Abstract
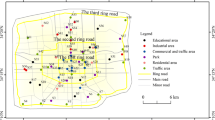
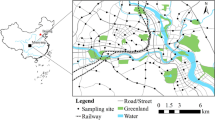
The paper reports the spatial distribution and contamination level of heavy metals (Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn and V) in urban topsoil from the interior area of the second ringroad of Xi’an city, China, based on X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy measurements. Geostatistical analysis shows that Co, Cu, and Pb have similar spatial distribution patterns. Heavy traffic density mainly contributed to the high concentrations of Co, Cu and Pb. The spatial distribution of Cr coincides with the industrial activity, whereas the spatial distribution of Zn differs from other heavy metals. The high concentrations of Zn coincide with heavy traffic and high population density. For Mn, Ni and V, natural factors are important in controlling their distribution. The calculated geoaccumulation indices indicate that urban topsoil inside the Xi’an second ringroad was uncontaminated by Cr, V, Mn and Ni, while Pb, Cu, Co and Zn are classified as uncontaminated to moderately contaminated with means of 0.64, 0.46, 0.26 and 0.21, respectively. The Nemero synthesis pollution index of these heavy metals revealed that the topsoil inside Xi’an second ringroad has been heavily contaminated due to anthropogenic activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batjargal T, Otgonjargal E, Baek K, Yang J-S (2010) Assessment of metals contamination of soils in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. J Hazard Mate 184:872–876
Cai L, Huang L, Zhou Y, Xu Z, Peng X, Yao L, Zhou Y, Peng P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations of agriculture soils and vegetables from Dongguan, Guangdong. J Geogr Sci 20:121–134
Chen TB, Wong JWC, Zhou HY, Wong MH (1997) Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environ Pollut 96:61–68
Chen TB, Zheng YM, Lei M, Huang ZC, Wu HT, Chen H, Fan KK, Yu K, Wu X, Tian QZ (2005) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 60:542–551
Chen T, Liu X, Zhu M, Zhao K, Wu J, Xu J, Huang P (2008) Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban–rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 151:67–78
Chen X, Xia X, Zhao Y, Zhang P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 181:640–646
CNEMC (China national environmental monitoring center) (1990) The background values of elements in Chinese soils. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Duzgoren-Aydin NS, Wong CSC, Aydin A, Song Z, You M, Li XD (2006) Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou, SE China. Environ Geochem Health 28:375–391
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Gallego JLR, Ordoóňez A, Loredo J (2002) Investigation of trace element sources from an industrialized area (Avilés, northern Spain) using multivariate statistical methods. Environ Inter 27:589–596
Imperato M, Adamo P, Naimo D, Arienzo M, Stanzione D, Violante P (2003) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ Pollut 124:256–274
Ji YQ, Feng YC, Wu JH, Zhu T, Bai ZP, Duan CQ (2008) Using geoaccumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China. J Environ Sci 20:571–578
Jung MA (2001) Heavy metal contamination of soils and waters in and around the Imcheon Au–Ag mine, Korea. Appl Geochem 16:1369–1375
Krasilnikov P, Carré F, Montanarella L (2008) Soil geography and geostatistics, concepts and applications. JRC Scientific and Technical Reports, Chapter 2. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Krishna AK, Govil PK (2008) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around Manali industrial area, Chennai, Southern India. Environ Geo l54:1465–1472
Lee CS, Li XD, Shi WZ, Cheung SC, Thornton I (2006) Metal contamination in urban, suburban and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci Total Environ 356:45–61
Li X, Feng L (2010) Spatial distribution of hazardous elements in urban topsoils surrounding Xi’an industrial areas, (NW China): controlling factors and contamination assessments. J Hazard Mater 174:662–669
Li XD, Lee SL, Wong SC, Shi WZ, Thornton I (2004) The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environ Pollut 129:113–124
Lu X, Wang L, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Madrid L, Diaz-Barrientos E, Madrid F (2002) Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chemosphere 49:1301–1308
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieri M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243
McGrath D, Zhang C, Carton OT (2004) Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area, Ireland. Environ Pollut 127:239–248
Mielke HW, Gonzales CR, Smith MK, Mielke PW (2000) Quantities and associations of lead, zinc, cadmium, manganese, chromium, nickel, vanadium, and copper in fresh Mississippi delta alluvium and New Orleans alluvial soils. Sci Total Environ 246:249–259
Morton-Bermea O, Hernández-Álvarez E, González-Hernández G, Romero F, Lozano R, Beramendi-Orosco LE (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoils from the metropolitan area of Mexico City. J Geochem Explor 101:218–224
Müller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J 2:108–118
Norra S, Weber A, Kramer U, Stuben D (2001) Mapping of trace metals in urban soils. J Soil Sediment 1:77–97
Raghunath R, Tripathi RM, Kumar AV, Sathe AP, Khandekar RN, Nambi KSV (1999) Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn exposures of 6 to 10-year-old children in Mumbai. Environ Res Sect A 80:215–221
Rico D, Martín-González A, Díaz S, de Lucas P, Gutiérrez J-C (2009) Heavy metals generate reactive oxygen species in terrestrial and aquatic ciliated protozoa. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 149:90–96
Romic M, Romic D (2003) Heavy metals distribution in agricultural topsoils in urban area. Environ Geo 43:795–805
SEPAC (State Environmental Protection Administration of China) (1995) Environmental quality standard for soils (GB15618-1995). Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2003) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Inter 29:979–985
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, Teng J (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156:251–260
Song D (1988) Record of Xi’an’s Geography. Shaanxi People’s Publishing House, Xi’an (in Chinese)
Surthland RA, Tolosa CA, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2000) Characterization of selected element concentrations and enrichment ratios in background and anthropogenically impacted roadside areas. Arch Environ Con Tox 38:428–438
Tao S (1995) Kriging and mapping of copper, lead, and mercury contents in surface soil in Shenzhen area. Water Air Soil Pollut 83:161–172
Wang XS, Qin Y (2006) Spatial distribution of metals in urban topsoils of Xuzhou (China): controlling factors and environmental implications. Environ Geol 49:905–914
Wang J, Ren H, Liu J, Yu J, Zhang X (2006) Distribution of lead in urban soil and its potential risk in Shenyang city, China. Chin Geogr Sci 16:127–132
Wei BG, Jiang FQ, Li XM, Mu SY (2009) Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban road dusts from Urumqi, NW China. Microchem J 93:147–152
Wilcke W, Müller S, Kanchanakool N, Zech W (1998) Urban soil contamination in Bangkok: heavy metal and aluminum partitioning in topsoils. Geoderma 86:211–228
XAMBS (Xian Municipal Bureau of Statistics) (2010) Xi’an statistical yearbook in 2010. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xie YF, Chen TB, Lei M, Yang J, Guo QJ, Song B, Zhou XY (2011) Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere 82:468–476
Yang Z, Lu W, Long Y, Bao X, Yang Q (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun city, China. J Geochem Explor 108:27–38
Zhang XY, Lin FF, Wong MTF, Feng XL, Wang K (2009) Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environ Monit Assess 154:439–449
Zhu BQ, Chen YW, Peng JH (2001) Lead isotope geochemistry of the urban environment in the Pearl River delta. Appl Geochem 16:409–417
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the program for New Century Excellent Talents in University under Grant NCET-05-0861 and Fundamental Research Funds for the Chinese Central Universities through Grants 2010ZYGX014 and GK200901008. We thank Editor-in-Chief Dr. James W. LaMoreaux and anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions and critical reviews of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Lu, X., Li, L.Y. et al. Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an second ringroad, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 68, 1979–1988 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1885-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1885-7