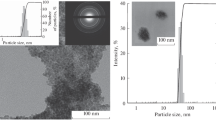
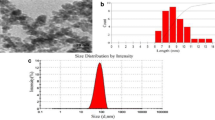
Abstract
The usefulness of magnetite nanoparticles to improve contrast in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of tumor visualization was actively investigated currently. In this work, we conducted MRI and morphological examination of internal organs of 30 white outbred rats with transplanted liver tumor PC-1 after intravenous administration of magnetite hydrosols. Intravenous administration of citrate-stabilized magnetite nanoparticles in a dosage of 20 μg/kg and 16 mg/kg resulted in a disruption of blood filling of the organs, mainly due to the plethora. The dystrophic cell damage was observed in liver and in kidneys. The activation of immune processes in spleen was fixed after intravenous administration of citrate stabilized magnetite nanoparticles. In both doses, the nanoparticles were founded in the heart and brain, but the significant iron accumulation was detected in the tumor by methods of MRI and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) only in dosage of 16 mg/kg. It is possible to conclude that selected dosage is sufficient for accumulation of nanoparticles in tumor, but it does not cause significant changes in the internal organs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
De, M., Ghosh, P. S., Rotello, V. M. (2008). Applications of nanoparticles in biology. Advanced Materials, 20, 4225–4241. doi:10.1002/adma.200703183.
Levy, M., Lagarde, F., Maraloiu, V.-A., Blanchin, M.-G., Gendron, F., Wilhelm, C., et al. (2010). Degradability of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in a model of intracellular environment: follow-up of magnetic, structural and chemical properties. Nanotechnology, 21, 395103. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/39/395103.
Laurent, S., Forge, D., Port, M., Roch, A., Robic, C., Vander Elst, L., et al. (2008). Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chemical Reviews, 108, 2064–2110. doi:10.1021/cr068445e.
Liz-Marzaґn, L. M., & Kamat, P. V. (2003). Nanoscale materials. Boston: Kluwer.
Kim, D. K., Zhang, Y., Voit, W., Rao, K. V., Muhammed, M. (2001). Synthesis and characterization of surfactant-coated superparamagnetic monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 225, 30–36. doi:10.1016/S0304-8853(00)01224-5.
Zhang, Y., Kohler, N., Zhang, M. (2002). Surface modification of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake. Biomaterials, 23, 1553–1561.
Massia, S. P., Stark, J., Letbetter, D. S. (2000). Surface immobilized dextran limits cell adhesion and spreading. Biomaterials, 21, 2253–2261.
Yu, J.-H., Lee, C.-W., Im, S.-S., Lee, J.-S. (2003). Structure and magnetic properties of SiO2 coated Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized by chemical vapor condensation process. Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 4, 55–59.
Chen, M., Yamamuro, S., Farrell, D., Majetich, S. A. (2003). Gold-coated iron nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Journal of Applied Physics, 93, 7551. doi:10.1063/1.1555312.
Lin, J., Zhou, W., Kumbhar, A., Fang, J., Carpenter, E. E., O’Connor, C. J. (2001). Gold-coated iron (Fe@Au) nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and magnetic field-induced self-assembly. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 159, 26–31.
Svenskaya, Y. I., Navolokin, N. A., Bucharskaya, A. B., Terentyuk, G. S., Kuz’mina, A. O., Burashnikova, M. M., et al. (2014). Calcium carbonate microparticles containing a photosensitizer photosens: preparation, ultrasound stimulated dye release, and in vivo application. Nanotechnologies in Russia, 9, 398–409. doi:10.1134/S1995078014040181.
Lubbe, A. S., Alexiou, C., Bergemann, C. (2001). Clinical applications of magnetic drug targeting. Journal of Surgical Research, 95, 200–206.
Kaminski, M. D., & Rosengart, A. J. (2005). Detoxification of blood using injectable magnetic nanoparticles: a conceptual technology description. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 293, 398–403.
Chin, A. B., & Yaacob, I. I. (2007). Synthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via microemulsion and massart’s procedure. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 191, 235–237.
Albornoz, C., & Jacobo, S. E. (2006). Preparation of a biocompatible magnetic film from an aque-ous ferrofluid. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 305, 12–15.
Kim, E. H., Lee, H. S., Kwak, B. K., Kim, B. K. (2005). Synthesis of ferrofluid with magnetic nanoparticles by sonochemical method for MRI contrast agent. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 289, 328–330.
Wan, J., Chen, X., Wang, Z., Yang, X., Qian, Y. (2005). A soft-template-assisted hydrothermal approach to single-crystal Fe3O4 nanorods. Journal of Crystal Growth, 276, 571–576.
Kimata, M., Nakagawa, D., Hasegawa, M. (2003). Preparation of monodisperse magnetic particles by hydrolysis of iron alkoxide. Powder Technology, 132, 112–118.
German, S. V., Inozemtseva, O. A., Navolokin, N. A., Pudovkina, E. E., Zuev, V. V., Volkova, E. K., et al. (2013). Synthesis of magnetite hydrosols and assessment of their impact on living systems at the cellular and tissue levels using MRI and morphological investigation. Nanotechnologies in Russia, 8, 573–580. doi:10.1134/S1995078013040034.
Sizova, E., Miroshnikov, S., Yausheva, E., Polyakova, V. (2015). Assessment of morphological and functional changes in organs of rats after intramuscular introduction of iron nanoparticles and their agglomerates. BioMed Research International. Article ID 243173, 7 pages. doi:10.1155/2015/243173.
Navolokin, N. A., Maslyakova, G. N., Bucharskya, A. B., Kong, X. M. (2012). Morphological changes in the kidney, liver and spleen during prolonged administration of iron nanoparticles. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/345/1/012043.
Prodan, A. M., Iconaru, S. L., Ciobanu, C. S., Chifiriuc, M. C., Stoicea, M., Predoi, D. (2013). Iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: characterization and toxicity evaluation by in vitro and in vivo assays. Journal of Nanomaterials. doi:10.1155/2013/587021.
German, S. V., Navolokin, N. A., Kuznetsova, N. R., Zuev, V. V., Inozemtseva, O. A., Anis, A. A., et al. (2015). Liposomes loaded with hydrophilic magnetite nanoparticles: preparation and application as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 135, 109–115. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.07.042.
German, S. V., Inozemtseva, O. A., Markin, A. V., Metvalli, K., Khomutov, G. B., Gorin, D. A. (2013). Synthesis of magnetite hydrosols in inert atmosphere. Colloid Journal, 75, 483–486.
Dzamukova, M. R., Naumenko, E. A., Rozhina, E. V., Trifonov, A. A., Fakhrullin, R. F. (2015). Cell surface engineering with polyelectrolyte-stabilized magnetic nanoparticles: a facile approach for fabrication of artificial multicellular tissue-mimicking clusters. Nano Research, 8(8), 2515–2532.
International Guiding Principles for Biomedical Research Involving Animals (2012) http://www.cioms.ch/index.php/12-newsflash/227-cioms-and-iclas-release-the-new-international-guidingprinciples-for-biomedical-research-involving-animals.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Government of the Russian Federation (grant no.14.Z50.31.0004 to support scientific research projects implemented under the supervision of leading scientists at Russian institutions and Russian institutions of higher education) and the Russian Scientific Foundation (project no. 14-15-00128) and Saratov State University. The work done by NAN was supported by the Russian President’s Scholarship SP-523.2016.4 (2016-2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navolokin, N.A., Bucharskaya, A.B., German, S.V. et al. The Morphological Changes in the Internal Organs in Tumor-Bearing Rats at Intravenous Injection of Citrate-Stabilized Magnetite Nanoparticles. BioNanoSci. 6, 162–168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0200-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0200-6