Abstract
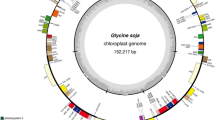
Semi-wild soybean, Glycine gracilis, harbors unique gene resources for the soybean breeding programs, which would help to understand the process of soybean domestication. Here, we sequenced and characterized the complete chloroplast genome sequence of the semi-wild soybean. The genome of G. gracilis has 152,218 bp in length with 35.37% GC content. It contains two inverted repeats blocks of 25,574 bp, separated by the large single-copy block of 83,175 bp and small single-copy block of 17,895 bp. A total of 111 unique genes were annotated, including 77 protein coding genes, 30 tRNA genes and 4 rRNA genes. Phylogenetic analysis of the ten sequenced Glycine chloroplast genomes revealed that the semi-wild soybean G. gracilis is closer to cultivated soybean G. max than wild soybean G. soja. The newly sequenced complete chloroplast genome of G. gracilis will provide useful resources for the further genetic characterization that would enhance the conservation of this highly endangered species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Nelson RL (2004) Genetic variation and relationships among cultivated, wild, and semiwild soybean. Crop Sci 44:316–325
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Gao CW, Gao LZ (2016) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of wild soybean, Glycine soja. Conserv Genet Resour. doi: 10.1007/s12686-016-0659-z
Hermann FJ (1962) A revision of the genus Glycine and its immediate allies. Technical bulletins
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma KI, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3059–3066
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Saski C, Lee SB, Daniell H, Wood TC, Tomkins J, Kim HG, Jansen RK (2005) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Glycine max and comparative analyses with other Legume Genomes. Plant Mol Biol 59:309–322
Sherman-Broyles S, Bombarely A, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Doyle J (2014) Complete plastome sequences from Glycine syndetika and six additional perennial wild relatives of soybean. G3-Genes Genomes Genet 4:2023–2033
Wyman SK, Jansen RK, Boore JL (2004) Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 20:3252–3255
Yang L, Li X, Xiao X, Kejing W (2010) Genetic divergence in different seed weights within the subgenus soja and taxonomic assignment of semi-wild soybean (Glycine gracilis Skvortzow). Mol Plant Breed 48:9858–9860
Ye CY, Lin Z, Li G, Wang YY, Qiu J, Fu F, Zhang H, Chen L, Ye S, Song W (2014) Echinochloa chloroplast genomes: insights into the evolution and taxonomic identification of two weedy species. Plos ONE 9:e113657–e113657
Acknowledgements
We would thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for providing valuable comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by the Top Talents Program of Yunnan Province (20080A009), Project of Innovation Team of Yunnan Province, Hundred Oversea Talents Program of Yunnan Province, and Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) to L. Z. Gao.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, CW., Gao, LZ. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of semi-wild soybean, Glycine gracilis (Fabales: Fabaceae). Conservation Genet Resour 9, 343–345 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-016-0683-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-016-0683-z