Abstract
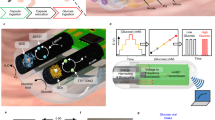
The development of a low-cost, robust, and versatile biosensors for the rapid detection of endogenous and exogenous metabolites in small animals is of great interest for health-care, pharmaceuticals, and in translational medicine. This work presents a complete in vitro characterization of a system of membranes for the development of a biosensor that will be integrated with the dedicated electronics into an implantable device for small animals. The system of membrane consists of an “inner” permselective layer, designed to filter the signal generated by the oxidation of interfering substances present in biological fluids; an “outer” layer made by an epoxy-enhanced polyurethane film, that regulates the passage of glucose and oxygen to the electrode surface and provides a biocompatible layer for a correct integration with the surrounding tissue. This system of membrane is employed in a glucose sensor that successfully monitors glucose in both the human and mouse physiological range, in PBS and in human serum at 37 ∘C. The sensor showed good stability for 30 days, and the permselective membrane effectively filtered out ascorbic acid and uric acid. Moreover, with the same system of membrane, we developed a biosensor for detection of the anti-inflammatory drug acetaminophen. The integration with the dedicated electronics is successfully used to measure glucose in the physiological range.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nichols, S.P., Koh, A., Storm, W.L., Shin, J.H., & Schoenfisch, M.H. (2013). Biocompatible materials for continuous glucose monitoring devices. Chemical Reviews, 113(4), 2528–2549.
Jucker, M. (2010). The benefits and limitations of animal models for translational research in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature medicine, 16(11), 1210–1214.
Abbott, A. (2009). Return of the rat. Nature News, 460(7257), 788–788.
Incorporated, G. Glysens’s icgm tm glucose monitoring products.
Gough, D.A., Kumosa, L.S., Routh, T.L., Lin, J.T., & Lucisano, J.Y. (2010). Function of an implanted tissue glucose sensor for more than 1 year in animals. Science Translational Medicine, 2(42), 42ra53–42ra53.
Mortellaro, M., & DeHennis, A. (2014). Performance characterization of an abiotic and fluorescent-based continuous glucose monitoring system in patients with type 1 diabetes. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 61(0), 227–231.
Senseonics TM, Senseonics sensor.
Phillips, J.E., Bogema, S., Fu, P., Furmaga, W., Wu, A.H., Zic, V., & Hammett-Stabler, C. (2003). Signify®er drug screen test evaluation: comparison to triage®drug of abuse panel plus tricyclic antidepressants. Clinica chimica acta, 328(1), 31–38.
Peace, M.R., Tarnai, L.D., & Poklis, A. (2000). Performance evaluation of four on-site drug-testing devices for detection of drugs of abuse in urine. Journal of analytical toxicology, 24(7), 589–594.
Baj-Rossi, C., Kilinc, E.G., Ghoreishizadeh, S.S., Casarino, D., Jost, T.R., Dehollain, C., Grassi, F., Pastorino, L., De Micheli, G., & Carrara, S. (2014). Full fabrication and packaging of an implantable multi-panel device for monitoring of metabolites in small animals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 8(5), 636–647.
Carrara, S., Baj-Rossi, C., Ghoreishizadeh, S., Riario, S., Surrel, G., Stradolini, F., Boero, C., De Micheli, G., Kilinc, E., & Dehollain, C. (2015). Full system for translational studies of personalized medicine with free-moving mice. In International symposium on circuit and systems (ISCAS).
Ghoreishizadeh, S.S., Baj-Rossi, C., Cavallini, A., Carrara, S., & De Micheli, G. (2014). An integrated control and readout circuit for implantable multi-target electrochemical biosensing. IEEE Transaction on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 8(6), 891–898.
Kilinc, E., Conus, G., Weber, C., Kawkabani, B., Maloberti, F., & Dehollain, C. A system for wireless power transfer of micro-systems in-vivo implantable in freely moving animals, IEEE Sensors Journal.
Grassi, F., & Jost, T.R. (2014). Private communication, Tech. rep., Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB) Bellinzona.
Boock, R., & Rixman, M. (2013). Silicone based membranes for use in implantable glucose sensors US Patent 8,543,184 (09.
Bindra, D.S., Zhang, Y., Wilson, G.S., Sternberg, R., Thevenot, D.R., Moatti, D., & Reach, G. (1991). Design and in vitro studies of a needle-type glucose sensor for subcutaneous monitoring. Analytical Chemistry, 63 (17), 1692–1696.
Aussedat, B., Dupire-Angel, M., Gifford, R., Klein, J., Wilson, G., & Reach, G. (2000). Interstitial glucose concentration and glycemia: implications for continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology And Metabolism, 278(4), E716–E728.
Cavallini, A., Baj-Rossi, C., Ghoreishizadeh, S., De Micheli, G., & Carrara, S. (2012). Design, fabrication, and test of a sensor array for perspective biosensing in chronic pathologies, no EPFL-CONF-182530.
Cavallini, A., Rezzonico Jost, T., Ghoreishizadeh, S., Olivo, J., Op de Beeck, M., Gorissen, B., Grassi, F., De Micheli, G., & Carrara, S. A subcutaneous biochip for remote monitoring of human metabolism: packaging and biocompatibility assessment.
Zhang, Y., Hu, Y., Wilson, G.S., Moatti-Sirat, D., Poitout, V., & Reach, G. (1994). Elimination of the acetaminophen interference in an implantable glucose sensor. Analytical Chemistry, 66(7), 1183–1188.
Mocak, J., Bond, A., Mitchell, S., & Scollary, G. (1997). A statistical overview of standard (iupac and acs) and new procedures for determining the limits of detection and quantification: application to voltammetric and stripping techniques. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 69(2), 297–328.
Miller, J.N., & Miller, J.C. (2005). Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry, sixth Edition Pearson Education.
Hinson, J.A., Pike, S.L., Pumford, N.R., & Mayeux, P.R. (1998). Nitrotyrosine-protein adducts in hepatic centrilobular areas following toxic doses of acetaminophen in mice. Chemical research in toxicology, 11(6), 604–607.
Masubuchi, Y., Suda, C., & Horie, T. (2005). Involvement of mitochondrial permeability transition in acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Journal of hepatology, 42(1), 110–116.
Dai, Y.-Q., Zhou, D.-M., & Shiu, K.-K. (2006). Permeability and permselectivity of polyphenylenediamine films synthesized at a palladium disk electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 52(1), 297–303.
Chen, X., Hu, Y., & Wilson, G.S. (2002). Glucose microbiosensor based on alumina sol-gel matrix /electropolymerized composite membrane. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 17(11), 1005–1013.
Pan, D., Chen, J., Yao, S., Tao, W., & Nie, L. (2005). An amperometric glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase immobilized in electropolymerized poly (o-aminophenol) and carbon nanotubes composite film on a gold electrode. Analytical Sciences, 21(4), 367–372.
Murphy, L.J. (1998). Reduction of interference response at a hydrogen peroxide detecting electrode using electropolymerized films of substituted naphthalenes. Analytical Chemistry, 70(14), 2928–2935.
Muguruma, H., Hiratsuka, A., & Karube, I. (2000). Thin-film glucose biosensor based on plasma-polymerized film: simple design for mass production. Analytical chemistry, 72(11), 2671–2675.
Sternberg, R., Bindra, D.S., Wilson, G.S., & Thevenot, D.R. (1988). Covalent enzyme coupling on cellulose acetate membranes for glucose sensor development. Analytical Chemistry, 60(24), 2781–2786.
Rodríguez, M.C., & Rivas, G.A. (2004). Assembly of glucose oxidase and different polyelectrolytes by means of electrostatic layer-by-layer adsorption on thiolated gold surface. Electroanalysis, 16(20), 1717–1722.
He, C., Liu, J., Zhang, Q., & Wu, C. (2012). A novel stable amperometric glucose biosensor based on the adsorption of glucose oxidase on poly(methyl methacrylate)–bovine serum albumin core–shell nanoparticles. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 166–167(0), 802–808.
Yu, B., Long, N., Moussy, Y., & Moussy, F. (2006). A long-term flexible minimally-invasive implantable glucose biosensor based on an epoxy-enhanced polyurethane membrane. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 21(12), 2275–2282.
Ren, J., Shi, W., Li, K., & Ma, Z. (2012). Ultrasensitive platinum nanocubes enhanced amperometric glucose biosensor based on chitosan and nafion film. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 163(1), 115–120.
Piechotta, G., Albers, J., & Hintsche, R. (2005). Novel micromachined silicon sensor for continuous glucose monitoring. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 21(5), 802–808.
Brauker, J.H., Shults, M.C., & Tapsak, M.A. Membrane for use with implantable devices (03 2004).
Tipnis, R., Vaddiraju, S., Jain, F., Burgess, D.J., & Papadimitrakopoulos, F. (2007). Layer-by-layer assembled semipermeable membrane for amperometric glucose sensors. Journal of diabetes science and technology, 1 (2), 193–200.
Si, P., Kannan, P., Guo, L., Son, H., & Kim, D. -H. (2011). Highly stable and sensitive glucose biosensor based on covalently assembled high density au nanostructures. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 26(9), 3845–3851.
Şenel, M., & Nergiz, C. (2012). Novel amperometric glucose biosensor based on covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase on poly(pyrrole propylic acid)/au nanocomposite. Current Applied Physics, 12(4), 1118–1124.
Fang, L., Liang, B., Yang, G., Hu, Y., Zhu, Q., & Ye, X. (2014). Study of glucose biosensor lifetime improvement in 37  ∘c serum based on pani enzyme immobilization and plga biodegradable membrane. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 56 (0), 91–96.
Muldrew, K.L., James, L.P., Coop, L., McCullough, S.S., Hendrickson, H.P., Hinson, J.A., & Mayeux, P.R. (2002). Determination of acetaminophen-protein adducts in mouse liver and serum and human serum after hepatotoxic doses of acetaminophen using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 30(4), 446–451.
Ghoreishizadeh, S., Kilinc, E.G., Baj-Rossi, C., Dehollain, C., Carrara, S., & De Micheli, G. (2013). An implantable bio-micro-system for drug monitoring. IEEE, 218–221.
Acknowledgments
Enver G. Kilinc, Catherine Dehollain, Francesca Stradolini, Stefano Riario, Tanja Rezzonico Jost, Fabio Grassi, and André Badertscher are acknowledged for their collaboration to the present work. The SNF Sinergia Project, code CRSII2 1476941 and title “Innovative Enabling Micro Nano Bio technologies for Implantable systems in molecular medicine and personalised therapy - project prolongation” financially supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baj-Rossi, C., Ghoreishizadeh, S.S., Micheli, G.D. et al. An Innovative System of Membranes for the Monitoring of Endogenous and Exogenous Metabolites. BioNanoSci. 6, 85–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0196-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0196-y