Abstract
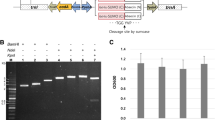
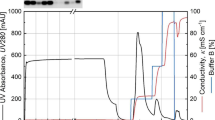
Low molecular weight guanyl-preferring ribonuclease (RNase) secreted by Bacillus pumilus is referred to as binase and regarded as a potential agent to target oncogenic diseases and viral infections. Depending on research purposes, native binase or tagged and mutated forms are required for application. Specific inhibition of binase activity is achieved by binding to RNase inhibitor barstar. Native and mutant forms of binase are routinely obtained by ion-exchange chromatography, while tagged versions of binase, which can be purified faster and less tedious than non-tagged, are currently unavailable. Here, recombinant DNA techniques were employed to improve binase overexpression in bacterial host cells, its purification, and subsequent detection in downstream assays using affinity tag. Here, recombinant DNA techniques were employed to improve binase overexpression in bacterial host cells. Binase-barstar genetic cassette was modified to obtain strong two-gene operon with the possibility of rapid exchange of binase and/or barstar genes with homologous or mutated ones as well as the generation of C-terminally His-tagged binase and/or barstar. The binase-barstar operon was introduced into pET26b vector as well as into pET26b-pET15b hybrid vector that was created in this study. As a result, plasmids allowed the induced production of extracellular non-tagged, N- or C-terminal His-tagged binase and synchronous intracellular production of non-tagged or C-His-tagged barstar. The constructs can be further sub-cloned in gram-positive bacterial hosts to ensure native production conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitkevich, V. A., Kretova, O. V., Petrushanko, I. Y., Burnysheva, K. M., Sosin, D. V., Simonenko, O. V., et al. (2013). Ribonuclease binase apoptotic signature in leukemic Kasumi-1 cells. Biochimie, 95, 1344–1349.
Shah Mahmud, R., Ulyanova, V., Malanin, S., Dudkina, E., Vershinina, V., et al. (2015). Draft whole-genome sequence of Bacillus altitudinis strain B-388, a producer of extracellular RNase. Genome Announcements. doi:10.1128/genomeA.01502-14.
Ilinskaya, O. N., Singh, I., Dudkina, E., Ulyanova, V., Kayumov, A., Barreto, G. (2016). Direct inhibition of oncogenic KRAS by Bacillus pumilus ribonuclease (binase). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1863, 1559–1567.
Dudkina, E., Kayumov, A., Ulyanova, V., Ilinskaya, O. (2014). New insight into secreted ribonuclease structure: binase is a natural dimer. PloS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115818.
Schulga, A., Kurbanov, F., Kirpichnikov, M., Protasevich, I., Lobachov, V., Ranjbar, B., et al. (1998). Comparative study of binase and barnase: experience in chimeric ribonucleases. Protein Engineering, 11, 775–782.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (3rd ed.). NY: CSHL Press.
Ul’ianova, V. V., Vershinina, V. I., Kharitonova, M. A., Sharipova, M. R. (2007). The effect of Spo0A and AbrB proteins on expression of the genes of guanyl-specific ribonucleases from Bacillus intermedius and Bacillus pumilus in Bacillus subtilis recombinant strains. Microbiology, 76, 563–568.
Znamenskaia, L. V., Gabdrakhmanova, L. A., Chernokal’skaia, E. B., Leshchinskaia, I. B. (1995). Biosynthetic regulation of extracellular ribonucleases in native strains of bacilli and in recombinant strains of Escherichia coli. Mikrobiologiia, 64, 616–622.
Erster, O., & Liscovitch, M. (2010). A modified inverse PCR procedure for insertion, deletion, or replacement of a DNA fragment in a target sequence and its application in the ligand interaction scan method for generation of ligand-regulated proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, 634, 157–174.
Wood, D. W. (2014). New trends and affinity tag designs for recombinant protein purification. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 26, 54–61.
Zdobnova, T. A., Stremovskiy, O. A., Lebedenko, E. N., Deyev, S. M. (2012). Self-assembling complexes of quantum dots and scFv antibodies for cancer cell targeting and imaging. PloS One, 7(10), e48248.
Stepanov, A. V., Belogurov, A. A., Jr., Ponomarenko, N. A., Stremovskiy, O. A., Kozlov, L. V., Bichucher, A. M., et al. (2011). Design of targeted B cell killing agents. PloS One, 6(6), e20991.
Edelweiss, E., Balandin, T. G., Ivanova, J. L., Lutsenko, G. V., Leonova, O. G., Popenko, V. I., et al. (2008). Barnase as a new therapeutic agent triggering apoptosis in human cancer cells. PloS One, 3(6), e2434.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research no. 15-04-07864, partnership program between Kazan Federal University and Justus-Liebig-University, Giessen, and the program of competitive growth of KFU. DNA sequencing was performed in the Interdisciplinary Centre for Collective Use of KFU (ID RFMEFI59414X0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulyanova, V., Shah Mahmud, R., Klug, G. et al. A Set of Genetic Constructs for Binase and Barstar Overproduction. BioNanoSci. 7, 222–225 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0349-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0349-z