Abstract
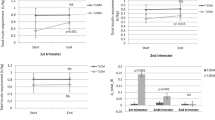
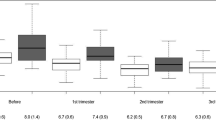
The aim of the study was to evaluate the features of the effect of different modes of insulin therapy on pregnancy outcomes in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) with different levels of albuminuria. The study involved 155 women with T1DM during pregnancy, using various modes of insulin, and 42 infants born to women with T1DM. In order to identify a possible relationship between the level of proinflammatory cytokines and growth factors in pregnant women with T1DM and terms of delivery, we measured the daily urinary excretion of IL-1β, MCP-1, and TGF-β1 in 21 women at different trimesters of pregnancy. The use of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) in pregnant women with T1DM allows to prolong the pregnancy for 2–4 weeks as compared to the timing of delivery of pregnant women with T1DM receiving multiple subcutaneous injections of insulin (MPII). Pregnant women with MPII in 100% cases of the presence of microalbuminuria and proteinuria had premature delivery. Elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and MCP-1) and TGF-β1 may possibly serve as a predictor of pre-term delivery in pregnant women with diabetes type 1, starting with the early stages of pregnancy. The use of insulin by CSII in pregnant women with T1DM reduces the percentage of pre-term deliveries, regardless of the stage of diabetic nephropathy. It improves the condition of infants born at term in women with T1DM using a therapy with insulin pumps compared to that with MPII such as less common manifestation of diabetic fetopathy as macrosomia and hypoglycemia at birth, reducing the need for resuscitation in newborns.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaouat, G., Menu, E., Delage, G. (1995). Immuno-endocrine interaction in early pregnancy. Human Reproduction, 10(Suppl. 2), 55–59.
Tiselko, A. V. (2006). Experience in the use of insulin pump therapy in pregnant women with diabetes. Farmateka, N17, 17–18.
Arbatskaya, N. U., & Demidova, I. U. (2010). Rational insulin therapy of diabetes during pregnancy. The effective pharmacotherapy. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 5–6, 2–7.
Gazizova, G. R., Valeeva, F. V., Alimetova, Z. R., Sharipova, J. U. (2012). Effect of route of administration of insulin on pregnancy outcomes and the status of children born in patients with type 1 diabetes. General Practitioner Guideline, 8, 44–47.
Ray, J. G., O’Brien, T. E., Chan, W. S. (2001). Preconception care and the risk of congenital anomalies in the offspring of women with diabetes mellitus: a meta–analysis. QJM, 94, 435–444.
Valeeva, F. V., Gazizova, G. R., Gaysina, L. R. (2015). Urinary excretion of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, MCP-1 and fibrogenic growth factor TGF-β1 in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes (T1DM). 8th International Conference on Advanced Technologies & Treatment for Diabetes. Abstracts. – Paris, France, P.152.
Valeeva, F. V., Alimetova, Z. R., Sharipova, J. U., Achmetzyanova, T. N. (2013). Stability of renal cytomembran in pregnant women with diabetes type 1 depending on the mode of insulin administration. The 7th International DIP Symposium. Diabetes, Hypertension, Metabolic Syndrome & Pregnancy. Abstracts. – Florence, Italy, P. 628.
Acknowledgements
The work is performed according to the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gazizova, G., Gaysina, L., Valeeva, F. et al. Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with Type 1 Diabetes Depending on the Different Modes of Insulin Therapy. BioNanoSci. 7, 390–395 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0371-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0371-1