Abstract
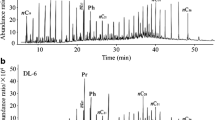
Biodegradation, one of the most important weathering processes, alters the composition of spilled oil, making it difficult to identify the source of the release and to monitor its fate in the environment. A laboratory experiment was conducted to simulate oil spill weathering process of microbial degradation to investigate compositional changes in a range of source- and weathering-dependent molecular parameters in oil residues, and the conventional diagnostic ratios for oil spill identification were also evaluated. The conventional diagnostic ratios of n-alkane displayed obvious changes after biodegradation, especially for Pr/n-C17 and Ph/n-C18 with relative standard deviation more than 118.84 %, which suggests they are invalid for oil source identification of the middle-serious spill. Many polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are more resistant to biodegradation process than their saturated hydrocarbon counterparts, thus making PAHs to be one of the most valuable fingerprinting classes of hydrocarbons for oil identification. Biomarker ratios of hopanes and steranes were also useful for source identification even after moderate biodegradation, and the diagnostic ratios from them could be used in tracking origin and sources of hydrocarbon pollution. Finally, the carbon isotopic type curve may provide another diagnostic means for correlation and differentiation of spilled oils, and be particularly valuable for lighter refined products or severely biodegraded oils, the source of which may be difficult to identify by routine biomarker techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asif M, Grice K, Fazeelat T (2009) Assessment of petroleum biodegradation using stable hydrogen isotopes of individual saturated hydrocarbon and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distributions in oils from the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan. Org Geochem 40:301–311
Bao JP, Zhu CS (2008) Effect of biodegradation on the maturity parameters of sterane and trepan in crude oil from Liaohe basin. Sci China Ser D 38:38–46
Bao JP, Zhu CS, Ma AL, Zhu JZ, Zhang J (2002) Quantitative study of biomarker composition in biodegraded oils. J Oil Gas Technol 24:24–26
Barakat AO, Qian Y, Kim M, Kennicutt MC (2001) Chemical characterization of naturally weathered oil residue in arid terrestrial environmental in Al-Alamein, Egypt. Environ Sci Technol 27:291–310
Barakat AO, Mostafa AR, Qian Y, Kennicutt MC (2002) Application of petroleum hydrocarbon chemical fingerprinting in oil spill investigations—gulf of Suez, Egypt. Spill Sci Technol Bull 7:229–231
Béhar F, de Barros Penteado HL, Lorant F, Budzinski H (2006) Study on biodegradation processes along the Carnaubais trend, Potiguar Basin (Brazil)—Part1. Org Geochem 37:1042–1051
Boehm PD, Fiest DL, Mackay D, Paterson S (1982) Physical chemical weathering of petroleum hydrocarbons from the Ixtoc I blowout: chemical measurements and a weathering model. Environ Sci Technol 16:498–505
Bost FD, Frontera-Suau R, McDonald TJ, Peters KE, Morris PJ (2001) Aerobic biodegradation of hopanes and norhopanes in Venezuelan crude oils. Org Geochem 32:105–114
Chandru K, Zakaria MP, Anita S, Shahbazi A, Sakari M, Bahry PS, Mohamed CA (2008) Characterization of alkanes, hopanes, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in tar-balls collected from the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 56:950–962
D’Auria M, Emanuele L, Racioppi R, Velluzzi V (2009) Photochemical degradation of crude oil: Comparison between direct irradiation, photocatalysis, and photocatalysis on zeolite. J Hazard Mater 164:32–38
de Oteyza Garcia, Grimalt JO (2006) GC and GC-MS characterization of crude oil transformation in sediments and microbial mat samples after the 1991 oil spill in the Saudi Arabian Gulf coast. Environ Pollut 139:523–531
Douglas GS, Bence AE, Prince RC, Mcmillen SJ, Butler EL (1996) Environmental stability of selected petroleum hydrocarbon source and weathering ratios. Environ Sci Technol 30:2332–2339
Duan Y, Zhang H, Wu BX, Zheng ZY (2003) Carbon isotopic studies of individual n-alkanes in crude oils from Qaidam basin. J Mineral Petrol 23:91–94
Duan Y, Wang CY, Zheng CY, Wu BX, Zheng GD (2008) Geochemical study of crude oils from Xifeng oilfield of Ordos basin, China. J Southeast Asian Earth Sci 31:341–356
Garrett RM, Pickering IJ, Haith CE, Prince RC (1998) Photooxidation of crude oils. Environ Sci Technol 32:3719–3723
George SC (2008) Preservation of hydrocarbons and biomarkers in oil trapped inside fluid inclusions for >2 billion years. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 72:844–870
Hegazi AH, Anderson JT, Abu-Elgheit MA, El-Gayar MSh (2004) Source diagnostic and weathering indicators of tar-balls utilizing acyclic, polycyclic and S-heterocyclic components. Chemosphere 55:1051–1065
Kingston PF (2002) Long-term environmental impact of oil spills. Spill Sci Technol Bull 7:53–61
Li SM, Guo D (2010) Characteristics and application of compound specific isotope in oil-source identification for oils in Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Geoscience 24:252–258
Li Y, Xiong YQ, Yang WY, Xie YL, Li SY, Sun YG (2009) Compound-specific stable carbon isotopic composition of petroleum hydrocarbons as a tool for tracing the source of oil spills. Marine Poll Bull 58:114–117
Mansuy I, Philp RP, Allen J (1997) Source identification of oil spills based on the isotopic composition of individual components in weathered oil samples. Environ Sci Technol 31:3417–3425
Moldowan JM, Dahl J, McCaffrey MA, Smith WJ, Fetzer JC (1995) Application of biological marker technology to bioremediation of refinery by-products. Energy Fuels 9:155–162
Mukherji S, Jagadevan S, Mohapatra G, Vijay A (2004) Biodegradation of diesel oil by an Arabian Sea sediment culture isolated from the vicinity of an oil field. Bioresour Technol 95:281–286
Munoz D, Guiliano M, Doumenq P, Jacquot F, Scherrer P, Mille G (1997) Long term evolution of petroleum biomarkers in mangrove soil (Guadeloupe). Mar Pollut Bull 34:868–874
Murray AP, Summons RE, Boreham CJ, Dowling LM (1994) Biomarker and n-alkane isotope profiles for tertiary oils: relationship to source rock depositional setting. Org Geochem 22:521–542
Peters KE, Moldowan JM (1991) Effects of source, thermal maturity, and biodegradation on the distribution and isomerization of homohopanes in petroleum. Org Geochem 17:47–61
Peters KE, Moldowan JM (eds) (1993) The biomarker guide. Interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Peters KE, Walters CC, Moldowan JM (eds) (2005) The Biomarker Guide, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, London
Pieri N, Jacquot F, Mille G, Planche JP, Kister J (1996) GC–MS identification of biomarkers in road asphalts and in their parent crude oils. Relationships between crude oil maturity and asphalt reactivity towards weathering. Org Geochem 25:51–68
Prince RC, Owens EH, Sergy GA (2002) Weathering of an Arctic oil spill over 20 years: the BIOS experiment revisited. Marine Poll Bull 44:1236–1242
Prince RC, Garrett RM, Bare RE, Grossman MJ, Townsend T, Suflita JM, Lee K, Owens EH, Sergy GA, Braddock JF, Lindstrom JE, Lessard RR (2003) The roles of photooxidation and biodegradation in long-term weathering of crude and heavy fuel oils. Spill Sci Technol Bull Spill 8:145–156
Shen P (1995) Compositional characteristics of carbon and hydrogen isotopes in light hydrocarbons. Sci China Ser B 38:221–227
Stout SA, Uhler AD, McCarthy KJ (2001) A strategy and methodology for defensibly correlating spilled oil to source candidates. Environ Forensics 2:87–98
Wang ZD, Fingas MF (2003) Development of oil hydrocarbon fingerprinting and techniques. Marine Poll Bull 47:423–452
Wang Z, Fingas M, Landriault M, Sigouin L, Feng Y, Mullin J (1997) Using systematic and comparative analytical data to identify the source of an unknown oil on contaminated birds. J Chromatogr A 775:251–265
Wang ZD, Fingas M, Sigouin L (2001) Characterization and identification of a ‘‘mystery” oil spill from Quebec (1999). J Chromatogr A 909:155–169
Xu YC, Shen P, Liu WH, Guan P, Huang DF (2001) Isotopic composition characteristics and identification of immature and low-mature oils. Chin Sci Bull 46:1923–1929
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Key Projects in the Yantai Science and Technology Pillar Program (2011060) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40806048, 41171424). The authors also extend great appreciation to the constructive comments from anonymous reviewers and editor-in-chief.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Gao, X., Sun, Z. et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic ratios for the identification of spilled oils after biodegradation. Environ Earth Sci 68, 917–926 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1792-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1792-y