation. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(2):396–401. doi:10.1183/09031936.00004912.
Maki T, Hayakawa K, Pham LD, Xing C, Lo EH, Arai K. Biphasic mechanisms of neurovascular unit injury and protection in CNS diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013;12(3):302–15.
Acosta SA, Tajiri N, Shinozuka K, Ishikawa H, Grimmig B, Diamond DM, et al. Long-term upregulation of inflammation and suppression of cell proliferation in the brain of adult rats exposed to traumatic brain injury using the controlled cortical impact model. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53376. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053376.
Borlongan CV, Glover LE, Tajiri N, Kaneko Y, Freeman TB. The great migration of bone marrow-derived stem cells toward the ischemic brain: therapeutic implications for stroke and other neurological disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;95(2):213–28. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.005.
Safa RN, Peng XY, Pentassuglia L, Lim CC, Lamparter M, Silverstein C, et al. Neuregulin-1beta regulation of embryonic endothelial progenitor cell survival. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300(4):H1311–9. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01104.2009.
Hedhli N, Dobrucki LW, Kalinowski A, Zhuang ZW, Wu X, Russell 3rd RR, et al. Endothelial-derived neuregulin is an important mediator of ischaemia-induced angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;93(3):516–24. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr352.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the following grants:
R37NS037074-13 (EHL)
R01NS076694-02(EHL)
P01NS055104-05 (EHL)
K08N5057339-04 (JL)
China Scholarship Council (#201206170107; LW)
The authors thank Dr. Mark Vangel and Dr. Hang Lee (Harvard Catalyst) for statistical support.
The authors thank Dr. Kayakawa for his help in learning the neutrophil assay protocol.
Conflict of Interest
Limin Wu, Samantha Walas, Wendy Leung, David Sykes, Jiang Wu, Eng H. Lo, and Josephine Lok declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects.
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Walas, S., Leung, W. et al. Neuregulin1-β Decreases IL-1β-Induced Neutrophil Adhesion to Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Transl. Stroke Res. 6, 116–124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0347-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0347-9