Abstract
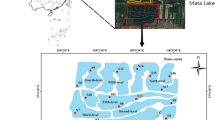
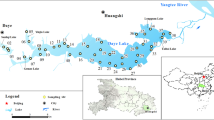
Nansi Lake is the largest and most important freshwater reservoir for the South-North Water Diversion Project located in Shandong Province, China. The characteristics of the nutrient compositions and distribution in the lake sediment may significantly influence the upper-level water quality, which has not been well studied. In this study, the distribution characteristics of the total phosphorus (TP), total organic matter (OM) and total nitrogen (TN) contents in the shallow sediments of Nansi Lake were investigated. The experimental results showed that the sedimentary TP, OM, and TN levels of the entire Nansi Lake (expressed as dry weight percentage) were (0.030 ± 0.003)–(0.129 ± 0.018) %, (1.14 ± 0.18)–(10.60 ± 1.30) % and (0.105 ± 0.021)–(0.71 ± 0.08) %, respectively. The three nutrient indicators appeared to be higher in the upstream lake than in the downstream lake. Concentrations of TN and OM were both particularly higher in aquaculture zones of Nansi Lake, where excessive fish feed may largely contribute to the high TN and OM in the sediment. Furthermore, there was a significantly positive correlation (n = 28, R 2 = 0.7870) between TN and OM. According to the pollution index (P i ) and enrichment factor, there is moderate enrichment of TN and OM in the sediment, while minor enrichment of TP in Nansi Lake. Calculations of the OM index and organic nitrogen index suggested that the surface sediment of the entire Nansi Lake has been contaminated by OM and organic nitrogen. Therefore, there is a pressing need to further investigate the release characteristics of these nutrient contaminants from the sediment of Nansi Lake and potential impacts on the surface water quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An W, Li X (2008) Phosphate adsorption characteristics on surface sediments of Nansi Lake and its main inflow rivers. Environ Sci (in Chinese with English Abstract) 29(1):295–302
An WC, Li XM (2009) Phosphate adsorption characteristics at the sediment-water interface and phosphorus fractions in Nansi Lake, China, and its main inflow rivers. Environ Monit Assess 148(1–4):173–184
Chen F, Xia Z, Song C, Li J, Zhou Y (2007) Relationships between organic matter in sediments and internal nutrient loadings in shallow lakes in Hubei province of China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Hydrobiol Sin 31(4):467–472
Davison W, Heaney SI (1978) Ferrous iron-sulfide interactions in anoxic hypolimnetic waters. Limnol Oceanogr 23(6):1194-1200
Feng F, Wang H, Fang T, Liu J (2006) The correlation between microbial biomass and carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus in the sediments of Lake Donghu. China Environ Sci (in Chinese with English Abstract) 26(3):342–345
Hilton J, O’Hare M, Bowes MJ, Jones JI (2006) How green is my river? A new paradigm of eutrophication in rivers. Sci Total Environ 365(1–3):66–83
Jiang X, Wang S (2012) In Methods for sediment quality evaluation. Science press, Beijing
Jin XC, Wang SR, Pang Y, Wu FC (2006) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 139(2):288–295
Kim LH, Choi E, Stenstrom MK (2003) Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere 50(1):53–61
Li G, Zhou J (2006) Effects of environmental factors on release of sediment phosphorus in Nansi Lake. Agro Environ Sci (in Chinese with English Abstract) 25:653–656
Liu E, Shen J, Yang L, Sun Q, Wang J (2008) Occurrence of phosphorus in sediments of Nansi Lake and its main inflow rivers. Geochimica (in Chinese with English Abstract) 37(3):290–296
Mudroch A, Azcue J (1995) In manual of aquatic sediment sampling. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 194–220
Orr TB, Meister SM, Halbrook RS (2004) Density and sediment organic matter content as potential confounding factors in sediment toxicity tests with Hyalella azteca. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73(2):371–378
Pei H, Liu Q, Hu W, Xie J (2011) Phytoplankton community and the relationship with the environment in Nansi Lake, China. Int J Environ Res 5(1):167–176
Qin B, Zhu G (2005) Distribution, circle and exchange characteristic of sediment nutrients in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Area. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci (in Chinese) 35:1–10
Sakan SM, Dordevic DS, Manojlovic DD, Predrag PS (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J Environ Manage 90(11):3382–3390
Sasikala S, Tanaka N, Wah HSYW, Jinadasa KBSN (2009) Effects of water level fluctuation on radial oxygen loss, root porosity, and nitrogen removal in subsurface vertical flow wetland mesocosms. Ecol Eng 35(3):410–417
Schindler DW (2006) Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication. Limnol Oceanogr 51(1):356–363
Spears BM, Carvalho L, Perkins R, Kirika A, Paterson DM (2007) Sediment phosphorus cycling in a large shallow lake: spatio-temporal variation in phosphorus pools and release. Hydrobiologia 584:37–48
USEPA (2007) In Method 3051a: microwave assisted acid dissolution of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Wang X, Feng Y, Xue J (2007) Study on content of total phosphorus and forms of inorganic phosphorus in sediments of Chaohu Lake. J Soil Water Conserv 21:56–59
Wu H, Ru X (2012) The analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution in Lake Nansi Basin. In: International Symposium Geomatics for Integrated Water Resources Management (GIWRM), pp 1–3
Wu F, Qing H, Wan G (2001) Regeneration of N, P and Si near the sediment/water interface of lakes from Southwestern China Plateau. Water Res 35(5):1334–1337
Wu Z, Zhang J, Jin L, Yang L (2012) Space time comparative analysis of surface sediment organic matter, TN and TP in Nansi Lake. Environ Sci Technol (In Chinese with English Abstract) 35(6I):358–364
Yang L, Shen J, Liu E, Ji J (2007) Characteristics of nutrients distribution from recent sediment in Lake Nansi. Lake Sci (in Chinese with English Abstract) 19(4):390–396
Yu H, Zhang W, Lu S, Yan S, Hu R, Chen L (2010) Spatial distribution characteristics of surface sediments nutrients in Lake Hongze and their pollution status evaluation. Environ Sci (in Chinese with English Abstract) 31(4):961–968
Zhang Z, Lv Y, Zhang Y (2012a) Study on the release characteristics of nutrient salt in the residual feed in aquaculture water. J Shandong Jianzhu Univ (in Chinese with English Abstract) 27(6):588–592
Zhang ZB, Tan XB, Wei LL, Yu SM, Wu DJ (2012b) Comparison between the lower Nansi Lake and its inflow rivers in sedimentary phosphorus fractions and phosphorus adsorption characteristics. Environ Earth Sci 66(5):1569–1576
Zhou L, Feng Q, Wang H, Ji L (2007) Phosphorus speciation and phosphorus release from surface sediments in Nansi Lake. Environ Sci Technol (in Chinese with English Abstract) 30(6):37–39
Zhu G, Qin B, Gao G, Zhang L, Fan C (2004) Fractionation of phosphorus in sediments and its relation with soluble phosphorus contents in shallow lakes located in the middle and lower reaches of Changjiang River, China. Acta Sci Circumstantia (in Chinese with English Abstract) 24(3):381–388
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Major National Water Sci-Tech Projects of China (No.2009ZX07210-009) and the Department of Environmental Protection of Shandong Province (No. 2060403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Lv, Y., Zhang, W. et al. Phosphorus, organic matter and nitrogen distribution characteristics of the surface sediments in Nansi Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 73, 5669–5675 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3821-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3821-5