Abstract
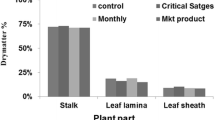
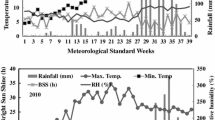
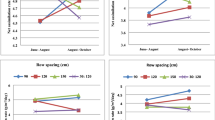
Mother corm size is the most important factor for production of replacement corms, flower, and stigma yield in saffron. In semi-arid regions, water shortage is a deterrent agent for appropriate corm growth of saffron. Therefore, in this experiment the effects of six levels of superabsorbent polymer (SAP) including 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 kg ha-1 was investigated on growth indices of replacement corms of saffron. For this purpose, an experiment was evaluated at the research farm of the Saffron Research Group, Sarayan Faculty of Agriculture, University of Birjand, Iran, during 2013-2015. Results showed that SAP application did not considerable effect on corm growth indices in the first life cycle of saffron. Nevertheless, consumption of 30-40 kg ha-1 SAP somewhat improved the number and total weight of replacement corms per clone. In the second life cycle of saffron, the positive impact of SAP was clearly observed on the growth of replacement corms. The application of 40 kg ha-1 SAP increased the amount of number of replacement corms per clone by 13%, total weight of replacement corms per clone by 36%, and scale weight of corms per clone by 50% compared with control. In addition, the amount of mean weight of replacement corms and mean number of buds per corm in treatment of application of 40 kg ha-1 SAP were 29 and 27% higher than the control treatment, respectively. SAP application decreased the amount of non-standard (< 8 g) corm production while significantly increased the percentage of corms with standard weight. Overall, the increasing effect of SAP application on corm weight, bud number, and standard corm yield was higher than the number of produced corms per clone. In addition, water-use efficiency in SAP application treatments (6.1 kg standard corm m-3) was more than the control (4.34 kg m-3) treatment. In total, SAP application is an appropriate strategy for production of standard saffron corms in semi-arid regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghhavani-Shajari M, Rezvani-Moghaddam P, Koocheki AR, Fallahi HR, Taherpour-Kalantari R. 2015. Evaluation of the effects of soil texture on yield and growth of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Saffron Agron. Tech. 2: 311–322
Ahmadee M, Khashei Suiki A, Sayyari MH. 2014. Type and amount evaluation of natural clinoptilolite zeolites impacts on saffron (Crocus sativus L.) emergence. J. Saffron Res. 1. 97–109
Alipoor Miandehi Z, Mahmoodi S, Behdani MA, Sayyari MH. 2015. Effects of corm weight and application of fertilizer types on some growth characteristics and yield of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) under Mahvelat conditions. J. Saffron Res. 2: 97–112
Azizi-Zohan AA, Kamkar-Haghighi AA, Sepaskhah AR. 2006. Effect of irrigation method and frequency on corm and Saffron production (Crocus sativus L.). J. Sci. Tech. Agri. Nat. Res. 10: 45–54
Behdani MA. 2011. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.), In KVPeter, ed, Future Crops, ed 1, Daya Publishing House, New Delhi, India. 286 p
De-Juan JA, Corcoles HL, Munoz RM, Picornell MR. 2009. Yield and yield components of saffron under different cropping systems. Ind. Crops Prod. 30: 212–219
Fallahi HR, Feli A, Salari-Nasab S. 2014a. Study the effects of super absorbent on growth of saffron. Proceedings of the 3rd National Conference on the Scientific Achievements of Saffron. Torbat Heydariyeh University, Iran 26-27 November 2014. p 17
Fallahi HR, Paravar A, Behdani MA, Aghhavani-Shajari M, Fallahi MJ. 2014b. Effects of Saffron corm and leaf extracts on early growth of some plants to investigate the possibility of using them as associated crop. Not. Sci. Biol. 6: 282–287
Fallahi HR, Alami S, Behdani MA, Aghhavani Shajari M. 2015. Evaluation of local and scientific knowledge in saffron agronomy (Case study: Sarayan). J. Saffron Res. 3: 31–50
Jahan M, Nassiri Mohallati M, Ranjbar F, Aryaee M, Kamayestani N. 2015. The effects of super absorbent polymer application into soil and humic acid foliar application on some agrophysiological criteria and quantitative and qualitative yield of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under Mashhad conditions. J. Agroecol. 6: 753–766
Gao L, Wang S, Zhao X. 2013. Synthesis and characterization of agricultural controllable humic acid superabsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 25: 69–76
Gresta F, Lombardo GM, Siracusa L, Ruberto G. 2008. Saffron, an alternative crop for sustainable agricultural systems: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 28: 95–112
Khorramdel S, Gheshm R, Amin Ghafori A, Esmaielpour B. 2014. Evaluation of soil texture and superabsorbent polymer impacts on agronomical characteristics and yield of saffron. J. Saffron Res. 1: 120–135
Koocheki AR. 2004. Indigenous knowledge in agriculture with particular reference to saffron production in Iran. Acta. Hort. 650: 175–182
Koocheki AR. 2013. Research on production of Saffron in Iran: Past trend and future prospects. Saffron Agron. Tech. 1: 3–21
Koocheki A, Seyyedi SM, Jamshid Eyni M. 2014. Effect of irrigation levels and high corm density on growth and phosphorus uptake of daughter corms of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Iranian J. Crop Sci. 16: 222–235
Koocheki A, Rezvani-Moghaddam P, Fallahi HR. 2015a. Effects of planting dates, irrigation management and cover crops on growth and yield of saffron (Crocus sativa L.). J. Agroecol.
Koocheki A, Rezvani-Moghaddam P, Fallahi HR, Aghhavani-Shajari M. 2015b. Growth response of saffron replacement corms to planting date, irrigation management and associated crops. Saffron Agron. Tech. In Press
Koocheki AR, Fallahi HR, Amiri MB, Ehyaei HR. 2015c. Effects of humic acid application and mother corm weight on yield and growth of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). J. Agroecol. In Press
Kumar R, Singh V, Devi K, Sharma M, Singh MK, Ahuja PS. 2009. State of art of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) agronomy: a comprehensive review. Food Rev. Int. 25: 44–85
Mohammad-Abadi AA, Rezvani-Moghaddam P, Fallahi HR. 2011. Effects of planting pattern and the first irrigation date on growth and yield of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) J. Agroecol. 3: 84–93
Razavi SS, Davary K. 2014. The role of virtual water in water resource management. J. Water Sustain. Dev. 1: 9–18
Renau-Morata B, Nebauer SG, Sánchez M, Molina RV. 2012. Effect of corm size, water stress and cultivation conditions on photosynthesis and biomass partitioning during the vegetative growth of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 39: 40–46
Rezvani-Moghaddam P, Mohammad-Abadi AA, Fallahi HR, Aghhavani-Shajari. M 2014. Effects of nutrient management on flowe yield and corm characteristics of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). J. Hort. Sci. 28: 427–434
Sadeghi B, Hossieni M, Masrouri M, Mollafilabi A. 2014. The effect of nutrition on corm-bed for enlargement of saffron corms. Research Project of Institute of Food Science and Technology, Khorasan Razavi, Iran. 23p. (In Persian)
Shahid SA, Qidwai AA, Anwar F, Ullah I, Rashid U. 2012. Improvement in the water retention characteristics of sandy loam soil using a newly synthesized poly (acrylamide-o-acrylic Acid)/AlZnFe2O4 superabsorbent hydrogel nanocomposite material. Molecules 17: 9397–9412
Shooshtarian S, Abedi-Kupai J, TehraniFar A. 2012. Evaluation of application of superabsorbent polymers in green space of arid and semi-arid regions with emphasis on Iran. Int. J. Forest, Soil Erosion 2: 24–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallahi, HR., Zamani, G., Mehrabani, M. et al. Influence of superabsorbent polymer rates on growth of saffron replacement corms. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 19, 77–84 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-015-0083-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-015-0083-z